(Press-News.org) Few questions have captivated humankind more than the origin of life on Earth. How did the first living cells come to exist? How did these early protocells develop the structural membranes necessary for cells to thrive and assemble into complex organisms?
New research from the lab of University of California San Diego Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry Neal Devaraj has uncovered a plausible explanation involving the reaction between two simple molecules. This work appears in Nature Chemistry.
Life on Earth requires lipid membranes – the structure of a cell that houses its interior mechanics and acts as a scaffold for many biological reactions. Lipids are made from long chains of fatty acids, but before the existence of complex life, how did these first cell membranes form from the simple molecules present on Earth billions of years ago?
Scientists believe that simple molecules of short fatty chains of fewer than 10 carbon-carbon bonds (complex fatty chains can have nearly twice that many bonds) were abundant on early Earth. However, molecules with longer chain lengths are necessary to form vesicles, the compartments that house a cell’s complicated machinery.
While it may have been possible for some simple fatty molecules to form lipid compartments on their own, the molecules would be needed in very high concentrations that likely did not exist on a prebiotic Earth – a time when conditions on Earth may have been hospitable to life but none yet existed.
“On the surface, it may not seem novel because lipid production happens in the presence of enzymes all the time,” stated Devaraj, who is also the Murray Goodman Endowed Chair in Chemistry and Biochemistry. “But over four billion years ago, there were no enzymes. Yet somehow these first protocell structures were formed. How? That’s the question we were trying to answer.”
To uncover an explanation for these first lipid membranes, Devaraj’s team started with two simple molecules: an amino acid named cysteine and a short-chain choline thioester, similar to molecules involved in the biochemical formation and degradation of fatty acids.
The researchers used silica glass as a mineral catalyst because the negatively charged silica was attracted to the positively charged thioester. On the silica surface, the cysteine and thioesters spontaneously reacted to form lipids, generating protocell-like membrane vesicles stable enough to sustain biochemical reactions. This happened at lower concentrations than what would be needed in the absence of a catalyst.
“Part of the work we’re doing is trying to understand how life can emerge in the absence of life. How did that matter-to-life transition initially occur?” said Devaraj. “Here we have provided one possible explanation of what could have happened.”
Full list of authors: Christy J. Cho, Taeyang An, Alessandro Fracassi, Roberto J. Brea and Neal K. Devaraj (all UC San Diego); Yei-Chen Lai, Alberto Vázquez-Salazar and Irene A. Chen (all UCLA).
This research was supported, in part, by National Science Foundation (EF-1935372) and the National Institutes of Health (R35-GM141939).
END
On the origin of life: How the first cell membranes came to exist
New research provides a possible explanation on the development of early Earth protocells
2024-11-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New evidence-based information from NCCN offers tangible and moral support for people trying to quit smoking
2024-11-13
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [November 13, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—today announced the publication of a new patient guideline designed to provide critical support and guidance for individuals with cancer who are seeking to quit smoking. Continued smoking elevates the risk of developing additional cancers, reduces the effectiveness of treatment, exacerbates treatment side effects, and is associated with shorter survival. The new NCCN Guidelines for Patients®: Quitting Smoking explains how to best use the tools that exist to help anyone quit ...
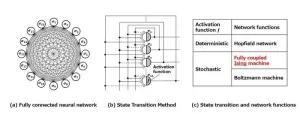
Solving complex problems faster: Innovations in Ising machine technology
2024-11-13
Computers are essential for solving complex problems in fields, like scheduling, logistics, and route planning, but traditional computers struggle with large-scale combinatorial optimization, as they can’t efficiently process vast numbers of possibilities. To address this, researchers have explored specialized systems.
One such system is the Hopfield network, a significant artificial intelligence breakthrough from 1982, proven in 1985 to solve combinatorial optimization by representing solutions as energy levels and naturally finding the lowest energy, or optimal, solution. ...
Grief-specific cognitive behavioral therapy vs present-centered therapy
2024-11-13
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial demonstrates that cognitive behavioral therapy for prolonged grief was superior to present-centered therapy after treatment and at follow-up with regard to comorbid symptoms. Both treatments were shown to be effective and acceptable, showing the potential for dissemination and increasing patient choice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rita Rosner, PhD, email rita.rosner@ku.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
New species discovered with refined DNA technology
2024-11-13
Sometimes plants are so similar to each other that the methods developed by 18th century scientist Carl Linnaeus for identifying species are not enough. In a thesis from the University of Gothenburg, completely new species of daisies have been discovered when analysed using modern DNA technology.
There are currently estimated to be around 8.7 million different species on Earth, of which around 2.2 million are found in the oceans. Many species can be identified in the classical way, by their physical characteristics, the morphology. For over a decade, botanists and zoologists have also been using DNA sequencing to more accurately identify species. ...
C-PATH announces Gender Equitable Medicines for Parkinson's Disease (GEM-PD) initiative
2024-11-13
INFORMATION EMBARGOED UNTIL WEDNESDAY, NOV. 13, 2024, 7 a.m. ET
C-Path Announces Gender Equitable Medicines for Parkinson's Disease (GEM-PD) Initiative
C-Path expands its worldwide leadership in accelerating drug development in neurology; seeks additional collaborators to broaden impact.
TUCSON, Ariz., November 13, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced a landmark initiative, Gender Equitable Medicines for Parkinson's Disease (GEM-PD), dedicated to globally ...
Faster flowing glaciers could help predict nearby volcanic activity
2024-11-13
Glaciers that are within three miles of a volcano move nearly 50% quicker than average, a new study has found, which could help create early warning of future eruptions.
In a new article published in Communications Earth & Environment today, researchers from the University of Aberdeen, University of Birmingham and Manchester Metropolitan University analysed velocity data from 85% of the world’s approximately 217,000 glaciers. After controlling for factors such as climate, ice thickness and surface slope, the team found that glaciers near active volcanoes typically flowed 46% faster than other glaciers.
Glaciers ...
MIT engineers make converting CO2 into useful products more practical
2024-11-13
As the world struggles to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, researchers are seeking practical, economical ways to capture carbon dioxide and convert it into useful products, such as transportation fuels, chemical feedstocks, or even building materials. But so far, such attempts have struggled to reach economic viability.
New research by engineers at MIT could lead to rapid improvements in a variety of electrochemical systems that are under development to convert carbon dioxide into a valuable commodity. ...
Primary care professionals key to helping people achieve & maintain heart health
2024-11-13
Statement Highlights:
A new scientific statement outlines the role of primary care professionals in helping their patients achieve Life’s Essential 8, the key measures for improving and maintaining cardiovascular health defined by the American Heart Association.
The new statement highlights how primary care clinicians can help patients follow and maintain the Association’s Life’s Essential 8 health metrics for optimal cardiovascular health, which includes four health behaviors (diet, physical activity, nicotine exposure and sleep) and four health ...
Early detection, intensive treatment critical for high-risk patients with Kawasaki Disease
2024-11-13
Embargoed until 4:00 a.m. CT/5:00 a.m. ET Wed., Nov. 13, 2024
DALLAS, Nov. 13, 2024 — Advances in cardiac imaging techniques and risk categorization have led to improvements in diagnosis, initial treatment and long-term management of patients with Kawasaki Disease, according to a new scientific statement published today in the American Heart Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
The new statement, “Update on Diagnosis and Management of Kawasaki Disease,” summarizes the data published since the 2017 American Heart Association Scientific Statement ...
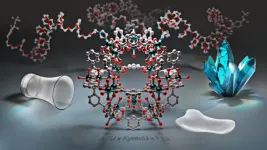
A phase-transformable membrane for efficient gas separation could revolutionize industrial applications
2024-11-13
Industrial gas separation, essential for clean energy and environmental protection, demands efficiency and adaptability. Current materials, however, lack the flexibility to selectively separate gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and hydrogen (H₂) while remaining energy-efficient. Researchers at the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (WPI-iCeMS) at Kyoto University and the Department of Chemical Engineering at National Taiwan University have developed a phase-transformable membrane that could meet these needs.
This innovative membrane design relies on a unique combination of metal-organic polyhedra (MOP) with polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains. “Traditional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] On the origin of life: How the first cell membranes came to existNew research provides a possible explanation on the development of early Earth protocells