(Press-News.org) Gene editing could create hypoallergenic cats, according to a sequence analysis of the protein that triggers allergies to cats. Some 15% of people are allergic to cats, and symptoms can be severe. Martin D. Chapman and colleagues investigated CH1 and CH2, genes that code for the allergen, Fel d 1. Cats produce Fel d 1 in their sebaceous, salivary, perianal, and lachrymal glands. The function of Fel d 1 is unknown but comparisons of Fel d 1 sequences and homologs from 276 domestic or exotic cats—including cougars, cheetahs, lions, tigers, and jaguars, among others—suggests that CH1 and CH2 have been under active selection, and thus potentially confer some fitness advantage. Fel d 1 may be involved in immune regulation, skin protection, or chemical communication among cats. However, cats genetically modified to lack CH2 seem healthy and low levels of conserved sequences between species suggest that the allergen is either nonessential or that the function of Fel d 1 varies among cat species. Two of the analyzed cats—a cougar and a black-footed cat, a small wildcat from Southern Africa—had mutations that likely prevented Fel d 1 expression, further indicating that the allergen may not be essential for cats. According to the authors, using CRISPR technology to delete CH1 and CH2 could create hypoallergenic cats.
END
Engineering hypoallergenic cats
2024-11-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Microwave-induced pyrolysis: A promising solution for recycling electric cables
2024-11-26
The demand for electronics has led to a significant increase in e-waste. In 2022, approximately 62 million tons of e-waste were generated, marking an 82% increase from 2010. Projections indicate that this figure could rise to 82 million tons by 2030. E-waste contains valuable materials such as metals, semiconductors, and rare elements that can be reused. However, in 2022, only 22.3% of e-waste was properly collected and recycled, while the remaining materials, estimated to be worth almost $62 billion, were discarded in landfills. Although efforts to improve e-waste recycling continue, the process remains labor-intensive, and a significant portion of e-waste ...
Cooling with light: Exploring optical cooling in semiconductor quantum dots
2024-11-26
Cooling systems are an integral part of many modern technologies, as heat tends to wear down materials and decrease performance in several ways. In many cases, however, cooling can be an inconvenient and energy-intensive process. Accordingly, scientists have been seeking innovative and efficient methods to cool substances down.
Solid-state optical cooling is a prominent example that leverages a very unique phenomenon called anti-Stokes (AS) emission. Usually, when materials absorb photons from incoming light, their electrons transition into an “excited” state. Under ideal conditions, as electrons return to their original ...
Breakthrough in clean energy: Scientists pioneer novel heat-to-electricity conversion
2024-11-26
Thermoelectric materials, which convert heat into electricity, are valuable tools for capturing waste heat and turning it into usable electricity. These materials are especially useful in industries and vehicles where engines produce a lot of waste heat, improving energy efficiency by converting it into additional power. They also exhibit potential for portable power generation, in remote sensors and satellites where traditional power sources may be impractical.
Traditional thermoelectric devices, known as parallel thermoelectric devices, generate a voltage in the same direction as the heat ...
Study finds opposing effects of short-term and continuous noise on western bluebird parental care
2024-11-26
Recent research led by Kerstin Ozkan and published in PeerJ Life and Environment has uncovered the complex and contrasting effects of human-generated noise on Western Bluebird (Sialia mexicana) parental behavior, raising critical questions about how anthropogenic noise affects wildlife in both urban and non-urban settings. The study, titled “Divergent effects of short-term and continuous anthropogenic noise exposure on Western Bluebird parental care behavior,” explores how different types of noise exposure alter the bird's ...
Quantifying disease impact and overcoming practical treatment barriers for primary progressive aphasia
2024-11-26
Imagine gradually losing the ability to express yourself — not because you've forgotten the words, but because they simply won't come out. This is the reality for individuals living with primary progressive aphasia (PPA), a rare form of dementia that usually begins in middle age and increasingly impairs language abilities over time.
Researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine are working to illuminate the struggles of those living with this condition and pioneer accessible treatment models. They recently published new studies that measure PPA’s significant impact ...
Sports betting and financial market data show how people misinterpret new information in predictable ways
2024-11-26
Let’s say it’s a home game for the Golden State Warriors and Steph Curry shows he’s still got it, sinking back-to-back three-pointers minutes into the first quarter. The fans at Chase Center take notice, and so do the betting markets, where the odds move in the Warriors’ favor.
Yet it’s a long game. The away team comes back, and with just 10 seconds to go, the Warriors are down by two and have just missed a shot. A victory is unlikely, and the betting odds should have shifted to reflect that near-certainty. ...
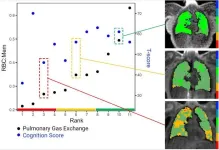
Long COVID brain fog linked to lung function
2024-11-26
CHICAGO – In patients with long COVID, lower pulmonary gas exchange may be associated with impaired cognitive function, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, approximately 17.6% of adults in the U.S. have experienced a post-COVID condition commonly referred to as long COVID. People with long COVID may exhibit a wide variety of symptoms, including difficulty concentrating (“brain fog”), change in sense of smell or taste, fatigue, joint or muscle pain, dyspnea (shortness of breath), digestive ...
Concussions slow brain activity of high school football players
2024-11-26
CHICAGO – A new study of high school football players found that concussions affect an often-overlooked but important brain signal. The findings are being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Reports have emerged in recent years warning about the potential harms of youth contact sports on developing brains. Contact sports, including high school football, carry a risk of concussion. Symptoms of concussion commonly include cognitive disturbances, such as difficulty with balancing, ...
Study details how cancer cells fend off starvation and death from chemotherapy
2024-11-26
Laboratory experiments with cancer cells reveal two ways in which tumors evade drugs designed to starve and kill them, a new study shows.
While chemotherapies successfully treat cancers and extend patients’ lives, they are known not to work for everyone for long, as cancer cells rewire the process by which they convert fuel into energy (metabolism) to outmaneuver the drugs’ effects. Many of these drugs are so-called antimetabolics, disrupting cell processes needed for tumor growth and survival.
Three such drugs used in the study — raltitrexed, N-(phosphonacetyl)-l-aspartate (PALA), and brequinar ...
Transformation of UN SDGs only way forward for sustainable development
2024-11-26
Climate change is the single biggest threat to the global environment and socio-economic development – demanding an urgent transformation of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), according to a new study.
The UN SDGs were created to end poverty, build social-economic-health protection and enhance education and job opportunities, while tackling climate change and providing environmental protection.
Following last week’s COP29 environmental summit in Baku, University of Birmingham experts say that, as climate action is linked to sustainable development, systematic integration of climate resilience into every ...