(Press-News.org) Repeated exposure to lies online may influence the beliefs of professional content moderators, with consequences for online platforms. Hundreds of thousands of content moderators, typically based in non-Western countries, identify and weed out problematic and false content on social platforms. However, constant exposure to misinformation could convince some content moderators that false claims are true, in what is known as the “illusory truth effect.” Hause Lin and colleagues assessed the extent of this effect among professional content moderators in India and the Philippines and explored whether encouraging an accuracy mindset reduces the effect. The authors asked 199 content moderators to rate 16 COVID-19 news headlines, first on their interestingness and then, after a break, on their accuracy—along with 32 new COVID-19 news headlines. As predicted by the illusory truth effect, headlines seen for the second time were 7.1% more likely to be judged as accurate than non-repeated headlines. However, in a similar experiment in which content moderators were asked to rate accuracy first—thereby encouraging an accuracy mindset—repeated headlines were not rated as more accurate than new headlines. Similar experiments with members of the public in India and the Philippines found similar effects. According to the authors, the results suggest that the illusory truth effect is not idiosyncratic to Western populations, suggesting that content moderators may become less effective over time due to being chronically exposed to falsehoods, which could compromise the safety and integrity of online platforms. Accuracy mindset prompts could help, the authors note.
END
Content moderators are influenced by online misinformation
2024-11-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adulting, nerdiness and the importance of single-panel comics
2024-11-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – While comics have become a culturally popular and widely studied art form in recent decades, one format remains overlooked: the single-panel comic.
Comics like “The Family Circus,” “Ziggy” and “Little Lulu” are often seen as simplistic and not worthy of critical attention, argues Michelle Ann Abate, author of the new book Singular Sensations: A Cultural History of One-Panel Comics in the United States.
“There tends to be a belief there ...
Study helps explain how children learned for 99% of human history
2024-11-19
PULLMAN, Wash. — Unlike kids in the United States, hunter-gatherer children in the Congo Basin have often learned how to hunt, identify edible plants and care for babies by the tender age of six or seven.
This rapid learning is facilitated by a unique social environment where cultural knowledge is passed down not just from parents but from the broader community, according to a new Washington State University-led study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research helps explain how many cultural traits have been preserved for thousands of years among ...
The impact of misinformation on Spanish-language social media platforms
2024-11-19
US Latinos who rely on social media in Spanish for their news are more vulnerable to political misinformation than those who use English-language social media, according to a study. Misinformation swirls on social media in every language, but social media companies struggle to combat disinformation circulating in Spanish on major social media platforms. In a study done in partnership with Jonathan Nagler of NYU’s Center for Social Media and Politics as part of the group’s Bilingual Election Monitor project, Marisa Abrajano and colleagues surveyed over 1,000 English-dominant, bilingual, and Spanish-dominant Latino users of ...
Populations overheat as major cities fail canopy goals: new research
2024-11-19
A new study led by RMIT University in Australia measuring access to nature for eight major global cities found most still have inadequate canopy cover, despite access to an abundance of trees.
Less than 30% of buildings in New York City, Amsterdam, Buenos Aires, Denver, central Sydney and central Melbourne were in neighbourhoods with adequate canopy cover.
New York and Amsterdam both scored almost 0% for canopy cover despite 92% and 50% of buildings having views of at least three trees, respectively.
The research, a collaboration with the Technical University of Munich, studied over 2.5 million buildings across ...
By exerting “crowd control” over mouse cells, scientists make progress towards engineering tissues
2024-11-19
Genes aren’t the sole driver instructing cells to build multicellular structures, tissues, and organs. In a new paper published in Nature Communications, USC Stem Cell scientist Leonardo Morsut and Caltech computational biologist Matt Thomson characterize the influence of another important developmental driver: cell density, or how loosely or tightly cells are packed into a given space. In both computational models and laboratory experiments, the team of scientists used cell density as an effective tool for controlling how mouse cells pattern themselves into complex structures.
“This paper represents progress towards our big picture goal of engineering synthetic ...
First American Gastroenterological Association living guideline for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis
2024-11-19
Bethesda, MD (Nov. 15, 2024) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released a new clinical guideline on the pharmacological management of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis, published today in Gastroenterology. This guideline groups the 12 currently available advanced treatments based on efficacy, to simplify the decision-making process for gastroenterologists and the approximately 1.25 million patients in the U.S. living with ulcerative colitis.
“Since the first biologic ...
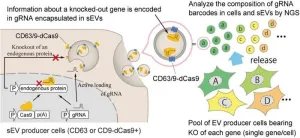
Labeling cell particles with barcodes
2024-11-19
Cell-to-cell communication through nanosized particles, working as messengers and carriers, can now be analyzed in a whole new way, thanks to a new method involving CRISPR gene-editing technology. The particles, known as small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), play an important role in the spread of disease and as potential drug carriers. The newly developed system, named CIBER, enables thousands of genes to be studied at once, by labeling sEVs with a kind of RNA “barcode.” With this, researchers hope to find what factors are involved in sEV release from ...
Groundwater pumping drives rapid sinking in California
2024-11-19
A new study shows land in California’s San Joaquin Valley has been sinking at record-breaking rates over the last two decades as groundwater extraction has outpaced natural recharge.
The researchers found that the average rate of sinking for the entire valley reached nearly an inch per year between 2006 and 2022.
Researchers and water managers have known that sinking, technically termed “subsidence,” was occurring over the past 20 years. But the true impact was not fully appreciated because the total subsidence had not been quantified. This was in part due to a gap in data. Satellite radar systems, which provide the most precise measure of elevation changes, ...
Neuroscientists discover how the brain slows anxious breathing
2024-11-19
LA JOLLA (November 19, 2024)—Deep breath in, slow breath out… Isn’t it odd that we can self-soothe by slowing down our breathing? Humans have long used slow breathing to regulate their emotions, and practices like yoga and mindfulness have even popularized formal techniques like box breathing. Still, there has been little scientific understanding of how the brain consciously controls our breathing and whether this actually has a direct effect on our anxiety and emotional state.
Neuroscientists ...
New ion speed record holds potential for faster battery charging, biosensing
2024-11-19
PULLMAN, Wash. – A speed record has been broken using nanoscience, which could lead to a host of new advances, including improved battery charging, biosensing, soft robotics and neuromorphic computing.
Scientists at Washington State University and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have discovered a way to make ions move more than ten times faster in mixed organic ion-electronic conductors. These conductors combine the advantages of the ion signaling used by many biological systems, including the human body, with the electron signaling used by computers.
The new development, detailed in the journal ...