ODS FeCrAl alloys endure liquid metal flow at 600 °C resembling a fusion blanket environment
Scientists examined the chemical durability and anti-corrosion potential of oxide layers formed on oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) FeCrAl alloys in a liquid metal blanket environment
2024-11-25
(Press-News.org)
Researchers explored protective coatings on advanced to resist corrosion in fusion reactors. They tested α-Al2O3 oxide layers on ODS alloys in a high-temperature, flowing lithium-lead environment. Even bare ODS alloys formed a durable γ-LiAlO2 layer in situ, which suppressed further corrosion. The layers exhibited strong adhesion under mechanical stress, making these findings crucial for improving material durability in fusion reactors and high-temperature energy systems.
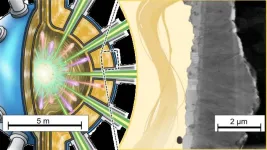
Fusion reactors, a promising source of sustainable energy, require advanced materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments created by liquid metal coolants such as lithium and lithium-lead (LiPb) alloy. These coolants are essential in fusion reactors to extract heat and breed tritium, but their corrosive nature threatens the integrity of the structural materials used. LiPb is particularly aggressive, as it has a high concentration of lithium, which reacts with structural materials, causing corrosion and material degradation over time.
ODS FeCrAl alloys, known for their excellent high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, have been proposed as promising candidates for fusion reactors and other high-temperature applications like concentrated solar power systems. These alloys rely on the formation of protective oxide layers, such as α-Al2O3, which offers stability and durability under high temperatures. However, in a liquid LiPb environment, the chemical interactions between the alloy and the coolant raise concerns about the stability and longevity of these protective layers.
In this view, a team of researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo), led by Associate Professor Masatoshi Kondo in collaboration with Yokohama National University, Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development and Department of Research, National Institute for Fusion Science, conducted corrosion tests on oxide layers formed on ODS FeCrAl alloys under prolonged exposure to flowing liquid LiPb at elevated temperatures. Their study was published in the journal Corrosion Science on September 17, 2024.
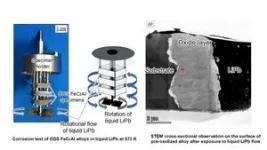
The researchers carried out corrosion tests using two types of ODS FeCrAl alloys: SP10 and NF12. The tests were performed under both static and stirred-flow conditions at 873 K to simulate realistic scenarios in fusion reactor coolant systems. They employed advanced metallurgical analysis techniques, including scanning transmission electron microscopy coupled with electron energy loss spectroscopy, to investigate the composition and microstructure of the protective oxide layers formed on the alloy surfaces.
They found that the pre-formed α-Al2O3 layer effectively suppressed initial corrosion but partially transformed into α-/γ-LiAlO2 due to the adsorption of lithium. Interestingly, even without pre-oxidation, the ODS alloys in situ developed a durable γ-LiAlO2 layer, which served as a self-forming protective barrier. Microstructural analysis using advanced electron microscopy revealed the penetration of lithium into the α-Al2O3 layer, leading to the chemical transformation. Despite this, both α-Al2O3 and γ-LiAlO2 layers demonstrated strong resistance to exfoliation. Micro-scratch tests confirmed that these layers adhered strongly to the alloy surface, with minimal degradation, even under high thermal stresses caused by LiPb solidification.
“The lithium-aluminum oxide layer’s durability shows that these alloys could last longer in high-temperature, high-stress settings. This layer serves as a sustainable shield that continues protecting reactor components even after initial wear,” explains Kondo.
As nuclear technology evolves, these findings bring us one step closer to developing reactors that can run safely for extended duration, making sustainable energy sources more feasible. "Our findings show that ODS FeCrAl alloys, with their ability to form durable protective layers, could play a vital role in the future of fusion reactors and other high-temperature power systems,” says Kondo, highlighting the impact of the research study.
About Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo)
Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) was established on October 1, 2024, following the merger between Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), with the mission of “Advancing science and human wellbeing to create value for and with society.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-25
Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MTDPS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a marked decrease in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). This condition can cause symptoms including muscle weakness, fatigue, and neurological issues, particularly affecting the liver and brain in cases of hepatocerebral MTDPS. Mitochondrial diseases, which represent some of the most common types of metabolic disorders, can result in the failure of multiple organ systems. Currently, over 400 genes linked to these diseases have been identified. Notably, many of these genes are associated with the mitochondrial contact site and cristae ...
2024-11-25
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly useful for the prediction of emergency events such as heart attacks, natural disasters, and pipeline failures. This requires state-of-the-art technologies that can rapidly process data. In this regard, reservoir computing, specially designed for time-series data processing with low power consumption, is a promising option. It can be implemented in various frameworks, among which physical reservoir computing (PRC) is the most popular. PRC with optoelectronic artificial synapses (junction structures that permit a nerve cell to transmit an electrical or chemical signal to another cell) that mimic human ...
2024-11-25
When bats can’t hear, new research finds that these hearing-dependent animals employ a remarkable compensation strategy.
They adapt immediately and robustly, suggesting for the first time that bats’ brains are hard-wired with an ability to launch a Plan B in times of diminished hearing.
The Johns Hopkins University work, newly published in Current Biology, raises questions about whether other animals and even humans might be capable of such deft accommodations.
“Bats have this amazing flexible adaptive behavior that they can employ anytime,” said senior author ...
2024-11-25
CHICAGO – Levothyroxine, the second most commonly prescribed medication among older adults in the U.S., may be associated with bone loss, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Levothyroxine, marketed under multiple brand names including Synthroid, is a synthetic version of a hormone called thyroxine and is commonly prescribed to treat the condition hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid. In people with hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroxine on its own, often resulting in fatigue, weight gain, hair loss and other symptoms. If left untreated, hypothyroidism ...
2024-11-25
CHICAGO – Researchers have identified acute effects of cigarette and e-cigarette smoking on vascular function, even without nicotine. The results of the ongoing research are being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
E-cigarettes, also known as vapes, are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid to produce an aerosol, which is then inhaled into the lungs. Vapes contain significantly fewer chemicals and toxins than are found in tobacco smoke. As a result, e-cigarettes are believed by many to be less harmful than cigarette smoking. Vapes also come in various flavors, making them popular among young people.
“E-cigarettes ...
2024-11-25
Researchers at the University of Lausanne have identified a novel role for the brain’s ‘locus coeruleus’ in sleep and its disruptions. This brain region facilitates the transition between NREM and REM sleep states while maintaining an unconscious vigilance toward the external world. Stress disrupts its functions and negatively impacts on sleep quality.
Sleep disorders affect an increasing number of people, with potentially serious consequences for their health. Mammalian sleep consists of cycles between two states: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye ...
2024-11-25
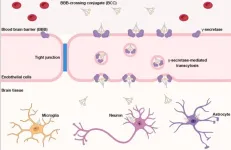
New York, NY [November 25, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed an innovative approach—demonstrated in mouse models and isolated human brain tissue—to safely and effectively deliver therapeutics into the brain, providing new possibilities for treating a wide range of neurological and psychiatric diseases.
Published in the November 25 online issue of Nature Biotechnology [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02487-7], the study introduces a first-of-its-kind blood-brain barrier-crossing conjugate (BCC) system, designed to overcome the protective barrier that typically blocks large biomolecules from ...
2024-11-25
The ancient Vikings certainly had the travel bug. Between the late eighth century and approximately 1050 CE, they roamed the Atlantic in their longships all the way to Newfoundland, Labrador, and Greenland, as well as exploring the Mediterranean and continental Eurasia.
Among the places the Vikings are known to have settled were the Faroe Islands, an archipelago of 18 islands in the North Atlantic. They probably weren’t the first to do so: archaeologists have found evidence that these islands had been inhabited since approximately 300 CE, possibly ...
2024-11-25
Affordability in Canada affects not just groceries but also medications, with 1 in 20 people unable to take their medications as prescribed because of cost, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241024.
Prescription medications are not universally covered under Canada’s 13 provincial and territorial health insurance systems. In 2021, Canadian households paid more than $7.4 billion out of pocket for prescription medications.
The study, which included a nationally representative ...
2024-11-25
Remotely operated camera traps, sound recorders and drones are increasingly being used in conservation science to monitor wildlife and natural habitats, and to keep watch on protected natural areas.
But Cambridge researchers studying a forest in northern India have found that the technologies are being deliberately misused by local government and male villagers to keep watch on women without their consent.
Cambridge researcher Dr Trishant Simlai spent 14 months interviewing 270 locals living around the Corbett Tiger Reserve, a national park in northern India, including many women from nearby villages.
His report, published today in the journal Environment and Planning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] ODS FeCrAl alloys endure liquid metal flow at 600 °C resembling a fusion blanket environment
Scientists examined the chemical durability and anti-corrosion potential of oxide layers formed on oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) FeCrAl alloys in a liquid metal blanket environment