Using sunlight to recycle black plastics
2024-11-25
(Press-News.org) Not all plastics are equal — some types and colors are easier to recycle than others. For instance, black foam and black coffee lids, which are often made of polystyrene, usually end up in landfills because color additives lead to ineffective sorting. Now, researchers report in ACS Central Science the ability to leverage one additive in black plastics, with the help of sunlight or white LEDs, to convert black and colored polystyrene waste into reusable starting materials.
“Simple, visible light irradiation holds the potential to transform the chemical recycling of plastics, using the additives already found in many commercial products,” say the paper’s authors, Sewon Oh, Hanning Jiang and Erin Stache.
An emerging strategy for plastic recycling involves using light to help break down plastic into chemically useful materials that can be recycled into new products. This process requires a helper compound to convert light into the heat needed to break apart polymer bonds. However, finding the right helper that won’t create more waste and is easily incorporated into recycled materials remains a challenge for researchers. Seeking to create a circular economy for plastic recycling, Stache and a team of researchers took advantage of something already found in black polystyrene waste — an additive known as carbon black.
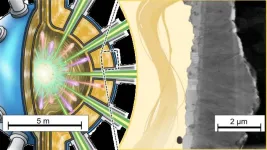
The researchers tested a method to recycle lab-made black polystyrene: They ground a mixture of polystyrene and carbon black to a fine powder, placed the powder in a sealed glass vial and then set the vial under high-intensity white LEDs for 30 minutes. The carbon black converted the LED light into heat. The heat then broke apart the polystyrene’s molecular structure, creating a mixture of shorter one-, two- and three-styrene units. And these three components cleanly separated within the reaction apparatus. In experiments, the team recycled the leftover carbon black and styrene monomer into polystyrene, demonstrating the circularity of the new method.
Applying the technique to post-consumer black plastic from food containers and coffee cup lids, the researchers cut the waste into small pieces and found that up to 53% of the polystyrene converted to styrene monomer. Waste samples contaminated with canola oil, soy sauce and orange juice broke down slightly less efficiently. When the researchers switched the light source from LEDs to focused sunlight outdoors, they observed a higher reaction efficiency (80%). Additionally, a multicolored mixture of black, yellow, red and colorless polystyrene waste converted to styrene in sunlit conditions at a higher rate (67%) compared to white LEDs (45%). The researchers attribute the higher efficiencies to the greater light intensity achieved by focused sunlight. By demonstrating sunlight’s ability to break down colored polystyrene waste, the researchers say that their method could create a closed-loop recycling process for this type of plastic.
The authors acknowledge funding from Cornell University and Princeton University as well as a Catalysis Science Early Career award from the U.S. Department of Energy.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, e-books and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Registered journalists can subscribe to the ACS journalist news portal on EurekAlert! to access embargoed and public science press releases. For media inquiries, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-25
Researchers explored protective coatings on advanced to resist corrosion in fusion reactors. They tested α-Al2O3 oxide layers on ODS alloys in a high-temperature, flowing lithium-lead environment. Even bare ODS alloys formed a durable γ-LiAlO2 layer in situ, which suppressed further corrosion. The layers exhibited strong adhesion under mechanical stress, making these findings crucial for improving material durability in fusion reactors and high-temperature energy systems.
Fusion reactors, a promising source of sustainable energy, require advanced materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments ...
2024-11-25
Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MTDPS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a marked decrease in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). This condition can cause symptoms including muscle weakness, fatigue, and neurological issues, particularly affecting the liver and brain in cases of hepatocerebral MTDPS. Mitochondrial diseases, which represent some of the most common types of metabolic disorders, can result in the failure of multiple organ systems. Currently, over 400 genes linked to these diseases have been identified. Notably, many of these genes are associated with the mitochondrial contact site and cristae ...
2024-11-25
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly useful for the prediction of emergency events such as heart attacks, natural disasters, and pipeline failures. This requires state-of-the-art technologies that can rapidly process data. In this regard, reservoir computing, specially designed for time-series data processing with low power consumption, is a promising option. It can be implemented in various frameworks, among which physical reservoir computing (PRC) is the most popular. PRC with optoelectronic artificial synapses (junction structures that permit a nerve cell to transmit an electrical or chemical signal to another cell) that mimic human ...
2024-11-25
When bats can’t hear, new research finds that these hearing-dependent animals employ a remarkable compensation strategy.
They adapt immediately and robustly, suggesting for the first time that bats’ brains are hard-wired with an ability to launch a Plan B in times of diminished hearing.
The Johns Hopkins University work, newly published in Current Biology, raises questions about whether other animals and even humans might be capable of such deft accommodations.
“Bats have this amazing flexible adaptive behavior that they can employ anytime,” said senior author ...
2024-11-25
CHICAGO – Levothyroxine, the second most commonly prescribed medication among older adults in the U.S., may be associated with bone loss, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Levothyroxine, marketed under multiple brand names including Synthroid, is a synthetic version of a hormone called thyroxine and is commonly prescribed to treat the condition hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid. In people with hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroxine on its own, often resulting in fatigue, weight gain, hair loss and other symptoms. If left untreated, hypothyroidism ...
2024-11-25
CHICAGO – Researchers have identified acute effects of cigarette and e-cigarette smoking on vascular function, even without nicotine. The results of the ongoing research are being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
E-cigarettes, also known as vapes, are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid to produce an aerosol, which is then inhaled into the lungs. Vapes contain significantly fewer chemicals and toxins than are found in tobacco smoke. As a result, e-cigarettes are believed by many to be less harmful than cigarette smoking. Vapes also come in various flavors, making them popular among young people.
“E-cigarettes ...
2024-11-25
Researchers at the University of Lausanne have identified a novel role for the brain’s ‘locus coeruleus’ in sleep and its disruptions. This brain region facilitates the transition between NREM and REM sleep states while maintaining an unconscious vigilance toward the external world. Stress disrupts its functions and negatively impacts on sleep quality.
Sleep disorders affect an increasing number of people, with potentially serious consequences for their health. Mammalian sleep consists of cycles between two states: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye ...
2024-11-25
New York, NY [November 25, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed an innovative approach—demonstrated in mouse models and isolated human brain tissue—to safely and effectively deliver therapeutics into the brain, providing new possibilities for treating a wide range of neurological and psychiatric diseases.
Published in the November 25 online issue of Nature Biotechnology [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02487-7], the study introduces a first-of-its-kind blood-brain barrier-crossing conjugate (BCC) system, designed to overcome the protective barrier that typically blocks large biomolecules from ...
2024-11-25
The ancient Vikings certainly had the travel bug. Between the late eighth century and approximately 1050 CE, they roamed the Atlantic in their longships all the way to Newfoundland, Labrador, and Greenland, as well as exploring the Mediterranean and continental Eurasia.
Among the places the Vikings are known to have settled were the Faroe Islands, an archipelago of 18 islands in the North Atlantic. They probably weren’t the first to do so: archaeologists have found evidence that these islands had been inhabited since approximately 300 CE, possibly ...
2024-11-25
Affordability in Canada affects not just groceries but also medications, with 1 in 20 people unable to take their medications as prescribed because of cost, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241024.
Prescription medications are not universally covered under Canada’s 13 provincial and territorial health insurance systems. In 2021, Canadian households paid more than $7.4 billion out of pocket for prescription medications.
The study, which included a nationally representative ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Using sunlight to recycle black plastics