(Press-News.org) New study from deCODE genetics/Amgen highlights the importance of BMI in pathogenesis of disease, suggesting that reducing BMI alone could lower the risk of several diseases.
Scientists at deCODE genetics, subsidiary of Amgen, published a study today in Nature Communications that sheds light on how Body Mass Index (BMI) influences the risk of various diseases that are comorbid with obesity. The study, which used genetic data from Iceland and the UK Biobank, looked at whether disease risk associated with BMI-related sequence variants are explained completely or partially by their effect on BMI.
The results showed that for some conditions, such as fatty liver disease, glucose intolerance, and knee replacement, the genetic link to disease disappeared when BMI was taken into account. For other conditions, like type 2 diabetes, heart failure, and stroke, the effects were largely reduced but not entirely explained by BMI.
The study found similar patterns in men and women, although there were some differences, especially for myocardial infarction (heart attack), suggesting that sex may play a role in how BMI influences disease risk. The scientists also noted that other factors, such as changes in BMI over time rather than BMI measured at one point in time or other factors strongly correlated with BMI, might explain some of the remaining risk.
This research highlights the importance of BMI in the pathogenesis of diseases that are more common in obese people than others suggesting that just reducing BMI could lower the risk of these diseases.
END
New study explores the role of BMI in disease risk
New study from deCODE genetics/Amgen highlights the importance of BMI in disease pathology, suggesting that reducing BMI could lower the risk of several diseases.
2024-11-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Guardian, kids, or companions? What do dogs mean to us today
2024-11-12
What role do dogs play in today’s world? For many, they are more than just pets. New findings from the Department of Ethology at Eötvös Loránd University show that whether seen as friends, family members, children or guardians, these roles affect the way dogs are cared for, suggesting shifting dynamics in human-animal bonds shaped by societal trends and individual owner profiles.
In Western cultures, more and more people see their dogs as their best friends, family members or even their furry children. In fact, ...
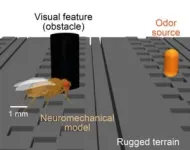
NeuroMechFly v2: Simulating how fruit flies see, smell, and navigate
2024-11-12
All animals, large or small, have to move at an incredible precision to interact with the world. Understanding how the brain controls movement is a fundamental question in neuroscience. For larger animals, this is challenging because of the complexity of their brains and nervous systems. But the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, has a smaller and therefore more easily mappable brain, allowing scientists to gain detailed insights into how its nervous system drives behavior.
To understand how the nervous system controls actions, researchers at the group of Pavan Ramdya at EPFL created a simulated reality where a virtual fly can operate ...
“Drowning” mangrove forests in Maldives signal global coastal threat
2024-11-12
Researchers have found evidence that mangrove forests – which protect tropical and subtropical coastlines – are drowning in the Maldives.
Their findings, published today (Tuesday 12 December) in Scientific Reports, indicate that rising sea level and a climate phenomenon known as the Indian Ocean Dipole have led to some Maldivian islands losing over half of their mangrove cover since 2020.
The research team, led by Northumbria University, warn that the findings have implications not only for the Maldives, but also for other island nations and coastal ecosystems around the world.
In 2020, more than a quarter of the Maldivian islands containing mangrove forests saw their trees experiencing ...
When muscles work out, they help neurons to grow, a new study shows
2024-11-12
There’s no doubt that exercise does a body good. Regular activity not only strengthens muscles but can bolster our bones, blood vessels, and immune system.
Now, MIT engineers have found that exercise can also have benefits at the level of individual neurons. They observed that when muscles contract during exercise, they release a soup of biochemical signals called myokines. In the presence of these muscle-generated signals, neurons grew four times farther compared to neurons that were not exposed to myokines. These cellular-level experiments suggest that exercise can have a significant biochemical effect on nerve growth.
Surprisingly, the researchers also ...
Smokers who switch to vaping see improved respiratory health
2024-11-12
A new paper in Nicotine and Tobacco Research, published by Oxford University Press, finds that people who switch from smoking cigarettes to vaping see improved respiratory health, but people who begin consuming electronic cigarettes while continuing to smoke regular cigarettes do not report improved respiratory symptoms.
Adults increasingly use electronic cigarettes to try to quit smoking because of the perceived reduced risk. But while vaping reduces exposure to toxic chemicals, it has been unclear whether switching from cigarettes to e-cigarettes results in a reduction of the respiratory problems—like wheezing and coughing—common in regular cigarette ...
Air pollution emerges as critical environmental risk factor for autism, emerging topic review finds
2024-11-12
Boston, Massachusetts, 12 November 2024 – Environmental exposure to air pollutants during critical developmental periods may significantly impact autism risk, according to a groundbreaking Emerging Topic review published 12 November 2024, in Brain Medicine. The study reveals how common air pollutants, including fine particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, can trigger complex biological cascades affecting brain development.
"Different kinds of neurological disorders, including autism spectrum disorder, can be associated ...
Autism and nitric oxide: Professor Haitham Amal unveils brain disorder breakthrough
2024-11-12
Boston, Massachusetts, 12 November 2024 – The complex interplay between nitric oxide and brain disorders takes center stage in the latest Genomic Press Interview, published November 12, 2024, in Brain Medicine. Professor Haitham Amal, head of the Laboratory of Neuromics, Cell Signaling, and Translational Medicine at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, shares insights into his groundbreaking research and personal motivation.
“Meeting families and children with autism in Boston during my time at MIT inspired me to focus on a single goal: to help develop biological diagnostics ...
Facing the wind: How trees behave across various forest settings and weather events
2024-11-12
Destructive winds during storms and cyclones often cause tree failures, especially through uprooting and stem breakage. However, how trees respond to wind under various forest configurations and weather conditions remains unclear. A recent study on Cryptomeria japonica plots shows that trees dissipate wind energy by switching between two swaying behaviors at specific wind speeds, offering insights that may help in improved forest management to minimize damage caused by storms.
Extreme weather events, such as tropical and extratropical cyclones and tornadoes, can cause widespread damage to forests, leading to environmental and financial ...
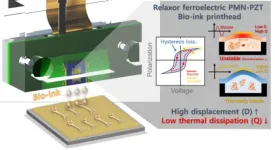
High-performance inkjet print head enhances bioprinting productivity
2024-11-12
Bioprinting is a technology used to create three-dimensional structures, such as human tissues or organs, using bio-inks made of cells and hydrogels. However, conventional inkjet technology has difficulty dispensing bio-inks that are sensitive to temperature due to the heat generated during operation. Furthermore, conventional 3D bioprinting mainly utilizes simple syringe-type printing devices with a single needle, making it time-consuming to produce artificial organs like the brain, lungs, and heart.
The Bionics Research Center team, led by Dr. Byung Chul Lee at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh), in ...
Opioid use disorder: Updated clinical practice guideline
2024-11-12
La version française suit
Opioid use disorder: updated clinical practice guideline
An updated evidence-based guideline aimed at helping clinicians and other health care providers manage patients with opioid use disorder recommends buprenorphine and methadone as first-line treatments. The guideline is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241173
Opioid use and opioid use disorder are the leading causes of drug-related deaths worldwide, and Canada ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] New study explores the role of BMI in disease riskNew study from deCODE genetics/Amgen highlights the importance of BMI in disease pathology, suggesting that reducing BMI could lower the risk of several diseases.