(Press-News.org) Geologists have uncovered strong evidence from Colorado that massive glaciers covered Earth down to the equator hundreds of millions of years ago, transforming the planet into an icicle floating in space.
The study, led by the University of Colorado Boulder, is a coup for proponents of a long-standing theory known as Snowball Earth. It posits that from about 720 to 635 million years ago, and for reasons that are still unclear, a runaway chain of events radically altered the planet’s climate. Temperatures plummeted, and ice sheets that may have been several miles thick crept over every inch of Earth’s surface.
“This study presents the first physical evidence that Snowball Earth reached the heart of continents at the equator,” said Liam Courtney-Davies, lead author of the new study and a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Geological Sciences at CU Boulder.
The team will publish its findings the week of Nov. 11 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Co-authors include Rebecca Flowers, professor of geological sciences at CU Boulder, and researchers from Colorado College, the University of California, Santa Barbara and University of California, Berkeley.
The study zeroes in on the Front Range of Colorado’s Rocky Mountains. Here, a series of rocks nicknamed the Tavakaiv, or “Tava,” sandstones hold clues to this frigid period in Earth’s past, Courtney-Davies said.
The researchers used a dating technique called laser ablation mass spectrometry, which zaps minerals with lasers to release some of the atoms inside. They showed that these rocks had been forced underground between about 690 to 660 million years ago—in all likelihood from the weight of huge glaciers pressing down above them.
Courtney-Davies added that the study will help scientists understand a critical phase in not just the planet’s geologic history but also the history of life on Earth. The first multicellular organisms may have emerged in oceans immediately after Snowball Earth thawed.
“You have the climate evolving, and you have life evolving with it. All of these things happened during Snowball Earth upheaval,” he said. “We have to better characterize this entire time period to understand how we and the planet evolved together.”
Searching for snow
The term “Snowball Earth” dates back to a paper published in 1992 by American geologist Joseph Kirschvink.
Despite decades of research, however, scientists are yet to agree whether the entire globe actually froze. Geologists, for example, have discovered the fingerprints of thick ice from this time period along ancient coastal areas, but not within the interior of continents close to the equator.
Which is where Colorado enters the picture. At the time, the region didn’t sit at the northern latitudes where it does today. Instead, Colorado rested over the equator as a landlocked part of the ancient supercontinent Laurentia.
If glaciers formed here, scientists believe, then they could have formed anywhere.
Going deep
The search for that missing piece of the puzzle brought Courtney-Davies and his colleagues to the Tava sandstones. Today, these features poke up from the ground in a few locations along Colorado’s Front Range, most notably around Pikes Peak. To the untrained eye, they might seem like ordinary-looking yellow-brown rocks running in vertical bands less than an inch to many feet wide.
But for geologists, these features have an unusual history. They likely began as sands at the surface of Colorado at some point in the past. But then forces pushed them underground—like claws digging into the Earth’s crust.
“These are classic geological features called injectites that often form below some ice sheets, including in modern-day Antarctica,” Courtney-Davies said.
He wanted to find out if the Tava sandstones were also connected to ice sheets. To do that, the researchers calculated the ages of mineral veins that sliced through those features. They collected tiny samples of the minerals, which are rich in iron oxide (essentially, rust), then hit them with a laser. In the process, the minerals released small quantities of the radioactive element uranium. Because uranium atoms decay into lead at a constant rate, the team could use them as a sort of timekeeper for the planet’s rocks.
It was a Eureka moment: The group’s findings suggest that the Tava sandstone had been pushed underground at the time of Snowball Earth. The group suspects that, at the time, thick ice sheets formed over Colorado, exposing the sands to intense pressures. Eventually, and with nowhere else to go, they pushed down into the bedrock below.
"We're excited that we had the opportunity to unravel the story of the only Snowball Earth deposits that have so far been identified in Colorado,” Flowers said.
The researchers aren't done yet: If such features formed in Colorado during Snowball Earth, they probably formed in other spots around North America, too, Courtney-Davies said:
“We want to get the word out so that others try and find these features and help us build a more complete picture of Snowball Earth."
END
Was ‘Snowball Earth’ a global event? New study delivers best proof yet
2024-11-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists issue call to action underlining importance of microbial solutions to tackle climate crisis
2024-11-11
Ahead of COP29, Applied Microbiology International (AMI) has partnered with leading global scientific organisations to issue a unified call to action, spotlighting microbial solutions as pivotal in combating climate change.
In a strategic publication, released in multiple high-impact scientific journals at once, the joint paper advocates for the establishment of a global science-driven climate task force. This initiative aims to expedite the deployment of microbiome technologies, providing stakeholders worldwide with access to effective and immediate solutions.
Signatories of the paper, ‘Microbial solutions must be deployed against the climate catastrophe’ ...
Ochsner Transplant Institute among site collaborators in New England Journal of Medicine HIV-to-HIV kidney transplant study
2024-11-11
NEW ORLEANS – The Ochsner Transplant Institute served as one of 26 U.S. transplant centers collaborating in an HIV-to-HIV kidney transplant study published by The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). The article, Safety of Kidney Transplantation from Donors with HIV, details findings supporting HIV-to-HIV kidney transplants as safe and just as effective as those using organs from donors without HIV.
Human immunodeficiency virus, commonly known as HIV, attacks cells in the body that fight infection and there is currently no known cure. In the U.S.,1.2 million people are living with HIV. According to the National ...
Scientists call for global action on microbial climate solutions
2024-11-11
Washington, D.C. — Nov. 11, 2024 — Today, leaders from scientific societies, institutions and publishing bodies issued an urgent call for the global community and governments to take immediate and decisive emergency climate action. This appeal is made through an editorial published in mSystems, released on the opening day of the 2024 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP29). Key contributors to this initiative include Virginia Miller, past president of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM); Jack Gilbert, Editor-in-Chief of mSystems; and Jay Lennon, ...
New antibody could be promising cancer treatment
2024-11-11
Researchers at Uppsala University and KTH Royal Institute of Technology have developed a new form of precision medicine, an antibody, with the potential to treat several types of cancer. Researchers have managed to combine three different functions in the antibody, which together strongly amplify the effect of T cells on the cancer tumour. The study has been published in Nature Communications.
Researchers have developed a unique type of antibody that both targets and delivers a drug package via the antibody itself, while simultaneously activating the immune system (“3-in-1 design”) for personalised immunotherapy treatments.
“We ...
The public implications of private substitutes for electric grid reliability
2024-11-11
Climate change events have, in recent years, placed increasing strain on public electrical grids in the United States. In response to this vulnerability, some consumers are turning to private alternatives to the electric utility, like generators and batteries. A new paper in the Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economists studies who adopts these private alternatives and how adoption responds to grid failures. The paper also studies how public electric grid reliability may change due to this proliferation and how these changes will affect the wellbeing of all households.
In ...
Religiosity, spirituality, and meaning-making generally associated with lower suicidality
2024-11-11
November 11, 2024 — All aspects of religiosity, spirituality, and meaning-making (R/S/M) relate to suicidality in people with a psychiatric diagnosis or a recent suicide attempt, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer.
"Protective dimensions seemed to exert relatively stable effects across different religions and life views," Bart van den Brink, MD, PhD, of the Department of ...
Eife studying legal surveillance as social determinant of health
2024-11-11
Erin Eife, Assistant Professor, Criminology, Law and Society, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding for the project: “Surveillance as a Social Determinant of Health: Understanding the Impact of Pending Charges on Health Outcomes.”
Eife will conduct this research under the advisement of Evan Lowder, Associate Professor, Criminology, Law and Society, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), and Lauren Brinkley-Rubinstein, Associate Professor in the Department of Population Health Sciences at Duke University.
Eife aims to produce knowledge about ...
Newly developed 100Gbps data transfer system for accelerating Open Science through industry-university collaboration in Japan
2024-11-11
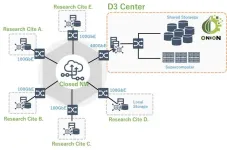
Tokyo & Osaka, Japan – Osaka University and NEC Corporation (NEC; TSE: 6701) are moving forward with efforts to realize a data infrastructure supporting Open Science. In 2021, The Joint Research Laboratory for Integrated Infrastructure of High Performance Computing and Data Analysis was established within the D3 Center, Osaka University (Director: Professor Susumu Date*1) by Osaka University and NEC. The result of the Joint Research Laboratory will be showcased at the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC24) scheduled ...
Navigating bias in AI-driven cancer detection
2024-11-11
“As we eagerly adopt Al models, we need to take a moment to think about the potential biases that they may contain.”
BUFFALO, NY - November 11, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on November 7, 2024, titled “ Beyond the hype: Navigating bias in AI-driven cancer detection.”
In this editorial, researchers from the Mayo Clinic emphasize the need to address potential biases in Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools used for cancer detection to ensure fair and equitable healthcare. Authors Yashbir Singh, Heenaben Patel, Diana V. Vera-Garcia, Quincy A. Hathaway, ...
Research shows stress about personal finances may make leaders abusive in workplace
2024-11-11
New research from Colorado State University shows that workplace leaders who are financially stressed are more likely to be abusive toward their subordinates – particularly if the leader is a man.
The findings, published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, provide insight into leader behavior due to a common source of stress. The research was led by Assistant Professor Keaton Fletcher in the Department of Psychology in partnership with Associate Professor Trevor Spoelma in the Anderson School of Management at the University ...