(Press-News.org) MELVILLE, N.Y., Nov. 19, 2024 – Alzheimer’s disease affects more than 50 million people worldwide, often devastating both the individuals who have it and their families and loved ones. It has no known cure, and the slow, progressive nature of the disease makes early diagnosis difficult.
Researchers from École de Technologie Supérieure and Dartmouth University are investigating the use of earpiece microphones to spot early signs of Alzheimer’s. Miriam Boutros will present their work on Tuesday, Nov. 19, at 4:15 p.m. ET, as part of the virtual 187th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, running Nov. 18-22, 2024.
People with Alzheimer’s exhibit a loss of motor control along with cognitive decline. One of the earliest signs of this decay can be spotted in involuntary eye movements known as saccades. These quick twitches of the eyes in Alzheimer’s patients are often slower, less accurate, or delayed compared to those in healthy individuals.
“Eye movements are fascinating since they are some of the most rapid and precise movements in the human body, thus they rely on both excellent motor skills and cognitive functioning,” said researcher Arian Shamei.
Detecting and analyzing saccades directly requires a patient to be monitored by eye-tracking equipment, which is not easily accessible for most people. Boutros and her colleagues are exploring an alternative method using a more ubiquitous and less intrusive technology: earpiece microphones. This research is led by Rachel Bouserhal at the Research in Hearing Health and Assistive Devices (RHAD) Laboratory at École de Technologie Supérieure and Chris Niemczak at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth University.
“We are using a device called a hearable,” said Boutros. “It is an earpiece with in-ear microphones that captures physiological signals from the body. Our goal is to develop health-monitoring algorithms for hearables, capable of continuous, long-term monitoring and early disease detection.”
Eye movements, including saccades, cause eardrum vibrations that can be picked up by sensitive microphones located within the ear. The researchers are conducting experiments with volunteers, giving them both hearables and conventional eye trackers. Their goal is to identify signals corresponding to saccades, and to differentiate between healthy signals and others that are indicative of neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s.
They hope one day their research will lead to devices that can perform noninvasive continuous monitoring for Alzheimer’s along with other neurological diseases.
“While the current project is focused on long-term monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease, eventually, we would like to tackle other diseases and be able to differentiate between them based on symptoms that can be tracked through in-ear signals,” said Shamei.
###
Media are invited to attend a virtual press conference about this research and other sessions on Monday, Nov. 18. A full schedule is available at https://acoustics.org/asa-press-conference-schedule-for-monday-nov-18-asa187. To register for virtual press conferences or sessions, email media@aip.org.
———————– MORE MEETING INFORMATION ———————–
Main Meeting Website: https://acousticalsociety.org/asa-virtual-fall-2024/
Technical Program: https://eppro01.ativ.me/src/EventPilot/php/express/web/planner.php?id=ASAFALL24
ASA PRESS ROOM
In the coming weeks, ASA’s Press Room will be updated with newsworthy stories and the press conference schedule at https://acoustics.org/asa-press-room/.
LAY LANGUAGE PAPERS
ASA will also share dozens of lay language papers about topics covered at the conference. Lay language papers are summaries (300-500 words) of presentations written by scientists for a general audience. They will be accompanied by photos, audio, and video. Learn more at https://acoustics.org/lay-language-papers/.
PRESS REGISTRATION
ASA will grant free registration to credentialed and professional freelance journalists. If you are a reporter and would like to attend the virtual meeting and/or press conferences, contact AIP Media Services at media@aip.org. For urgent requests, AIP staff can also help with setting up interviews and obtaining images, sound clips, or background information.
ABOUT THE ACOUSTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA
The Acoustical Society of America is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7,000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (the world’s leading journal on acoustics), JASA Express Letters, Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics, Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards on acoustics. The society also holds two major scientific meetings each year. See https://acousticalsociety.org/.
###
END
Listening for early signs of Alzheimer’s disease #ASA187
In-ear microphones could monitor sounds of eye movements for neurological decay.
2024-11-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research Spotlight: Gastroenterology education improved through inpatient care teaching model
2024-11-19
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Gastroenterologists who focus primarily on providing inpatient care, called GI Hospitalists, are becoming more common across the U.S. We developed a survey to assess the effect of GI Hospitalists on fellowship education and found that GI Hospitalists improve education through superior endoscopy teaching and longitudinal feedback.
What knowledge gap does your study help to fill?
The aim of this study was to directly assess GI fellows’ perceptions of the educational impact of GI Hospitalist faculty on GI fellowship training. ...
Texas A&M researchers uncover secrets of horse genetics for conservation, breeding
2024-11-19
Researchers at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) are helping uncover new information about the Y chromosome in horses, which will help owners identify optimal lineages for breeding and help conservationists preserve breed diversity.
“Because of its complex structure, the Y chromosome is much harder to sequence, making our knowledge of it far from complete,” said Dr. Gus Cothran, a professor emeritus in the VMBS’ Department of Veterinary Integrative Biosciences (VIBS). “In fact, scientists used to believe that the Y chromosome ...
Bioeconomy in Colombia: The race to save Colombia's vital shellfish
2024-11-19
Along Colombia's Pacific coast, a small shellfish called piangua has been a crucial part of local communities for generations. This humble mollusk is a vital source of income and nutrition for many coastal residents. As a regional resource that can be sustainably utilized, it represents a bioeconomy opportunity and is an example for other regions. But now, scientists are raising the alarm about its future.
A new study reveals that piangua populations are showing concerning signs of decline, largely due to overharvesting. Researchers used cutting-edge DNA analysis to examine these shellfish in two key locations along Colombia's ...
NFL’s Colts bring CPR education to flag football to improve cardiac emergency outcomes
2024-11-19
INDIANAPOLIS, November 18, 2024— The American Heart Association and the Indianapolis Colts this past weekend brought cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training to the Colts Regional Flag Football tournament. At the Kickoff event held at the Indiana Farm Bureau Football Center on Saturday, Nov. 16 more than 100 youth athletes, coaches and league administrators learned lifesaving skills to build their confidence and capabilities to respond in the event of a cardiac emergency. The following day, walk-up style Hands-Only CPR instruction was again available to guests attending the tournament at the Center Grove Bantom ...
Research: Fitness more important than fatness for a lower risk of premature death
2024-11-19
As rates of obesity, as defined by body mass index (BMI), continue to climb in the United States, so have efforts to lose weight, including a new era of weight-loss drugs. Yet a new systematic review and meta-analysis published today in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that cardiorespiratory fitness was a stronger predictor of both cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality than BMI.
The researchers found that fit individuals across all BMI categories had statistically similar risks of death from all causes or cardiovascular disease. By contrast, unfit individuals ...
Researchers use biophysics to design new vaccines against RSV and related respiratory viruses
2024-11-19
LA JOLLA, CA—In most people, the lung-infecting pathogens known as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) trigger mild cold-like symptoms. But in infants and seniors, these viruses can cause severe pneumonia and even death.
Vaccines against both viruses, however, have been difficult to design. Now, Scripps Research scientists have analyzed the structure and stability of a critical RSV and hMPV protein to better design vaccines that target it. Their research, ...
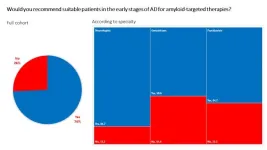
New study highlights physician perspectives on emerging anti-amyloid treatments for Alzheimer’s disease in Israel
2024-11-19
November 19, 2024 - Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel – In a recent study, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center has shed light on physician attitudes toward novel anti-amyloid treatments (ATT) for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), revealing a spectrum of opinions across key specialties. With Israel’s health system structured to provide universal healthcare, the high out-of-pocket costs for new AD therapies have raised questions among medical professionals about the feasibility and practicality of implementing these treatments.
The study, conducted ...
U of M research finds creativity camp improves adolescent mental health, well-being
2024-11-19
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (11/19/2024) — Published in Child Psychiatry and Human Development, a research team led by the University of Minnesota Medical School found that Creativity Camp, a two-week arts intervention delivered as a day camp, had a positive impact on mental health and well-being in adolescents with depression.
The idea behind the study is that engaging in the arts offers a pathway for exploring and expanding new ways of thinking, developing insights and sparking self-discovery.
“As a clinician, I am deeply aware of the urgent need for new treatment options for teens with depression. The findings in this report are promising, and I hope they ...
How human brain functional networks emerge and develop during the birth transition
2024-11-19
Brain-imaging data collected from fetuses and infants has revealed a rapid surge in functional connectivity between brain regions on a global scale at birth, possibly reflecting neural processes that support the brain’s ability to adapt to the external world, according to a study published November 19th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology led by Lanxin Ji and Moriah Thomason from the New York University School of Medicine, USA.
Understanding the sequence and timing of brain functional network ...
Low-dose ketamine shows promise for pain relief in emergency department patients
2024-11-19
Des Plaines, IL — A new study that investigates low-dose ketamine (LDK) as an adjunct to morphine for treating acute pain has been published in the October issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The study, titled Low-dose ketamine as an adjunct to morphine: A randomized controlled trial among patients with and without current opioid use highlights the potential of low-dose ketamine as a valuable tool in pain management, providing a safe and effective option for emergency medicine physicians managing acute pain.
Pain remains one of the most common and challenging complaints ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Listening for early signs of Alzheimer’s disease #ASA187In-ear microphones could monitor sounds of eye movements for neurological decay.