(Press-News.org) US Latinos who rely on social media in Spanish for their news are more vulnerable to political misinformation than those who use English-language social media, according to a study. Misinformation swirls on social media in every language, but social media companies struggle to combat disinformation circulating in Spanish on major social media platforms. In a study done in partnership with Jonathan Nagler of NYU’s Center for Social Media and Politics as part of the group’s Bilingual Election Monitor project, Marisa Abrajano and colleagues surveyed over 1,000 English-dominant, bilingual, and Spanish-dominant Latino users of Facebook and Instagram in the US, offering a monetary incentive for participation. Each participant was asked whether they believed seven false political narratives, including the claim that Venezuela was intentionally sending criminals to the US, the claim that most Planned Parenthood clinics have closed down across the country in the wake of Roe v. Wade being overturned, and the claim that the COVID-19 vaccine can make breast milk dangerous to infants. Latinos who use Spanish-language social media for news were 11 percentage points more likely to believe in false political narratives than those who use English-language social media for news. According to the authors, the study offers evidence that misinformation circulating on social media in Spanish leads to factually inaccurate political beliefs, which could have important consequences for democracy.
END
The impact of misinformation on Spanish-language social media platforms
2024-11-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Populations overheat as major cities fail canopy goals: new research
2024-11-19
A new study led by RMIT University in Australia measuring access to nature for eight major global cities found most still have inadequate canopy cover, despite access to an abundance of trees.
Less than 30% of buildings in New York City, Amsterdam, Buenos Aires, Denver, central Sydney and central Melbourne were in neighbourhoods with adequate canopy cover.
New York and Amsterdam both scored almost 0% for canopy cover despite 92% and 50% of buildings having views of at least three trees, respectively.
The research, a collaboration with the Technical University of Munich, studied over 2.5 million buildings across ...
By exerting “crowd control” over mouse cells, scientists make progress towards engineering tissues
2024-11-19
Genes aren’t the sole driver instructing cells to build multicellular structures, tissues, and organs. In a new paper published in Nature Communications, USC Stem Cell scientist Leonardo Morsut and Caltech computational biologist Matt Thomson characterize the influence of another important developmental driver: cell density, or how loosely or tightly cells are packed into a given space. In both computational models and laboratory experiments, the team of scientists used cell density as an effective tool for controlling how mouse cells pattern themselves into complex structures.
“This paper represents progress towards our big picture goal of engineering synthetic ...
First American Gastroenterological Association living guideline for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis
2024-11-19
Bethesda, MD (Nov. 15, 2024) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released a new clinical guideline on the pharmacological management of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis, published today in Gastroenterology. This guideline groups the 12 currently available advanced treatments based on efficacy, to simplify the decision-making process for gastroenterologists and the approximately 1.25 million patients in the U.S. living with ulcerative colitis.
“Since the first biologic ...
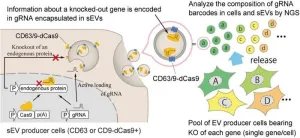
Labeling cell particles with barcodes
2024-11-19
Cell-to-cell communication through nanosized particles, working as messengers and carriers, can now be analyzed in a whole new way, thanks to a new method involving CRISPR gene-editing technology. The particles, known as small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), play an important role in the spread of disease and as potential drug carriers. The newly developed system, named CIBER, enables thousands of genes to be studied at once, by labeling sEVs with a kind of RNA “barcode.” With this, researchers hope to find what factors are involved in sEV release from ...
Groundwater pumping drives rapid sinking in California
2024-11-19
A new study shows land in California’s San Joaquin Valley has been sinking at record-breaking rates over the last two decades as groundwater extraction has outpaced natural recharge.
The researchers found that the average rate of sinking for the entire valley reached nearly an inch per year between 2006 and 2022.
Researchers and water managers have known that sinking, technically termed “subsidence,” was occurring over the past 20 years. But the true impact was not fully appreciated because the total subsidence had not been quantified. This was in part due to a gap in data. Satellite radar systems, which provide the most precise measure of elevation changes, ...
Neuroscientists discover how the brain slows anxious breathing
2024-11-19
LA JOLLA (November 19, 2024)—Deep breath in, slow breath out… Isn’t it odd that we can self-soothe by slowing down our breathing? Humans have long used slow breathing to regulate their emotions, and practices like yoga and mindfulness have even popularized formal techniques like box breathing. Still, there has been little scientific understanding of how the brain consciously controls our breathing and whether this actually has a direct effect on our anxiety and emotional state.
Neuroscientists ...
New ion speed record holds potential for faster battery charging, biosensing
2024-11-19
PULLMAN, Wash. – A speed record has been broken using nanoscience, which could lead to a host of new advances, including improved battery charging, biosensing, soft robotics and neuromorphic computing.
Scientists at Washington State University and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have discovered a way to make ions move more than ten times faster in mixed organic ion-electronic conductors. These conductors combine the advantages of the ion signaling used by many biological systems, including the human body, with the electron signaling used by computers.
The new development, detailed in the journal ...
Haut.AI explores the potential of AI-enhanced fluorescence photography for non-invasive skin diagnostics
2024-11-19
Tallinn, Estonia – 19th November 2024, 10 AM CET – Haut.AI, a pioneering artificial intelligence (AI) company for skincare and beauty applications, has published an exciting scientific review—one that explores state-of-the-art developments in skin fluorescence photography and its applications, focusing on combining it with AI algorithms for non-invasive skin diagnostics. The study highlights the power of AI to enhance skin fluorescence photography, allowing early, non-invasive detection of skin conditions. This approach allows skincare experts to diagnose underlying issues ...
7-year study reveals plastic fragments from all over the globe are rising rapidly in the North Pacific Garbage Patch
2024-11-19
A study published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research Letters reveals that centimetre-sized plastic fragments are increasing much faster than larger floating plastics in the North Pacific Garbage Patch [NPGP], threatening the local ecosystem and potentially the global carbon cycle.
The research, which draws from not-for-profit The Ocean Cleanup’s systematic surveys of the NPGP between 2015 and 2022, found an unexpected rise in mass concentration of plastic fragments that are ...
New theory reveals the shape of a single photon
2024-11-19
A new theory, that explains how light and matter interact at the quantum level has enabled researchers to define for the first time the precise shape of a single photon.
Research at the University of Birmingham, published in Physical Review Letters, explores the nature of photons (individual particles of light) in unprecedented detail to show how they are emitted by atoms or molecules and shaped by their environment.
The nature of this interaction leads to infinite possibilities for light to exist and propagate, or travel, through its surrounding environment. This limitless ...