Acquired immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) associated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine CoronaVac
2024-11-08
(Press-News.org)
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted the rapid development and administration of various vaccines worldwide, with some reports linking these vaccines to immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). This report presents two cases of TTP occurring after the administration of the inactivated vaccine CoronaVac from Sinovac Biotech, highlighting the potential association between this type of vaccine and TTP. The article also provides an analysis of TTP incidence in the Nanjing area of China, suggesting a possible correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and the occurrence of TTP.
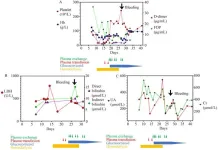
The first case details a 23-year-old female who developed symptoms of TTP three days after receiving her second dose of CoronaVac. Initially presenting with dizziness and weakness, her condition progressed to include thrombocytopenia, anemia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and α-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (α-HBDH) levels, with further deterioration indicated by decreased platelet count, hemoglobin levels, and the presence of schistocytes in peripheral blood smears. Despite negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test results, the patient was treated with dexamethasone, intravenous immunoglobulin, and platelet transfusion. Her condition improved following the introduction of glucocorticoids, plasma exchange, and rituximab, with a gradual return to normal values for ADAMTS13 antigen and inhibitory antibodies.
The second case involves a 45-year-old female who experienced fever and muscle soreness five days after her second dose of CoronaVac. She presented with high fever, hematological abnormalities, acute renal failure, and thrombocytopenia. Despite negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test results and initial suspicions of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) or severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), she was later diagnosed with TTP based on the presence of schistocytes in peripheral blood smears and significantly low ADAMTS13 levels. Treatment with plasma exchange and glucocorticoids led to her recovery, although she experienced a retroperitoneal hemorrhage that required surgical intervention.
The report also examines a series of TTP cases from 14 hospitals in the Nanjing area, showing an increase in TTP incidence from 2019 to 2022 that may be related to COVID-19 vaccination. The data suggests that while TTP is rare, with an average annual incidence of about one new case per million people, the incidence rates increased in years following the initiation of COVID-19 vaccination campaigns. It is hypothesized that the increase in TTP cases could be associated with the vaccines, although a direct causal link is not established.
Discussion within the report delves into the potential mechanisms by which COVID-19 vaccines could trigger TTP, focusing on the autoimmune response that may cross-react with ADAMTS13, leading to its deficiency and subsequent TTP development. The report also emphasizes the importance of accurate and timely diagnosis of TTP, as misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment, which may exacerbate the condition. Furthermore, it underscores the critical nature of plasma exchange and immunosuppression in the treatment of TTP, as evidenced by the successful management of the reported cases.
In conclusion, this report presents the first known cases of TTP associated with an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine and contributes to the growing body of knowledge on the potential adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccines. It also provides valuable insights into the diagnosis and treatment of TTP, highlighting the need for vigilance and appropriate clinical management in the context of COVID-19 vaccination programs. The findings suggest a potential link between COVID-19 vaccination and TTP incidence, warranting further investigation to understand the mechanisms involved and to guide the development of strategies for the prevention and management of vaccine-related TTP.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-08
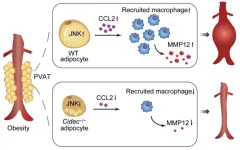
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a degenerative lesion characterized by structural disruption of the abdominal aortic wall and progressive dilatation into a pulsatile mass. AAA is strongly associated with obesity, partly due to abnormal dilatation of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in the abdomen, however, direct evidence is still lacking.
Cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor-like effector C (CIDEC), also known as fat-specific protein 27 (FSP27) in rodents, is a lipid droplet (LD)-associated protein that plays an important role in lipid storage. It has been reported that CIDEC/FSP27 promotes the growth of LDs by mediating the exchange and transfer of lipids ...
2024-11-08
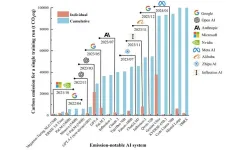
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology progresses, the energy demands of training complex models have surged, raising widespread concerns about associated carbon emissions. This rapid growth is fueled by global demand across industries and academia, leading to exponential increases in computing power that carry significant environmental consequences. Given these challenges, in-depth research is essential to fully understand AI's carbon footprint and develop strategies for mitigating its environmental impact.
In a view (DOI: 10.1007/s11783-024-1918-y) by ...
2024-11-08
Tsukuba, Japan—Students often appear for high-stakes tests that hold significant weight in determining their futures. One such examination, the Common Test for University Admissions, currently allows examinees using braille an extended examination time of 1.5 times the standard duration. However, with the recent increase in complex questions and questions involving charts and diagrams in such tests, it is necessary to review whether the current accommodations remain adequate.
The researchers assessed the validity of the current time extension for examination questions containing complex tables by measuring the time required to read the text and complex tables. The results showed that ...
2024-11-08
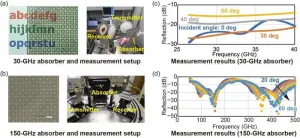
5G wireless communication services have rapidly expanded worldwide, leveraging millimeter-wave (mmW) frequencies in the 24 GHz to 71 GHz range (referred to as frequency range 2, or FR2). Looking ahead, Beyond 5G and 6G services, projected to offer ultra-fast connectivity exceeding 100 Gbit/s, are expected to be introduced in the 2030s. Frequencies in the 150-GHz to 300-GHz range are being considered as potential candidates for these future networks. However, critical components such as radio-wave absorbers, essential for packaging and modularization, still need to be developed. These absorbers play a key role in reducing ...
2024-11-08
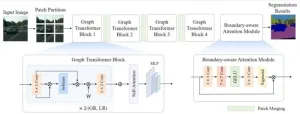
The transformer-based semantic segmentation approaches, which divide the image into different regions by sliding windows and model the relation inside each window, have achieved outstanding success. However, since the relation modeling between windows was not the primary emphasis of previous work, it was not fully utilized.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zizhang Wu published their new research on 15 October 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer ...
2024-11-08
TUCSON, Ariz., November 7, 2024 — Critical Path Institute® (C-Path) today announced key leadership appointments: Diane Stephenson, Ph.D., has been promoted to Vice President of Neurology, and Nadine Tatton, Ph.D., has been welcomed as the new Executive Director of C-Path’s Critical Path for Alzheimer’s Disease (CPAD) Consortium.
With over 30 years of specialized research in neuroscience and drug development and having served as the Executive Director of the Critical Path for Parkinson’s Consortium (CPP) for nearly 15 years, Dr. Stephenson has been an extraordinary partner in advancing our understanding ...
2024-11-08
First-of-its-kind analysis of US national data reveals significant disparities in individual well-being as measured by lifespan, education, and income.
White males make up largest share of the group with lowest well-being while American Indian and Alaska Native individuals, and Black males, face the most significant challenges to overall well-being.
Populations at the lowest levels of well-being across the US are especially concentrated in the Deep South, Appalachia, and the Rust Belt.
The ...
2024-11-08
Exercise-only programmes help cut the severity of the ‘baby blues’ and the risk of major clinical depression in new mums, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
But at least 80 weekly minutes of moderate intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, water aerobics, stationary cycling, and resistance training with bands, weights, or body weight are needed to achieve the effects, the findings show.
Maternal depression and anxiety are relatively common after giving birth and associated with reduced self-care and compromised infant caregiving and bonding, ...
2024-11-08
Changes in the make-up of the gut microbiome are linked to the onset of clinically evident rheumatoid arthritis in those at risk of the disease because of genetic, environmental, or immunological factors, suggests research published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
It’s not clear if this instability is a cause or consequence of disease development, emphasise the researchers, but the findings might nevertheless help to identify those at risk as well as paving the way for preventive and personalised treatment strategies, they suggest.
Previously published research consistently shows an unfavourable imbalance in ...
2024-11-08
Changes in the gut microbiome before rheumatoid arthritis is developed could provide a window of opportunity for preventative treatments, new research suggests.
Bacteria associated with inflammation is found in the gut in higher amounts roughly ten months before patients develop clinical rheumatoid arthritis, a longitudinal study by Leeds researchers has found.
Affecting more than half a million people in the UK, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that causes swelling, pain and stiffness in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Acquired immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) associated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine CoronaVac