(Press-News.org) Clinicians lack methods for early detection of sepsis, a dysregulated response to infection that can result in life-threatening organ failure if treatment is delayed. New research published in The FASEB Journal reveals the potential of a non-invasive strategy that assesses blood flow through skeletal muscle.
The strategy involves imaging methods—called hyperspectral near-infrared spectroscopy and diffuse correlation spectroscopy—commonly used at the bedside to monitor tissue conditions. In experiments conducted in rodents, use of these methods together detected signs of sepsis in the skeletal muscle microcirculation before vital organs like the brain had been affected.
Investigators next plan to test the combination technique’s ability to monitor microcirculatory function in patients in intensive care.
“Sepsis is a leading cause of death around the world that disproportionately affects vulnerable populations and those in low-resource settings,” said co–corresponding author Rasa Eskandari, an MD-PhD candidate at Western University, in Ontario, Canada. “Since early recognition can significantly improve outcomes and save lives, our team is committed to developing accessible technology for early sepsis detection and to guide timely interventions.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1096/fj.202401889R
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The FASEB Journal, the flagship publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, leads in publishing groundbreaking multidisciplinary research in biology and biomedical sciences. It spans all levels of biological organization, from molecular to population studies. The journal drives advances in basic, translational, pre-clinical, and early clinical research. Known for its rigorous peer-review process, The FASEB Journal is dedicated to advancing high-quality scientific discoveries and shaping the future of science.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a trusted leader in research and learning. Our industry-leading content, services, platforms, and knowledge networks are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our customers and partners, including researchers, students, instructors, professionals, institutions, and corporations. We empower knowledge-seekers to transform today’s biggest obstacles into tomorrow’s brightest opportunities. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Non-invasive imaging tests may lead to early sepsis detection
2024-12-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers assess the sustainability of the Pacific walrus population over the next 75 years
2024-12-04
The Pacific walrus, a critically important resource for Alaska and Chukotka Native communities, is subject to rapid habitat loss associated with climate change and increasing human activity in the Arctic. New research published in the Journal of Wildlife Management assessed the sustainability of varying degrees of Pacific walrus harvest to the end of the 21st century under different climate and human disturbance scenarios.
These scenarios ranged from optimistic to pessimistic, based largely on sea ice projections from ...
Does altered gait following ACL surgery contribute to additional knee problems?
2024-12-04
For people with an injured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the knee, surgical ACL reconstruction (ACLR) is an effective treatment for restoring joint stability, however, many treated patients still develop additional long-term knee problems, such as knee osteoarthritis. New research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research reveals that individuals exhibit an altered gait after ACLR, which can contribute to these problems.
For the study, investigators compared gait biomechanics between ...
Broken sleep a hallmark sign of living with the most common liver disease, scientists find
2024-12-04
The prevalence of MASLD (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease) is exploding in most regions of the world, boosted by increased obesity and sedentary lifestyles. MASLD (formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) is already the most common liver disorder: it affects 30% of adults and between 7% and 14% of children and adolescents, and this prevalence is predicted to rise to more than 55% of adults by 2040. People with MASLD run a heightened risk of diabetes, hepatocellular carcinoma, non-liver cancers, chronic kidney disease, age-related muscle loss, and cardiovascular ...
Gender inequities in sporting environment and resources may distort estimates of ACL injury rates among women
2024-12-04
A new study by the Harvard GenderSci Lab in the British Journal of Sports Medicine reveals systematic biases in a key metric used in estimates of sex disparities in ACL injury rates in sports. The article argues that gendered factors (e.g. availability and quality of resources, compensation structures, ability to train amidst competing responsibilities outside of sports) may undermine the comparability of injury rates between women and men. As a result, recent headlines claiming much higher rates of ACL injury among women and girls may be misleading.
Sports scientists calculate ...
Monell Chemical Senses Center and A*Star SIFBI sign agreement to collaborate in sensory science research and education
2024-12-04
PHILADELPHIA, PA and SINGAPORE – The Monell Chemical Senses Center, a global leader in advancing the scientific understanding of taste, smell, and related senses, and A*STAR Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (A*STAR SIFBI), a translational research institute for health and well-being focused on Asian phenotype have entered into a five-year research and education alliance.
Today, Dr Benjamin P.C. Smith, Monell Executive Director & President, met with Dr Sze Tan, A*STAR SIFBI Executive Director, to sign a Memorandum ...
Approaching the unexplored “plasma phase-space” with data science
2024-12-04
A paper summarizing the results of this research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on November 8.
Fusion energy is being researched and developed as a new source of electric power that will contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society. At the National Institute for Fusion Science, research on magnetically confined plasma is being conducted using the Large Helical Device*2 (LHD). The major difference between plasma and other gases is its low density. The density of magnetically confined plasma is only about one millionth that of the atmosphere, and collisions between constituent particles occur only rarely. As a result, the histogram ...
People who use vapes as well as cigarettes are less likely to quit and often switch to just smoking
2024-12-04
People who use both vapes and cigarettes are less likely to quit compared to people who only smoke or only vape, according to a study published today (Wednesday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
Instead, the research suggests that over time, most of these ‘dual users’ tend to revert to only smoking cigarettes.
The researchers say their findings suggest that taking up vaping while continuing to smoke will probably not help people to stop smoking.
The study, by researchers from Germany, the USA and Denmark, was ...
Can plastic-eating bugs help with our microplastic problem?
2024-12-04
Plastic pollution occurs in every ecosystem on the planet and lingers for decades. Could insects be part of the solution?
Previous research found that insects can ingest and absorb pure, unrefined microplastics—but only under unrealistic, food-scarce situations. In a new Biology Letters paper, UBC zoologist Dr. Michelle Tseng and alumna Shim Gicole tested mealworms in a more realistic scenario, feeding them ground-up face masks—a common plastic product—mixed with bran, a tastier option.
Reality bites
Mealworms are Nature’s scavengers and decomposers, ...
Ocean density identified as a key driver of carbon capture by marine plankton
2024-12-04
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00.05 GMT WEDNESDAY 4 DECEMBER / 19:05 ET TUESDAY 3 DECEMBER 2024
Ocean density identified as a key driver of carbon capture by marine plankton
New findings, published today in Royal Society Open Science, have revealed that changes in ocean density have a significant impact on the rate at which marine plankton incorporate carbon into their shells. This has profound implications for carbon cycling and the ocean’s ability to absorb atmospheric CO2 in response to climate change.
Up to now, researchers have focused on how ...
New drug candidate for spinocerebellar ataxia
2024-12-04
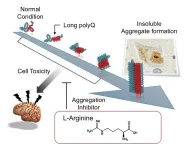
Niigata, Japan - A team led by Specially Appointed Associate Professor Tomohiko Ishihara and Professor Osamu Onodera at Niigata University, along with Professor Yoshitaka Nagai at Kindai University, conducted a randomized, double-blind trial on the efficacy and safety of L-arginine in treating Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 (SCA6).
I. Background of the Study
Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting the cerebellum, a part of the brain responsible for coordinating movement. Symptoms include difficulties with balance, coordination, and speech (ataxia ...