(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES, California, USA, 20 November 2024 – In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Professor Helen Lavretsky reveals how her pioneering work in integrative psychiatry is transforming approaches to mental health and aging. The interview, featured in the peer-reviewed medical research journal Brain Medicine (doi: 10.61373/bm024k.0130), offers unique insights into the evolution of integrative medicine from scientific skepticism to evidence-based acceptance.
Professor Lavretsky, current President of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry (2022-25), has successfully merged conventional psychiatric treatments with mind-body interventions, developing novel therapeutic combinations for treatment-resistant depression and cognitive disorders. Her groundbreaking studies on yoga and Tai Chi have established new paradigms in mental health care, supported by rigorous neurobiological research.
“Twenty years ago, through my practice of yoga as a stress reduction tool that improved my health, I put my attention on designing research studies of mind-body interactions,” Professor Lavretsky shares in the interview. “Some of the studies of yoga and Tai Chi became groundbreaking and set a new trend in research and clinical practice that emphasized whole person health and prevention.”
The interview explores critical questions about the future of preventive psychiatry. How might early intervention strategies reshape our understanding of aging-related mental health conditions? What role will integrative approaches play in addressing the growing global burden of neuropsychiatric disorders?
Professor Lavretsky's vision extends beyond traditional treatment models: “I hope that the field of psychiatry and mental health will open from a strict disease and acute-care-oriented field of medicine to embrace brain health-oriented prevention for neuropsychiatric disorders.”
Her research has particular relevance as healthcare systems worldwide grapple with aging populations and increasing mental health challenges. How can integrative medicine approaches be scaled effectively across different healthcare settings? What role might traditional healing practices play in modern psychiatric care?
The interview also highlights Professor Lavretsky's commitment to diversity in medical research, having mentored women and underrepresented minorities for over 25 years. This dedication to inclusive excellence raises important questions about representation in medical research and leadership.
Currently serving on the Advisory Research Council to the National Center of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, Professor Lavretsky continues to advance the field through publications, including her recent books Resilience and Aging: Research and Practice and Convergence Mental Health: A Transdisciplinary Approach to Innovation.
This Genomic Press Interview titled “Helen Lavretsky: Translational neuroscience of integrative medicine” being published on 20 November 2024 in Brain Medicine. The article is freely available online at https://url.genomicpress.com/2p8bu96z.
About Brain Medicine: Brain Medicine (ISSN: 2997-2639) is a peer-reviewed journal published by Genomic Press, New York. Brain Medicine is a new home for the cross-disciplinary pathway from innovation in fundamental neuroscience to translational initiatives in brain medicine. The journal’s scope includes the underlying science, causes, outcomes, treatments, and societal impact of brain disorders, across all clinical disciplines and their interface.
END
UCLA professor Helen Lavretsky reshapes brain health through integrative medicine research
Leading geriatric psychiatrist shares transformative journey and vision in exclusive Genomic Press Interview series
2024-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Astronauts found to process some tasks slower in space, but no signs of permanent cognitive decline
2024-11-20
A stay in space exerts extreme pressures on the human body. Astronauts’ bodies and brains are impacted by radiation, altered gravity, challenging working conditions, and sleep loss – all of which could compromise cognitive functioning. At the same time, they are required to perform complex tasks, and minor mistakes can have devastating consequences.
Little is known, however, about whether astronauts’ cognitive performance changes while in space. Now, working with 25 astronauts who spent an average of six month on the International Space Station (ISS), researchers in the US have examined changes in a wide range of cognitive performance domains. ...
Larger pay increases and better benefits could support teacher retention
2024-11-20
Larger pay increases and better benefits could help keep K-12 teachers in the teacher workforce, finds a new, nationally representative RAND survey.
U.S. teachers reported modest pay increases between the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 school years, only $2,000 on average and well below their desired increase of $16,000. Black teachers and teachers in states where collective bargaining is prohibited reported they received the smallest pay increases.
“Teachers who received larger pay increases also said they were less likely to intend to leave the profession,” ...
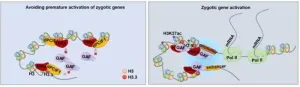
Researchers characterize mechanism for regulating orderly zygotic genome activation in early embryos
2024-11-20
Early development of an embryo is solely supported by maternally deposited RNAs and proteins until its own genome is activated through a process called zygotic genome activation (ZGA).
Recent research by Chinese scientists has revealed novel molecular mechanisms by which HIRA acts in concert with dPCIF1 to establish a totipotent chromatin and facilitate orderly zygotic genome activation in the early embryos of Drosophila.
Results of the study were published in PNAS on Nov. 14 as “HIRA and dPCIF1 coordinately establish totipotent chromatin and control orderly ZGA in Drosophila embryos.”
The ...
AI analysis of urine can predict flare up of lung disease a week in advance
2024-11-20
Researchers have used artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse patient urine samples and predict when symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will flare up according to a study published today (Wednesday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
The patients taking part in the study carried out a simple daily dipstick test on their urine and sent their results to researchers using their mobile phones.
Using AI to analyse the results, researchers were able to ‘forecast’ a deterioration in symptoms one week in advance. ...
New DESI results weigh in on gravity
2024-11-20
Gravity has shaped our cosmos. Its attractive influence turned tiny differences in the amount of matter present in the early universe into the sprawling strands of galaxies we see today. A new study using data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has traced how this cosmic structure grew over the past 11 billion years, providing the most precise test to date of gravity at very large scales.
DESI is an international collaboration of more than 900 researchers from over 70 institutions around the world and is managed by the Department of Energy’s ...
New DESI data shed light on gravity’s pull in the universe
2024-11-20
A University of Texas at Dallas physicist and his international colleagues in the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration are engaged in a multiyear data-gathering mission to try to answer one of the most puzzling observations in astrophysics: Why does the expansion of the universe appear to be accelerating?
Competing theories have attempted to explain this observation. One is that dark energy is somehow pushing galaxies apart. A second theory posits that gravity, the attractive force that in local environments like the solar system draws objects together, works differently at large cosmological scales and needs to be modified to explain cosmic ...
Boosting WA startups: Report calls for investment in talent, diversity and innovation
2024-11-20
A new report from the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre reveals Western Australia’s startup and innovation ecosystem requires targeted reforms and investment to unlock its full potential, calling for improvements in talent development, gender diversity and access to capital and infrastructure to support a more diversified economy.
The report, titled ‘Dare to Venture: Startups and the innovation ecosystem in Western Australia’, highlights WA’s strengths in mining, ...
New AEM study highlights feasibility of cranial accelerometry device for prehospital detection of large-vessel occlusion stroke
2024-11-20
Des Plaines, IL – A new study exploring the use of cranial accelerometry (CA) headsets for the prehospital detection of large-vessel occlusion (LVO) strokes has been published in a recent issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
LVO strokes, which represent one-third of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) cases in the United States, are responsible for two-thirds of poststroke dependence and 90% of poststroke mortality. The introduction of endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) over the past decade has significantly advanced the management of LVO strokes, emphasizing ...
High cardiorespiratory fitness linked to lower risk of dementia
2024-11-20
High cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with better cognitive performance and lower risk of dementia long term, including in people with a genetic predisposition to dementia, show the findings of a study published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is the capacity of the circulatory and respiratory systems to supply oxygen to muscles and declines increasingly with age as skeletal muscle is lost. CRF declines by around 3% to 6% per decade when people are in their 20s and 30s, but this accelerates to more than 20% per decade by the time people reach their 70s. Low CRF is a strong predictor of cardiovascular ...
Oral microbiome varies with life stress and mental health symptoms in pregnant women
2024-11-20
The number and type of microbes present in the saliva of pregnant women differ according to whether they are experiencing life stress and symptoms of anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), finds a study published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Although several studies have shown links between the diversity of microbes in the gastrointestinal tract and stress, anxiety and depression in pregnant women and new mothers, no previous study has looked at the association between the type and number of microorganisms in the mouth and throat—oral microbiome—and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] UCLA professor Helen Lavretsky reshapes brain health through integrative medicine researchLeading geriatric psychiatrist shares transformative journey and vision in exclusive Genomic Press Interview series