(Press-News.org) Ghent, 29 November 2024 – We are increasingly confronted with the impacts of climate change, with failed harvests being only one example. Addressing these challenges requires multifaceted approaches, including making plants more resilient. An international research team led by researchers at VIB-UGent has unraveled how the opening and closing of stomata - tiny pores on leaves – is regulated in response to high temperatures and drought. These new insights, published in Nature Plants, pave the way for developing climate change-ready crops.
Global climate change affects more and more people, with extreme weather conditions steadily becoming the norm. Beyond the immediate impacts like floods and severe droughts, it also significantly affects our natural ecosystems and crops, making it challenging in many regions to grow the food we rely on or to identify the right climate-adapted plants.
Prof. Ive De Smet (VIB-UGent Center for Plant Systems Biology): “For years our research has focused on the impact of extreme weather conditions on plants. The molecular insights we gain can lead to solutions to enhance plant resilience. In essence, we learn from the natural mechanisms that plants themselves deploy. For instance, how stomata on leaves play a crucial role in the plant’s interaction with the environment. This makes insights into their activation mechanisms highly valuable.”
Conflicting responses in stomata, the ‘sweat glands’ of plants
Plants respond to changing environmental conditions among others via opening or closing little pores in their epidermis. These so-called stomata regulate gas and water vapor exchange with the environment, function as entry points for pathogens, and are pivotal in shielding plants against abiotic stress. When temperatures are high, the stomata open to cool down, in dry conditions they close to prevent water loss. So, when conditions are dry and hot, this may evoke conflicting – and therefore less efficient - stomatal responses. The VIB-UGent team of Prof. Ive De Smet joined forces with research teams from the universities of Utrecht (NL), Valencia (Spain), and Wageningen (NL) and set out to unravel the underlying cellular mechanisms.
A well-regulated signaling axis
Dr. Xiangyu Xu (VIB-UGent), first author of the study: “Opening and closing of stomata are rapid responses that require switch-like signaling mechanisms. We know that phosphorylation-encoded switches within protein networks are reversible and tend to be faster than genetic switches. That’s why we studied the role of kinase-mediated phosphorylation relays in stomata opening and closing.”
Xu and his colleagues succeeded in identifying and characterizing a novel phosphorylation-dependent signaling axis that regulates stomatal aperture under high temperature and/or drought conditions. They demonstrated that TOT3, a high temperature-associated kinase, controls stomatal opening under high-temperature conditions, and that OST1, which regulates stomatal closure during drought stress, directly inactivates TOT3 through phosphorylation. This specific phosphorylation-mediated control of TOT3 activity acts as a switch to mediate stomatal aperture under high temperature and/or drought conditions.
Dr. Lam Dai Vu (VIB-UGent): “As a researcher, it is rewarding to unravel a new signaling axis that coordinates stomatal opening and closing in response to various stress signals. More importantly, in the context of global climate change, understanding these mechanisms holds potential for developing crops that are resilient to climate challenges.”
END
New insights in plant response to high temperatures and drought
2024-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Strategies for safe and equitable access to water: a catalyst for global peace and security
2024-11-29
Water can be a catalyst for peace and security with a critical role in preventing conflicts and promoting cooperation among communities and nations - but only if managed equitably and sustainably, a new study reveals.
Experts have devised a blueprint to ensure safe, equitable and sustainable global access to clean water. The seven-point strategy will allow water challenges to be governed effectively so they do not create conflict when access is restricted or usage unfairly shared.
Publishing ...
CNIO opens up new research pathways against paediatric cancer Ewing sarcoma by discovering mechanisms that make it more aggressive
2024-11-29
Ewing sarcoma is a tumour of the bones and soft tissues that occurs in children and young people. A quarter of patients do not respond well to therapy.
The group led by Ana Losada, at Spain’s National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), has discovered an alteration in the most aggressive cases that affects genes never previously related to this disease.
This finding expands the list of potential prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in the most aggressive cases of Ewing sarcoma.
The new research is published in EMBO Reports.
Ewing sarcoma is a tumour of the bones and soft tissues that occurs in children and young people. ...
Disease severity staging system for NOTCH3-associated small vessel disease, including CADASIL
2024-11-29
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest the NOTCH3-associated small vessel disease (NOTCH3-SVD) staging system will help to better harmonize NOTCH3-SVD and cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) cohort studies and registries; may improve individualized disease counseling, monitoring, and clinical management; and may facilitate patient stratification in clinical trials.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding ...
Satellite evidence bolsters case that climate change caused mass elephant die-off
2024-11-29
A new study led by King’s College London has provided further evidence that the deaths of 350 African elephants in Botswana during 2020 were the result of drinking from water holes where toxic algae populations had exploded due to climate change.
The lead author of the report says their analysis shows animals were very likely poisoned by watering holes where toxic blooms of blue-green algae, or cyanobacteria, had developed after a very wet year followed a very dry one.
Davide Lomeo, a PhD student in the Department of Geography at King’s College London and co-supervised by Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML) and ...
Unique killer whale pod may have acquired special skills to hunt the world’s largest fish
2024-11-29
Killer whales can feed on marine mammals, turtles, and fish. In the Gulf of California, a pod might have picked up new skills that help them hunt whale sharks – the world’s largest fish, growing up to 18 meters long.
Whale sharks feed at aggregation sites in the Gulf of California, sometimes while they are still young and smaller. During this life-stage, they are more vulnerable to predation, and anecdotal evidence suggests orcas could be hunting them. Now, researchers in Mexico have reported four separate hunting events.
“We show how orcas displayed a collaboratively hunting technique on whale sharks, characterized by ...
Emory-led Lancet review highlights racial disparities in sudden cardiac arrest and death among athletes
2024-11-29
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 6:30 PM November 28, 2024:
A recent major review of data published by the Lancet and led by Emory sports cardiologist Jonathan Kim, MD, shows that Black athletes are approximately five times more likely to experience sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) and sudden cardiac death (SCD) compared to White athletes, despite some evidence of a decline in rates of SCD overall. SCA and SCD have historically been a leading cause of mortality among athletes, particularly those involved in high-intensity sports.
The disparities in SCA/D rates highlights the need for increased research into the social determinants of health in younger athletes, a topic that remains ...
A new approach to predicting malaria drug resistance
2024-11-28
Researchers at University of California San Diego analyzed the genomes of hundreds of malaria parasites to determine which genetic variants are most likely to confer drug resistance. The findings, published in Science, could help scientists use machine learning to predict antimalarial drug resistance and more effectively prioritize the most promising experimental treatments for further development. The approach could also help predict treatment resistance in other infectious diseases, and even cancer.
“A lot of drug resistance research can only look at one chemical agent at a time, but what we’ve been able to do here is create a roadmap ...
Coral adaptation unlikely to keep pace with global warming
2024-11-28
Coral adaptation to ocean warming and marine heatwaves will likely be overwhelmed without rapid reductions of global greenhouse gas emissions, according to an international team of scientists.
Their study, led by Dr. Liam Lachs of Newcastle University, reveals that coral heat tolerance adaptation via natural selection could keep pace with ocean warming, but only if Paris Agreement commitments are realised, limiting global warming to two degrees Celsius.
“The reality is that marine heatwaves are triggering mass coral bleaching mortality events across the world’s shallow tropical reef ecosystems, and the increasing frequency and intensity of these events ...
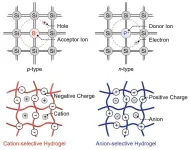
Bioinspired droplet-based systems herald a new era in biocompatible devices
2024-11-28
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 19:00 GMT / 14:00 ET THURSDAY 28 NOVEMBER 2024
Bioinspired droplet-based systems herald a new era in biocompatible devices
Oxford University researchers have developed a set of biocompatible devices, which can replicate or surpass many electronic functions but use ions as the signal carriers.
The ‘dropletronic devices’ are made from miniature soft hydrogel droplets and can be combined to produce diodes, transistors, reconfigurable logic gates, and memory storage devices that mimic biological synapses.
The research team generated a biocompatible, dropletronic ...
A fossil first: Scientists find 1.5-million-year-old footprints of two different species of human ancestors at same spot
2024-11-28
More than a million years ago, on a hot savannah teeming with wildlife near the shore of what would someday become Lake Turkana in Kenya, two completely different species of hominins may have passed each other as they scavenged for food.
Scientists know this because they have examined 1.5-million-year-old fossils they unearthed and have concluded they represent the first example of two sets of hominin footprints made about the same time on an ancient lake shore. The discovery will provide more insight into human evolution and how species cooperated and competed with ...