Gender inequities in sporting environment and resources may distort estimates of ACL injury rates among women
2024-12-04
(Press-News.org)
A new study by the Harvard GenderSci Lab in the British Journal of Sports Medicine reveals systematic biases in a key metric used in estimates of sex disparities in ACL injury rates in sports. The article argues that gendered factors (e.g. availability and quality of resources, compensation structures, ability to train amidst competing responsibilities outside of sports) may undermine the comparability of injury rates between women and men. As a result, recent headlines claiming much higher rates of ACL injury among women and girls may be misleading.
Sports scientists calculate rates of injury among women by counting numbers of ACL injuries and dividing that number by an estimate of playing and training time, known as “athlete-exposures.” The study by Danielsen and Gompers et al. is the first to examine the limitations of the construct of “athlete-exposures” through a gender lens.
The authors identify two key factors, stemming from a legacy of underinvestment in women’s sports, that likely skew comparisons by gender and artificially inflate measures of injury rates among women athletes: training to match ratio and team size. Systematic gender differences in both of these factors affect the gender-specific denominator that is used to compute injury rates, with women’s denominator not only being systematically smaller than that of men but also including a higher proportion of time at high-risk of injury (i.e., matches).
Accurately measuring sex disparities in ACL injury rates is important in order to inform potential strategies to reduce the risk of this debilitating injury for athletes. If the metrics used to quantify injury rates obscure key socially-mediated drivers of gender/sex disparities - i.e., training to match ratio and team size - promising opportunities for addressing such disparities and preventing injuries may be overlooked.
Key findings of the study include:
Failing to account for differences in gendered realities of women and men’s sports may lead to an inflation of estimates of injury disparities by gender/sex.
Sports scientists need to better distinguish between training and competition exposures and account for team size in order to avoid artificially inflating estimates of ACL injuries rates in women.
There are likely multiple gendered factors that can’t be captured by quantitative estimates of athlete exposure to injury risk, including inequities in compensation structure and quality of equipment and training. These factors should nonetheless be qualitatively considered and discussed to contextualize observed gender/sex disparities in injury rates.
Quotes:
Annika Gompers: “Athletes deserve solid statistics to understand the extent and drivers of disparities in ACL injury. Our work highlights that current research fails to account for biases in the data produced by gendered factors, which skews comparisons of injury rates between women and men. We call for more rigorous epidemiologic measurement of gender disparities going forward.”
Ann Caroline Danielsen: “We hope that this research will contribute to capturing patterns of ACL injury among women and men more accurately, and to identifying actionable avenues for addressing the socially-mediated drivers of ACL injuries among athletes.”
Sarah S. Richardson: “Gender assumptions can influence scientific knowledge in many different ways. When gendered assumptions are built into scientific measures, sex difference findings may not be accurate. Recent claims about higher vulnerability of women athletes to ACL knee injury are a case in point.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-04
PHILADELPHIA, PA and SINGAPORE – The Monell Chemical Senses Center, a global leader in advancing the scientific understanding of taste, smell, and related senses, and A*STAR Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (A*STAR SIFBI), a translational research institute for health and well-being focused on Asian phenotype have entered into a five-year research and education alliance.
Today, Dr Benjamin P.C. Smith, Monell Executive Director & President, met with Dr Sze Tan, A*STAR SIFBI Executive Director, to sign a Memorandum ...
2024-12-04
A paper summarizing the results of this research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on November 8.
Fusion energy is being researched and developed as a new source of electric power that will contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society. At the National Institute for Fusion Science, research on magnetically confined plasma is being conducted using the Large Helical Device*2 (LHD). The major difference between plasma and other gases is its low density. The density of magnetically confined plasma is only about one millionth that of the atmosphere, and collisions between constituent particles occur only rarely. As a result, the histogram ...
2024-12-04
People who use both vapes and cigarettes are less likely to quit compared to people who only smoke or only vape, according to a study published today (Wednesday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
Instead, the research suggests that over time, most of these ‘dual users’ tend to revert to only smoking cigarettes.
The researchers say their findings suggest that taking up vaping while continuing to smoke will probably not help people to stop smoking.
The study, by researchers from Germany, the USA and Denmark, was ...
2024-12-04
Plastic pollution occurs in every ecosystem on the planet and lingers for decades. Could insects be part of the solution?
Previous research found that insects can ingest and absorb pure, unrefined microplastics—but only under unrealistic, food-scarce situations. In a new Biology Letters paper, UBC zoologist Dr. Michelle Tseng and alumna Shim Gicole tested mealworms in a more realistic scenario, feeding them ground-up face masks—a common plastic product—mixed with bran, a tastier option.
Reality bites
Mealworms are Nature’s scavengers and decomposers, ...
2024-12-04
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00.05 GMT WEDNESDAY 4 DECEMBER / 19:05 ET TUESDAY 3 DECEMBER 2024
Ocean density identified as a key driver of carbon capture by marine plankton
New findings, published today in Royal Society Open Science, have revealed that changes in ocean density have a significant impact on the rate at which marine plankton incorporate carbon into their shells. This has profound implications for carbon cycling and the ocean’s ability to absorb atmospheric CO2 in response to climate change.
Up to now, researchers have focused on how ...
2024-12-04
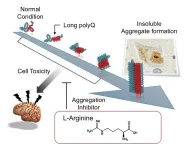
Niigata, Japan - A team led by Specially Appointed Associate Professor Tomohiko Ishihara and Professor Osamu Onodera at Niigata University, along with Professor Yoshitaka Nagai at Kindai University, conducted a randomized, double-blind trial on the efficacy and safety of L-arginine in treating Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 (SCA6).
I. Background of the Study
Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting the cerebellum, a part of the brain responsible for coordinating movement. Symptoms include difficulties with balance, coordination, and speech (ataxia ...
2024-12-04
Short bursts of incidental vigorous physical exertion, lasting less than a minute each, may almost halve the risk of a major cardiovascular event, such as heart attack or heart failure among women who don’t exercise regularly, finds research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Just 1.5-4 daily minutes of high intensity routine activities, such as brisk stair climbing or carrying heavy shopping, may help to stave off cardiovascular disease among those either unwilling or unable to take part in structured exercise or sport, conclude the international team ...
2024-12-04
The health and financial implications of the emerging threat of mosquito-borne chikungunya viral infection have most likely been significantly underestimated, with total costs probably approaching US$ 50 billion in 2011-20 alone, suggests a comprehensive data analysis, published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
In the short term, symptoms include fever, severe joint pain, rash and fatigue. While these often clear up, those affected can be left with long term, debilitating aftereffects, including chronic arthritic-type joint pain, fatigue, and depression, point out the researchers.
The ...
2024-12-04
An average of four minutes of incidental vigorous physical activity a day could almost halve the risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks, for middle-aged women who do not engage in structured exercise, according to new research from the University of Sydney, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
“We found that a minimum of 1.5 minutes to an average of 4 minutes of daily vigorous physical activity, completed in short bursts lasting up to 1 minute, were ...
2024-12-04
Today, women with oestrogen-sensitive breast cancer receive anti-hormonal therapy. Researchers now show that postmenopausal women with low-risk tumours have a long-term benefit for at least 20 years, while the benefit was more short-term for younger women with similar tumour characteristics who had not yet gone through the menopause. The results are reported in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI).
In Sweden, 9 000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, with hormone-sensitive breast cancer accounting for about 75 percent of women diagnosed with the disease. In patients with hormone-sensitive breast cancer tumour growth is mainly driven by oestrogen and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Gender inequities in sporting environment and resources may distort estimates of ACL injury rates among women