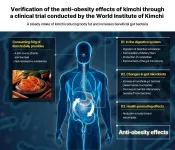
(Press-News.org) Approximately 16% of the global population, or about 890 million people, suffer from obesity. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized obesity as a significant health issue and highlighted its impact on the quality of life and overall health of individuals across the world. In response to this, the World Institute of Kimchi, South Korea, has been publishing a series of articles on the anti-obesity effects of kimchi in international journals. These articles, based on research studies on the subject, indicate that the regular consumption of kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented food, is effective in reducing body fat and may serve as a promising dietary strategy to combat obesity.
Recent investigations exploring the effects of kimchi on obesity have yielded compelling evidence supporting its efficacy. Notably, preclinical experiments in animal models of obesity revealed a substantial 31.8% reduction in body fat among those fed a kimchi diet1).
Additionally, an extensive analysis of data collected over 13 years from the Korea Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES), a large population-based study, found that appropriate kimchi intake is associated with a 15% reduction in body mass index (BMI) and a 12% decrease in obesity incidence among middle-aged males2). This study was published in Food & Function2), BMJ Open3) (a British medical journal published by a subsidiary of the British Medical Association) and was also reported in the U.S based NBC News4).
1) (Article) Kimchi Intake Alleviates Obesity-Induced Neuroinflammation by Modulating the Gut-Brain Axis (Food Res Int., IF 7.425) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111533
2) (Article) Effect of Kimchi Intake on Body Weight of General Community Dwellers: a Prospective Cohort Study (Food & Function, IF 6.317), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03900A
3) (Article) Association between kimchi consumption and obesity by BMI and abdominal obesity in Korean adults a cross-sectional analysis of the Health Examinees study (BMJ open, IF 2.9), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076650
4) (News article) https://www.nbcnews.com/news/asian-america/kimchi-lower-obesity-risk-midriff-bulge-korean-classic-rcna136445
Continuing this line of inquiry, a research study conducted by a team led by Dr. Sung-Wook Hong from the Kimchi Functionality Research Group at the World Institute of Kimchi, in collaboration with the Pusan National University Hospital, South Korea, focused on the anti-obesity effects of kimchi and its impact on gut microbiomes. This study investigated the changes in anthropometric measurements, blood biomarkers, and gut microbiomes of 55 overweight adults, comprising both males and females, with a BMI ranging from 23 to 30 kg/m². The participants consumed 3 kimchi capsules per meal (60g of kimchi per day) for 3 months. The kimchi capsules contained kimchi powder produced by freeze-drying cabbage kimchi fermented at 4℃ for 2 weeks. The research team analyzed the changes in the body fat composition of the participants and found that the group that consumed kimchi showed a 2.6% decrease in body fat, but the control group that did not take the kimchi capsules exhibited a 4.7% increase in body fat, showing a statistically significant difference between the two groups.
Further, the analysis of the microbiomes of the participants revealed that kimchi consumption resulted in an increase in the abundance of the beneficial gut bacterium, Akkermansia muciniphila*, and a reduction in the number of Proteobacteria, which are associated with obesity.
※ Akkermansia muciniphila: This is a species of gut bacterium that has been reported to reduce inflammation and improve the markers of metabolic syndrome and obesity through the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
The successful completion of this clinical trial on the body fat-reducing effects of kimchi indicates that a steady consumption of kimchi is effective in alleviating obesity symptoms through the modulation of the gut microbiota.
Dr. Hae-Choon Chang, Director of the World Institute of Kimchi, said, “The results of a preclinical study and a clinical trial have systematically verified the anti-obesity effects of kimchi, and present scientific evidence that would help to make the excellent properties of kimchi widely known, thereby laying the foundation for the growth of kimchi as a health food well recognized around the world.” She also said, “We will continue to devote our time, effort, and resources towards scientific research to reinforce the health-functional properties of kimchi, in improving gastrointestinal health in addition to its immune-enhancing and anti-cancer effects, thus firmly establishing the role of kimchi as a global health food.”
The clinical trial on the anti-obesity effects of kimchi was published in the October 2024 issue of the ‘Journal of Functional Foods.’
Meanwhile, in Korea, the country where kimchi originated, November 22 was officially designated as a national commemorative day for kimchi and named Kimchi Day in 2020. Kimchi is the first Korean food to be recognized in this manner for its unique health properties. Since then, Kimchi Festivals have been celebrated on Kimchi Day in the U.S., U.K., Argentina, and Brazil on November 22.
END
New Clinical Study Confirms the Anti-Obesity Effects of Kimchi
Regular Consumption Reduces Body Fat and Boosts Gut Health
2024-11-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Highly selective pathway for propyne semihydrogenation achieved via CoSb intermetallic catalyst
2024-11-19
Researchers delved deep into the regulation of cobalt active sites to enhance the selectivity of propylene to improve scalability and affordability of the production of this important chemical.
Chemical reactions are not always naturally optimized to yield the products in the quantities needed, especially on the scale needed for the amount of industry in the world today. Researchers from East China University of Science and Technology explored the options available to develop a more cost-effective, scalable and straightforward ...
GERD linked to cardiovascular risk factors: New insights from Mendelian randomization study
2024-11-19
A recent study published in the Journal of Translational Internal Medicine (https://doi.org/10.1515/jtim-2024-0017) reveals significant insights into the broader impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) on cardiovascular health. By using a rigorous bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) approach, the research provides compelling evidence that GERD—a condition traditionally recognized as a digestive disorder characterized by acid reflux and heartburn—may influence key cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, lipid ...
Content moderators are influenced by online misinformation
2024-11-19
Repeated exposure to lies online may influence the beliefs of professional content moderators, with consequences for online platforms. Hundreds of thousands of content moderators, typically based in non-Western countries, identify and weed out problematic and false content on social platforms. However, constant exposure to misinformation could convince some content moderators that false claims are true, in what is known as the “illusory truth effect.” Hause Lin and colleagues assessed the extent of this effect among professional content moderators in India and the Philippines and explored whether encouraging an accuracy mindset reduces the effect. ...
Adulting, nerdiness and the importance of single-panel comics
2024-11-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – While comics have become a culturally popular and widely studied art form in recent decades, one format remains overlooked: the single-panel comic.
Comics like “The Family Circus,” “Ziggy” and “Little Lulu” are often seen as simplistic and not worthy of critical attention, argues Michelle Ann Abate, author of the new book Singular Sensations: A Cultural History of One-Panel Comics in the United States.
“There tends to be a belief there ...
Study helps explain how children learned for 99% of human history
2024-11-19
PULLMAN, Wash. — Unlike kids in the United States, hunter-gatherer children in the Congo Basin have often learned how to hunt, identify edible plants and care for babies by the tender age of six or seven.
This rapid learning is facilitated by a unique social environment where cultural knowledge is passed down not just from parents but from the broader community, according to a new Washington State University-led study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research helps explain how many cultural traits have been preserved for thousands of years among ...
The impact of misinformation on Spanish-language social media platforms
2024-11-19
US Latinos who rely on social media in Spanish for their news are more vulnerable to political misinformation than those who use English-language social media, according to a study. Misinformation swirls on social media in every language, but social media companies struggle to combat disinformation circulating in Spanish on major social media platforms. In a study done in partnership with Jonathan Nagler of NYU’s Center for Social Media and Politics as part of the group’s Bilingual Election Monitor project, Marisa Abrajano and colleagues surveyed over 1,000 English-dominant, bilingual, and Spanish-dominant Latino users of ...
Populations overheat as major cities fail canopy goals: new research
2024-11-19
A new study led by RMIT University in Australia measuring access to nature for eight major global cities found most still have inadequate canopy cover, despite access to an abundance of trees.
Less than 30% of buildings in New York City, Amsterdam, Buenos Aires, Denver, central Sydney and central Melbourne were in neighbourhoods with adequate canopy cover.
New York and Amsterdam both scored almost 0% for canopy cover despite 92% and 50% of buildings having views of at least three trees, respectively.
The research, a collaboration with the Technical University of Munich, studied over 2.5 million buildings across ...
By exerting “crowd control” over mouse cells, scientists make progress towards engineering tissues
2024-11-19
Genes aren’t the sole driver instructing cells to build multicellular structures, tissues, and organs. In a new paper published in Nature Communications, USC Stem Cell scientist Leonardo Morsut and Caltech computational biologist Matt Thomson characterize the influence of another important developmental driver: cell density, or how loosely or tightly cells are packed into a given space. In both computational models and laboratory experiments, the team of scientists used cell density as an effective tool for controlling how mouse cells pattern themselves into complex structures.
“This paper represents progress towards our big picture goal of engineering synthetic ...
First American Gastroenterological Association living guideline for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis
2024-11-19
Bethesda, MD (Nov. 15, 2024) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released a new clinical guideline on the pharmacological management of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis, published today in Gastroenterology. This guideline groups the 12 currently available advanced treatments based on efficacy, to simplify the decision-making process for gastroenterologists and the approximately 1.25 million patients in the U.S. living with ulcerative colitis.
“Since the first biologic ...
Labeling cell particles with barcodes
2024-11-19
Cell-to-cell communication through nanosized particles, working as messengers and carriers, can now be analyzed in a whole new way, thanks to a new method involving CRISPR gene-editing technology. The particles, known as small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), play an important role in the spread of disease and as potential drug carriers. The newly developed system, named CIBER, enables thousands of genes to be studied at once, by labeling sEVs with a kind of RNA “barcode.” With this, researchers hope to find what factors are involved in sEV release from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] New Clinical Study Confirms the Anti-Obesity Effects of KimchiRegular Consumption Reduces Body Fat and Boosts Gut Health