(Press-News.org) Many young girls in low- and middle-income countries become pregnant early, which can be dangerous for them and for their babies. Studies show that girls who stay in school are less likely to get pregnant at a young age. Financial support can encourage girls to stay in school and delay pregnancy and marriage in some settings. However, a new large study from Zambia found that two years of financial support combined with comprehensive sexuality education and community dialogue meetings, moderately reduced births during the support period, but not after the financial support ended. As a result, the overall effect on births before age 18 was limited over the 4.5 years study period even though more girls completed junior secondary school. Longer-term efforts to make high school more affordable are likely to be important to keep girls in school and more clearly reduce adolescent pregnancies in low- and middle-income countries.
The study, to be published in eClinicalmedicine on 14th November, randomized 157 rural Zambian schools into three groups: one received economic support, another received economic support plus sexuality education and community dialogue, and the third served as a control group. The study included 5000 girls about to finish primary school (average age 14). Researchers from the University of Zambia, University of Bergen, Chr. Michelsen Institute, and the Norwegian School of Economics conducted the trial.
Previous research shows that poverty is a major reason why girls drop out of school and get pregnant early. Other reasons include social pressure to have children, and lack of knowledge about and access to birth control. The limited effects of the studied support package probably reflect that the support period was too short and many families could not afford school fees after the financial support ended. Most participants were around 16 and still at risk of early pregnancy. If the support had continued until they finished secondary school or turned 18, fewer girls may have gotten pregnant before 18. Also, better access to health services and contraceptives for young people is probably needed to reduce teenage pregnancies more effectively.
According to Professor Ingvild Sandøy, at the University of Bergen in Norway, the study is in line with previous research indicating that short-term poverty-reducing measures such as cash transfers should be combined with other initiatives to achieve substantial reductions in teenage pregnancies in low- and middle-income countries. Professor Patrick Musonda from the University of Zambia adds that Zambia’s recent removal of secondary school fees is a good initiative. It will likely keep children in school longer and help prevent many young girls from getting pregnant.
The funding for the study came from the Research Council of Norway, and the Swedish International Development Agency (through the Swedish Embassy in Zambia).
END
How can we reduce adolescent pregnancies in low- and middle-income countries?
New study from the University of Bergen (Norway) and the University of Zambia published Nov. 14, 2024
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When sun protection begets malnutrition: vitamin D deficiency in Japanese women
2024-11-14
Vitamin D, an essential nutrient, is naturally produced through sun exposure and certain foods. However, excessive sunburn prevention measures are causing a severe problem of vitamin D deficiency, particularly among young women in Japan.
Since vitamin D deficiency is also related to pregnancy-induced hypertension and low birth weight in children, it is important to quickly identify those at high risk and provide appropriate health guidance. However, the method currently established for measuring serum vitamin D levels is expensive and ...
Cannabis use can cause chromosomal damage, increasing cancer risk and harming offspring
2024-11-14
Cannabis use causes cellular damage that increases the risk of highly cancerous tumours, according to a new paper published in the scientific journal Addiction Biology. The paper describes cannabis as a “genotoxic” substance because it damages a cell's genetic information, which can lead to DNA mutations, accelerated aging, and cancer. To make matters worse, this genotoxicity may be transmitted via damaged egg and sperm to the cannabis user’s offspring, making the risk of cannabis ...
Survey finds many Americans apply misguided and counterproductive advice to combat holiday weight gain
2024-11-14
Orlando, Fla - For those striving to maintain a healthy lifestyle, holiday celebrations can feel like a minefield of dietary pitfalls, bound to derail the progress you’ve made through diet and exercise the rest of the year. In fact, a new national survey by Orlando Health finds nearly two in five (39%) Americans worry about how much they eat over the holidays. The good news is that dietitians say there’s no need to feel guilty about a few holiday treats.
“Holidays come around once a year, and indulging in a few traditional foods and favorite recipes that may have a little extra ...
New study reveals half a century of change on Britain’s iconic limestone pavements
2024-11-14
Fifty years of change on iconic limestone pavements has revealed mixed fortunes for one of the most distinctive landscapes in the UK.
The landscapes - which will be familiar to visitors to the Yorkshire Dales and fans of Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows film – have, in many places, seen reductions of specialist species and more common less desirable species become more abundant.
However, it is not all bad news as the picture is very mixed across the UK’s areas of limestone pavement with some areas increasing in plant biodiversity.
The ...
Green flight paths could unlock sustainable aviation, new research suggests
2024-11-14
‘Green flight paths’ between key global locations could help to fast-track fully decarbonised aviation, according to research led by an international team based at Heriot-Watt University in the United Kingdom and the American University of Sharjah in the United Arab Emirates.
The research, published in the in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s top international journal, Energy and Environmental Science, recommends that a small number of long-haul flights with high passenger volumes, ...
Community partners key to success of vaccine clinic focused on neurodevelopmental conditions
2024-11-14
A new paper shows how partnering with the community can lead to more inclusive health care, especially for individuals with autism and other neurodevelopmental disabilities. The article, published this week in Pediatrics, details the success of a unique COVID-19 and flu vaccine clinic at the UC Davis MIND Institute.
The clinic team includes developmental-behavioral pediatricians, child life specialists, nurses, psychologists, social workers and staff trained to help families navigate health care. The goal is not only to administer vaccines, but to help patients build skills needed to successfully complete medical procedures for the rest of their lives.
Listening to ...
Low-carbon collaborative dual-layer optimization for energy station considering joint electricity and heat demand response
2024-11-14
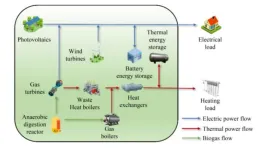
In a significant step towards achieving the "Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality" goals, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Institute of Technology, in collaboration with Hohai University, have developed a groundbreaking dual-layer optimization strategy for park-level integrated energy systems (PIES). This strategy, which integrates electricity and heat demand response, significantly boosts the economic efficiency and low-carbon operation ...
McMaster University researchers uncover potential treatment for rare genetic disorders
2024-11-14
Hamilton, ON, Nov. 14, 2024, In a groundbreaking study, researchers at McMaster University have identified a potential treatment for Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs diseases—two rare, often fatal lysosomal storage disorders that cause progressive damage to nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
After years of investigating the diseases’ underlying mechanisms, the research team has identified an existing FDA-approved drug that could significantly improve quality of life for affected patients and their families.
“Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs are devastating diseases,” ...
The return of protectionism: The impact of the Sino-US trade war
2024-11-14
Since 2018, Sino-US economic and trade relations have become increasingly tense. Between 2018 and 2019, the US imposed seven rounds of tariffs on China, to which China responded with retaliatory measures. The simple average tariff rates on US imports from China rose from 4.07% in January 2018 to 24.43% in December 2019, while the simple average tariff rates on Chinese imports from the US increased from 9.32% in January 2018 to 22.53% in December 2019 (see figure 1).
Consequently, the share of Chinese goods in US imports declined significantly — ...
UTokyo and NARO develop new vertical seed distribution trait for soybean breeding
2024-11-14
We have probably all seen a soybean plant, about 1 meter high with leaves and pods compactly arranged on a main stem with a few short side branches. The wild relative of the domesticated soybean is a long vine with pods widely distributed on many side branches. Plant breeding by farmers thousands of years ago is to thank for this dramatic change.
As human population increases and protein demand doubles, modern plant breeders must further optimize soybean plant architecture and per plant yield for modern farming systems. Conventional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
[Press-News.org] How can we reduce adolescent pregnancies in low- and middle-income countries?New study from the University of Bergen (Norway) and the University of Zambia published Nov. 14, 2024