(Press-News.org) Mountain lions in greater Los Angeles are proactively shifting their activity to avoid interacting with cyclists, hikers, joggers and other recreationists, finds a study from the University of California, Davis, Cal Poly Pomona and the National Park Service.
The study, published Nov. 15 in the journal Biological Conservation, found that mountain lions living in areas with higher levels of human recreation were more nocturnal than lions in more remote regions who were more active at dawn and dusk. The authors said their findings offer a hopeful example of human-wildlife coexistence amid a large, dense human population.
“People are increasingly enjoying recreating in nature, which is fantastic,” said lead author Ellie Bolas, a Ph.D. candidate in the UC Davis Department of Wildlife, Fish and Conservation Biology. “This flexibility we see in mountain lion activity is what allows us to share these natural areas together. Mountain lions are doing the work so that coexistence can happen.”
Mountain lions prefer to avoid people, but in a metro area of more than 18 million people, natural areas inhabited by mountain lions and other wildlife are also heavily used by recreationists. To learn whether and how lions were adjusting their activity in response to recreationists, the study authors monitored the movements of 22 mountain lions living in the Santa Monica Mountains and the surrounding region between 2011 and 2018.
The lions were captured and fitted with global positioning system (GPS) and accelerometer collars as part of a long-term study conducted by biologists at Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area, a unit of the National Park Service. The authors analyzed the collar data and quantified human recreation in the area using a global database of GPS-tracked activities that users opted to make public.
“These results are really important in that they show how humans may be affecting wildlife in less obvious ways than killing them with vehicles,” said Seth Riley, branch chief for wildlife at the park. “The study also continues to drive home the amazing fact that a population of a large felid predator persists in one of the largest urban areas in the world. That would not be possible if mountain lions weren’t able to adjust to human activity in ways like this.”
How mountain lions respond to more humans
The study showed that Griffith Park hosted the highest levels of recreational activity, while the Santa Susana Mountains and Los Padres National Forest were least active. How did mountain lions respond?
The least nocturnal mountain lion was female P13 in the central and western Santa Monica Mountains. Females, in general, were found to be more active closer to sunrise and during daylight hours as compared to males. The authors say this may be so they can avoid overlapping with male lions, who pose a threat to them and their kittens.
The most nocturnal were two male mountain lions living in small, isolated natural areas with many trails, high levels of recreation, and surrounded by intense development and freeways. Both individuals occupied two of the smallest home ranges ever recorded for adult males. P41, the study’s most nocturnal lion, lived in the Verdugo Mountains, a small mountain range spanning several cities.
The famous “Hollywood Cat,” P22, preferred to stay out of the limelight. P22, who managed to cross two busy freeways as a young lion to earn fame, hearts and a home in active Griffith Park, was the second most nocturnal lion studied. He died in 2022 when he was roughly 12 years old — one of the oldest cats in the study.
The authors said the urban experiences of P41, P22 and others in the study illustrate how, when faced with increased human activity, mountain lions actively seek to avoid people rather than becoming habituated to them.
How people can help
Still, the authors note, this doesn’t mean mountain lions should do all the work. People can help protect themselves and mountain lions by being aware that dawn or dusk is prime time for mountain lion activity. They can also be extra cautious when driving at night, when mountain lions in populated areas are more likely to be active.
Mountain lions in the Los Angeles area deal with many challenges — busy roadways where they’re often killed, wildfires, rodenticide exposure, low genetic diversity and fragmented habitat.
“Even something as innocuous as recreation can add to these other stressors we’re bringing into their lives, potentially by altering the amount of energy they have to expend for hunting and other needs,” Bolas said. “But we can feel a sense of optimism that they are flexible in the timing of their activity. Coexistence is happening, and it’s in large part because of what mountain lions are doing.”
The study’s additional co-authors include Adam Pingatore and Daniel Blumstein of UCLA, Maya Mathur of Harvard Westlake High School, Jeff Sikich of the National Park Service, Justine Smith of UC Davis, John Benson of University of Nebraska and Rachel Blakey of California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, and UCLA.
The study was supported through funding from the National Science Foundation, National Park Service, La Kretz Center for California Conservation at UCLA, and the UC Davis Graduate Group in Ecology Fellowship.
END
Mountain lions coexist with outdoor recreationists by taking the night shift
How mountain lions in Los Angeles are adjusting to avoid human interactions
2024-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Students who use dating apps take more risks with their sexual health
2024-11-15
In May, the WHO raised the alarm over the rise in incidence of sexually transmitted illnesses (STIs) in many regions of the world, currently running at more than a million new cases per day. Among high-income countries, the US has one of the highest prevalences of STIs, and this problem is getting worse. For example, the incidence of chlamydia has more than doubled since 2000, while gonorrhea increased by 40% and syphilis by 400%. The highest prevalence is among young adults between 20 and 34 years of age.
Over ...
Breakthrough idea for CCU technology commercialization from 'carbon cycle of the earth'
2024-11-15
The research team led by Dr. Hyung-Suk Oh and Dr. Woong Hee Lee at the Clean Energy Research Center at Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) has developed a silver-silica composite catalyst capable of reversible local pH control through a silica-hydroxide cycle, inspired by Earth’s natural cycles. This research draws inspiration from the carbonate-silicate cycle, known as the Earth’s inorganic carbon cycle, where carbon dioxide (CO₂) maintains balance. CO₂ is removed from ...
Keck Hospital of USC earns an ‘A’ Hospital Safety Grade from The Leapfrog Group
2024-11-15
LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC earned an “A” Hospital Safety Grade from The Leapfrog Group, an independent national nonprofit watchdog focused on patient safety.
This is the ninth “A” grade the hospital has received since 2019.
“An ‘A’ grade once again puts Keck Hospital among the safest hospitals in the nation, and reflects the hospital’s dedication to maintaining the highest standards of quality and safety protocols,” ...
Depression research pioneer Dr. Philip Gold maps disease's full-body impact
2024-11-15
Bethesda, Maryland, USA, 14 November 2024 – A landmark paper by distinguished neuroendocrine psychiatrist Dr. Philip W. Gold, published in Brain Medicine's Seymour Reichlin Centenary Festschrift collection, presents a masterful synthesis of how depression fundamentally alters the body's stress response systems, challenging long-held views of the condition.
The Viewpoint Review, published online November 14, 2024, represents a culmination of Dr. Gold's pioneering work in neuroendocrine psychiatry and honors the centenary of Dr. Seymour Reichlin, a foundational figure in neuroendocrinology whose ...
Rapid growth of global wildland-urban interface associated with wildfire risk, study shows
2024-11-15
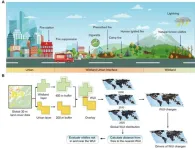
Rapid human expansion into natural landscapes, resulting in the growth of the wildland-urban interface (WUI), has heightened risks associated with wildfires.
Prof. WANG Jianghao’s team from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has recently mapped global WUI changes in 2000, 2010, and 2020, revealing alarming upward trends in WUI areas.
This work, published in Science Advances, provides critical insights into how urbanization can intensify potential wildfire risks faced by people worldwide.
Against ...
Generation of rat offspring from ovarian oocytes by Cross-species transplantation
2024-11-15
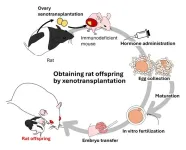
Niigata and Toyama, Japan - The idea of maturing oocytes in the ovary to produce offspring has been implemented in various ways. One such method, ovarian transplantation, is a relatively simple procedure for obtaining eggs, compared to in vitro culture of ovaries and follicles. However, it is still difficult to transplant ovaries into cellular immunodeficient mice and produce offspring from the eggs grown in the mice.
In order to produce offspring from xenotransplanted ovaries, Japanese researchers at Niigata University and University ...
Duke-NUS scientists develop novel plug-and-play test to evaluate T cell immunotherapy effectiveness
2024-11-15
Singapore, 15 November 2024 — A novel test developed by Duke-NUS researchers enables real-time monitoring of T cells that have been engineered to fight cancer, after re-introduction into the body of a cancer patient. This simple and innovative test provides clinicians with the ability to track the function of these cancer-fighting cells over the course of the treatment.
T cells are a type of immune cell that seeks out and destroys cells infected by viruses, bacteria as well as tumour cells. Originally ...
Compound metalens achieves distortion-free imaging with wide field of view
2024-11-15
In a recent study, researchers have developed a compound metalens that enables distortion-free imaging. The study, published in Engineering, presents a novel approach to on-demand distortion engineering using compound metalenses.
Metalenses have emerged as a promising technology with applications in beam steering, imaging, depth sensing, and display projection. However, optical distortion, a crucial factor in optical design, has been relatively unexplored in the context of meta-optics. The researchers addressed this gap by demonstrating ...
Age on the molecular level: showing changes through proteins
2024-11-15
With the worldwide population aging at an unprecedented rate, the prevention of age-related diseases has become a prominent issue. It is important to comprehensively and quantitatively evaluate the changes that aging causes at the molecular level in the body. By doing so, it may be possible to pinpoint specific aging factors and suppress age-related diseases.
Addressing this problem, previously conducted research established an atlas of changes in major tissues from aging by determining the extent to which mRNA was produced within living cells. However, there has not ...
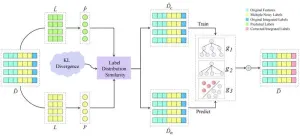
Label distribution similarity-based noise correction for crowdsourcing
2024-11-15
In crowdsourcing scenarios, we can obtain each instance's multiple noisy labels from different crowd workers and then infer its integrated label via label aggregation. In spite of the effectiveness of label aggregation methods, there still remains a certain level of noise in the integrated labels. Thus, some noise correction methods have been proposed to reduce the impact of noise in recent years. However, to the best of our knowledge, existing methods rarely consider an instance's information from both its features and multiple noisy labels simultaneously ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
[Press-News.org] Mountain lions coexist with outdoor recreationists by taking the night shiftHow mountain lions in Los Angeles are adjusting to avoid human interactions