(Press-News.org) Physicists are getting closer to controlling single-molecule chemical reactions – could this shape the future of pharmaceutical research?Controlling matter at the atomic level has taken a major step forward, thanks to groundbreaking nanotechnology research by an international team of scientists led by physicists at the University of Bath.
This advancement has profound implications for fundamental scientific understanding. It is also likely to have important practical applications, such as transforming the way researchers develop new medications.
Controlling single-outcome single-molecule reactions is now almost routine in research laboratories across the world. For example, over a decade ago, researchers from the technology giant IBM showcased their ability to manipulate individual atoms by creating A boy and his atom, the world's smallest movie. In the film, single molecules, consisting of two atoms bonded together, were magnified 100-million times and positioned frame-by-frame to tell a stop-motion story on an atomic scale.
Achieving control over chemical reactions with multiple outcomes, however, has remained elusive. This matters because generally only some outcomes of a chemical reaction are useful.
For instance, during drug synthesis, a chemical process that results in ‘cyclisation’ produces the desired therapeutic compound, however ‘polymerisation’, another outcome, leads to unwanted byproducts.
Being able to precisely control reactions to favour desired outcomes and reduce unwanted byproducts promises to improve the efficiency and sustainability of pharmaceutical processes.
Scanning tunnelling microscopy
The new study, published today in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, set out to demonstrate for the first time that competing chemical reaction outcomes can be influenced by using the atomic resolution of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM).
Conventional microscopes use light and lenses to magnify specimens, allowing us to view them with the naked eye or a camera. However, when it comes to atoms and molecules, which are smaller than even the shortest wavelengths of visible light, traditional methods fall short.
To explore these tiny realms, scientists turn to a scanning tunnelling microscope, which operates much like a record player.
With a tip that can be as fine as a single atom, scanning tunnelling microscopes move across a material's surface, measuring properties such as electric current to map each point. However, rather than pressing the tip into the surface like a record player needle, the tip hovers just a single atom’s width above it.
When connected to a power source, electrons travel down the tip and make a quantum leap across the atom-sized gap. The closer the tip is to the surface, the stronger the current; the farther away it is, the weaker the current. This well-defined relationship between tip distance and current allows the microscope to measure and map the surface of the atom or molecule based on the electric current strength. As the tip sweeps across the surface, it builds a precise, line-by-line image of the surface, revealing details invisible to conventional light microscopes.
Single-molecule reactions
Using the atomic precision of a scanning tunnelling microscope, scientists can go beyond mapping the surface of a molecule – they can both reposition single atoms and molecules, and influence and measure the likelihood of specific reaction pathways in individual molecules.
Explaining, Dr Kristina Rusimova, who led the study, said: “Typically, STM technology is employed to reposition individual atoms and molecules, enabling targeted chemical interactions, yet the ability to direct reactions with competing outcomes remained a challenge. These different outcomes happen with certain probabilities governed by quantum mechanics – rather like rolling a molecular die.
“Our latest research demonstrates that STM can control the probability of reaction outcomes by selectively manipulating charge states and specific resonances through targeted energy injection.”
Dr Peter Sloan, senior lecturer in the Department of Physics and co-author of the study, said: “We used the STM tip to inject electrons into toluene molecules, prompting the breaking of chemical bonds and either a shift to a nearby site, or desorption.
“We found that the ratio of these two outcomes was controlled by the energy of the electrons injected. This energy dependence allowed us to achieve control over the probability of each reaction outcome through the targeted "heating" of an intermediate molecular state, guided by precise energy thresholds and molecular barriers.”
PhD student Pieter Keenan, first-author on the research publication, said: “The key here was to maintain identical initial conditions for the test reactions—matching the precise injection site and excitation state – and then vary outcomes based solely on the energy of the injected electrons.
“Within a single molecule’s response to the energy input, the differing reaction barriers drive the reaction outcome probabilities. Altering only the energy input allows us, with high precision, to make a reaction outcome more likely than another – in this way we can ‘load the molecular dice’.”
Professor Tillmann Klamroth from Potsdam University in Germany, added: “This study combines advanced theoretical modelling with experimental precision, leading to a pioneering understanding of the reactions’ probabilities based on the molecular energy landscape. This paves the way for further advances in nanotechnology.”
Looking ahead, Dr Rusimova said: “With applications in both basic and applied science, this advancement represents a major step toward fully programmable molecular systems. We expect techniques such as this to unlock new frontiers in molecular manufacturing, opening doors to innovations in medicine, clean energy, and beyond.”
The research is published in the journal Nature Communications. It was funded by The Royal Society, and the Engineering and Physical Science Research Council (EPSRC).
END
Controlling matter at the atomic level: University of Bath breakthrough
Physicists are getting closer to controlling single-molecule chemical reactions – could this shape the future of pharmaceutical research?
2024-12-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
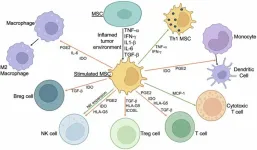
Mesenchymal stem cells in cancer immunotherapy: Promises and challenges
2024-12-03
“MSCs hold great promise as a therapeutic tool in cancer immunotherapy due to their immunomodulatory properties, tumor-homing abilities, and potential as carriers for delivering therapeutic agents.”
BUFFALO, NY – December 3, 2024 – A new review was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on November 22, 2024, entitled “Mesenchymal stem cells – the secret agents of cancer immunotherapy: Promises, challenges, and surprising twists.”
Authored by Theia Minev, Shani Balbuena, Jaya Mini Gill, ...
Developing and evaluating large language model–generated emergency medicine handoff notes
2024-12-03
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1,600 emergency medicine patient medical records, large language model (LLM)-generated emergency medicine-to-inpatient handoff notes were determined superior compared with physician-written summaries via conventional automated evaluation methods, but marginally inferior in usefulness and safety via a novel evaluation framework. This study suggests the importance of a physician-in-loop implementation design for this model and demonstrates an effective strategy to measure pre-implementation patient safety of LLM models.
Corresponding ...
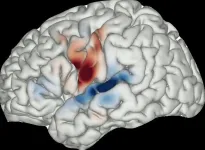
New study shows how dementia affects the brain's ability to empathise
2024-12-03
Patients with frontotemporal dementia often lack the ability to empathize. A study at Karolinska Institutet has now shown that these patients do not show the same brain activity as healthy individuals when they witness the pain of others, a finding that it is hoped will increase understanding of this specific dementia disease.
Around 25 000 Swedes are affected by dementia every year. Of these, about three percent are diagnosed with frontotemporal dementia. The disease is difficult to diagnose, but one of its characteristics is that sufferers lose the ability to empathize, which can lead to problems for them, and not least ...
An inflatable gastric balloon could help people lose weight
2024-12-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Gastric balloons — silicone balloons filled with air or saline and placed in the stomach — can help people lose weight by making them feel too full to overeat. However, this effect eventually can wear off as the stomach becomes used to the sensation of fullness.
To overcome that limitation, MIT engineers have designed a new type of gastric balloon that can be inflated and deflated as needed. In an animal study, they showed that inflating the balloon before a meal caused the animals to reduce their food intake by 60 percent.
This type of intervention ...
PCORI commits $156 million to new patient-centered health research studies
2024-12-03
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) has approved funding awards totaling more than $156 million for new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER), as well as research to improve methods and strengthen the science of engagement in CER. The awards will support 13 CER studies, including three focused on sleep interventions.
“Poor sleep affects more than 50 million people in the United States and is linked to multiple chronic conditions and negative health outcomes,” said PCORI Executive Director Nakela L. Cook, M.D., MPH. “These ...
Debra Bangasser honored with prestigious research award
2024-12-03
ATLANTA — Debra Bangasser, a professor of neuroscience and director of the Center for Behavioral Neuroscience (CBN) at Georgia State University, has been awarded the Daniel H. Efron Research Award by the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ACNP).
The award recognizes outstanding basic research contributions to the field of neuropsychopharmacology, which integrates neuroscience and pharmacology to advance understanding of the causes of psychiatric disorders and develop new therapies. Bangasser’s research identifies how stress throughout the lifespan affects the brain to promote ...
The Paul G. Allen Family Foundation awards $9 million to new Allen Distinguished Investigators
2024-12-03
SEATTLE, WASH.—December 3, 2024—The funding, provided through the Allen Distinguished Investigators, a program of The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group at the Allen Institute, will fuel innovative research in Organelle Communication and Membrane Biophysics. Together these awards represent a total of $9 million dollars in funding from the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation, which will be distributed between 14 researchers investigating the biological principles governing fundamental cellular functions and how they interact. These ...
Brain mapping advances understanding of human speech and hallucinations in schizophrenia
2024-12-03
Voice experiments in people with epilepsy have helped trace the circuit of electrical signals in the brain that allow its hearing center to sort out background sounds from their own voices.
Such auditory corollary discharge signals start and end in two subregions of the brain’s top folded surface, or cortex, a new study shows. One large part of the cortex, the motor cortex, is known to control the body’s voluntary muscle movements, including those involved in speech, while another large section, the auditory cortex, is known to control hearing.
In terms of evolution, the ability of animals and humans to tell ...
Researchers at Case Western Reserve, Mass Eye and Ear aim to prevent hearing loss by protecting inner-ear cells
2024-12-03
CLEVELAND—With a new five-year, $3.2 million grant from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communications Disorders, researchers at Case Western Reserve University and Mass Eye and Ear will study what causes acquired hearing loss (AHL) and seek new ways to protect against it.
AHL is among the most common health conditions affecting older adults, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Although hearing aids can help, AHL has no known cure and, in many cases, scientists are still unsure of its exact cause.
AHL significantly ...
FAU receives $6 million grant to propel expansion of the FAU Marcus Institute of Integrative Health
2024-12-03
Florida Atlantic University’s Marcus Institute of Integrative Health has been awarded a monumental $6 million grant from the late Bernie Marcus and The Marcus Foundation to broaden its services, enhance educational programs, and expand community wellness initiatives, ultimately aiming to create a national model that demonstrates the effectiveness of comprehensive integrative health as the optimal approach for achieving overall well-being for everyone.
This latest grant to FAU from The Marcus Foundation, which was made prior to the passing of Marcus in early November, brings its total contributions for advancing integrative health to more than $10 million, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Controlling matter at the atomic level: University of Bath breakthroughPhysicists are getting closer to controlling single-molecule chemical reactions – could this shape the future of pharmaceutical research?