(Press-News.org) University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered how long-term treatment of high blood pressure with commonly prescribed drugs can destroy the kidney’s ability to filter and purify blood. The finding could open the door to better ways to manage high blood pressure and other vascular diseases.
The class of drugs, known as renin–angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors, block the effects of the renin enzyme, relaxing blood vessels and allowing blood to flow more easily. They are widely used as first-line medications for hypertension (high blood pressure). But long-term use can take a terrible toll on the kidney, causing scarring and other dramatic physical changes that shift the organ’s focus from blood filtration to producing renin.
No longer able to clean the blood of impurities, the Frankensteined kidney becomes a “pathological neuro-immune endocrine organ,” as the UVA researchers describe it in a new scientific paper, that can cause serious health problems. But they say their discovery sets the stage for identifying ways to protect the kidney and better treat hypertension.
“The most commonly used and believed-to-be safe blood pressure medications may be damaging the kidneys,” said researcher R. Ariel Gomez, MD, of UVA’s Child Health Research Center. “We need to accurately understand the effects of long-term use of RAS inhibitors on the kidneys.”
Managing High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure affects more than 1.3 billion people around the world. The condition forces the heart to work too hard and can cause a host of other serious medical problems, such as stroke, myocardial infarction, kidney damage and vision loss.
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. Renin is a hormone enzyme that is produced by cells in the kidney which are stimulated when blood pressure drops.
RAS inhibitors are widely and effectively used for managing high blood pressure. They are quite safe when their use is supervised by a physician, but patients are routinely cautioned to contact their doctors if they notice signs of potential kidney damage such as reduced frequency of urination, swelling in the legs or feet or seizures.
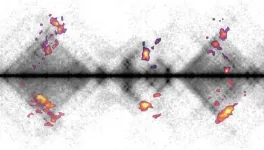
The potential effects of chronic inhibition of RAS on the kidney are well known, but experts have been uncertain what causes these harmful changes. UVA’s new discovery offers answers: Excessive stimulation of renin-producing cells in the kidney causes the cells to revert to an invasive, embryonic state. In this state, these cells that line the tiny arteries in the kidney begin to grow too large. They start to secrete renin and substances that trigger other changes: New nerves grow like weeds; immature smooth muscle cells build up; scars form around the tiny blood vessels, called arterioles; and inflammatory cells infiltrate. The end result is “silent but serious” vascular disease, the researchers note in their new paper.
“Our 3D imaging clearly revealed that long-term RAS inhibition leads to hyperinnervation of renal arteries, together with arteriolar hypertrophy and immune inflammatory cell infiltration,” said researcher Manako Yamaguchi, PhD. “This neuro-immune-endocrine cooperation synergistically promotes increased production of renin to maintain blood pressure homeostasis, but, on the other hand, severe arteriolar hypertrophy reduces the blood filtration function of the kidney.”
By understanding what is causing the harmful changes in the kidney, scientists are now positioned to find ways to stop it. That could lead to better ways to treat high blood pressure without unwanted side effects, the researchers hope.
“Our next goal is to elucidate the whole picture of the interactions between renin cells, smooth muscle cells, nerves and inflammatory cells under RAS inhibition,” said researcher Maria Luisa S. Sequeira-Lopez, MD. “These findings may open new avenues for the prevention of adverse effects when treating hypertension.”
Kidney Damage Findings Published
The article outlining the discovery is being featured as the cover story of the scientific journal Circulation Research. The UVA research team consisted of Yamaguchi, Lucas Ferreira de Almeida, Hiroki Yamaguchi, Xiuyin Liang, Jason P. Smith, Silvia Medrano, Sequeira Lopezand Gomez.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, grants R01HL148044, R01DK116718, P50DK 096373 and P50DK096373. The scientists have no financial interest in the work.
To keep up with the latest medical discoveries from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog.
MORE: Scientists discover important blood pressure-control "switch."
END
Discovery explains kidney damage caused by blood pressure drugs
2024-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NYU Langone performs world’s first fully robotic double lung transplant
2024-11-21
NEW YORK, NY, NOV. 21, 2024—A surgical team at NYU Langone Health has performed the first fully robotic double lung transplant in the world. The procedure marks a breakthrough in the potential of robotic surgery and minimally invasive patient care, making NYU Langone the new leader in robotic transplant surgery around the globe.
Stephanie H. Chang, MD, associate professor in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and surgical director of the Lung Transplant Program ...
APSS accepting sleep and circadian research abstracts and session proposals for SLEEP 2025 in Seattle
2024-11-21
DARIEN, IL – The Associated Professional Sleep Societies is accepting research abstracts and session proposal submissions for SLEEP 2025, the 39th annual meeting of the APSS, which will be held June 8 to 11 at the Seattle Convention Center.
Research abstracts will be accepted for oral and poster presentations. Hot topics for 2025 include machine learning and artificial intelligence, metabolomics and genomics, sleep and the glymphatic system, orexin pharmacology, and obesity management. Accepted abstracts ...
DNA repair: A look inside the cell’s ‘repair café’
2024-11-21
New research from the Kind Group at the Hubrecht Institute sheds light on how cells repair damaged DNA. For the first time, the team has mapped the activity of repair proteins in individual human cells. The study demonstrates how these proteins collaborate in so-called "hubs" to repair DNA damage. This knowledge offers opportunities to improve cancer therapies and other treatments where DNA repair is essential. The researchers published their findings in Nature Communications on November 21.
DNA is the molecule that carries our genetic information. It can be damaged by normal cellular processes as well as external factors such as UV radiation ...
Astronomers take the first close-up picture of a star outside our galaxy
2024-11-21
“For the first time, we have succeeded in taking a zoomed-in image of a dying star in a galaxy outside our own Milky Way,” says Keiichi Ohnaka, an astrophysicist from Universidad Andrés Bello in Chile. Located a staggering 160 000 light-years from us, the star WOH G64 was imaged thanks to the impressive sharpness offered by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer (ESO’s VLTI). The new observations reveal a star puffing out gas and dust, in the last stages before it becomes a supernova.
“We discovered an ...
Here’s something Americans agree on: Sports build character
2024-11-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In a polarized nation, there is one thing that nearly all Americans agree on, according to a recent study: Sports are good for us.
Researchers from The Ohio State University and Ithaca College found that more than 9 out of 10 Americans agreed that sports build character and improved one’s health, while 84% agreed playing sports makes one popular in school and 85% said it makes one more well-known in the community.
According to 67% of those surveyed, playing sports even leads to better grades in school.
While these beliefs may seem harmless, ...
Engineering nature’s blueprint: Dendron-based assemblies for chlorophyll’s materials
2024-11-21
Researchers often look to photosynthesis—a process that turns sunlight into chemical energy in plants and bacteria—as a model for innovation. Photosynthesis is in turn linked to chlorophyll pigments, tiny green molecules that play a key role in harvesting light. Naturally, these chlorophyll molecules are organized into precise structures to optimize light absorption in plants and bacteria, and efficiently capture sunlight for energy. Inspired by this natural structure, scientists have explored ways to synthetically assemble chlorophyll-based ...
Study reveals how cell types shape human brain networks
2024-11-21
Rutgers researchers at the Brain Health Institute (BHI) and Center for Advanced Human Brain Imaging Research (CAHBIR) have uncovered how different types of brain cells work together to form large-scale functional networks in the human brain – interconnected systems that support everything from sensory processing to complex decision-making – paving the way for new insights into brain health and disease.
By pinpointing these cellular foundations, the study, published in Nature Neuroscience, offers a deeper understanding of the cellular foundations of cognition and mental health.
The brain’s functional properties arise from the varied ...
New genetic explanation for heart condition revealed
2024-11-21
A potentially life-changing heart condition, dilated cardiomyopathy, can be caused by the cumulative influence of hundreds or thousands of genes and not just by a single “aberrant” genetic variant, as was previously thought, finds a new study led by researchers at UCL (University College London), Imperial College London and the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences.
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes progressively enlarged and weakened, reducing its ability to pump blood efficiently. It is estimated to affect up to 260,000 people in the UK (one in every 250 individuals) and is the leading cause of heart transplantation.
Previously, ...
Poor mental health linked to browsing negative content online
2024-11-21
People with poorer mental health are more prone to browsing negative content online, which further exacerbates their symptoms, finds a study led by UCL researchers.
The relationship between mental health and web-browsing is causal and bi-directional, according to the Wellcome-funded study published in Nature Human Behaviour.
The researchers have developed a plug-in tool* that adds ‘content labels’ to webpages—similar to nutrition labels on food—designed to help users make healthier and more informed decisions about the ...
People with migraine at high risk of depression during pandemic
2024-11-21
Toronto, ON – A recent longitudinal study from the University of Toronto reveals the mental health consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on older adults living with migraine.
Using a sample of more than 2,000 older adults with migraine from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging, researchers examined changes in depression status among this population during the pandemic. More than 1 in 7 older adults with migraine experienced depression for the first time during the COVID-19 pandemic, while approximately 1 in 2 with a previous history of depression experienced a recurrence during this period.
“People ...