Durian helps rice plants thrive in salty soil
2024-12-05
(Press-News.org) Extreme weather and pollution have increased the salt content in some soil, making growing conditions harsh for salt-sensitive crops like rice. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano detail a possible solution that doesn’t require genetic modification to make rice plants thrive in these conditions. In lab experiments, they determined that coating rice seedlings with magnesium-doped carbon dots — derived from durian peels — increased the seedlings’ antioxidant activity and photosynthesis, reducing the stress caused by salty soil.
To increase stress resistance in plants, the current state-of-the-art solution is gene editing. However, gene editing technologies can be cost-prohibitive, and some people are concerned about the health effects and safety of genetically modified foods. One potential alternative to genetic modification is coating plant leaves with nanoscale carbon dots that counteract oxidative stress by mimicking the plant’s antioxidant enzymes. So, Longwei Jiang, Jianguo Zeng and colleagues designed a carbon dot using pulverized durian peel that could neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and alleviate salt stress-induced damage in rice plants.
Durian peels are inedible and account for 70 to 85% of the fruit’s weight. The peel also contains a lot of carbon, making the discarded rind a good source for biomass-derived carbon dots. The researchers doped their durian-derived carbon dots with magnesium — an element essential for plant growth — and then sprayed them on rice seedlings planted in salt-free and salty soils.
The team found that seedlings treated with their dots contained lower levels of ROS and grew taller in salty soils than untreated seedlings. Furthermore, treated seedlings had activated plant defense and photosynthesis genes that weren’t activated in untreated seedlings. The researchers caution that more information is needed to better understand how exactly the dots are triggering these cellular and genetic changes; more information is also needed about the treated plants’ impact on the environment and the humans and animals that consume them. However, the study concludes that carbon dots represent a potential strategy for enhancing plant salt tolerance and provide valuable insights for their agriculture applications.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and Anhui Agricultural University talent introduction project.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, e-books and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Registered journalists can subscribe to the ACS journalist news portal on EurekAlert! to access embargoed and public science press releases. For media inquiries, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-05
Despite the massive hype surrounding Power-to-X (PtX), most of the world's announced green hydrogen projects lack financing. The market is deemed far too risky by stakeholders. And, there are many potential pitfalls. According to the authors of a study from the University of Copenhagen, actors must be ‘compelled’ to invest in a genuinely green manner.
Green hydrogen has long been touted as the climate-friendly energy solution of the future. Indeed, there has been no shortage of hype surrounding Power-to-X – which converts green electricity into hydrogen and other molecules. In Denmark, politicians have referred to PtX as a cornerstone of ...
2024-12-05
In the split second that is needed to view a stop sign and react to it, our brain navigates a complex process that transitions seamlessly from perception to action control. This ability to halt or inhibit actions, known as response inhibition, is fundamental to human cognition. It plays a key role in decision-making and self-control, enabling us to suppress impulsive or inappropriate behaviors. Understanding the mechanisms underlying this process is essential for grasping how we manage our thoughts and actions and for treating impulse control disorders like attention deficit hyperactivity ...
2024-12-05
From the 1960s to the 1980s, the use of lead in fuel, paints, and pipes caused widespread contamination. It is estimated that 170 million Americans alive today were exposed to high lead levels as children, which caused significant harm, including a measurable drop in IQ scores. While we now understand the dangers of these chemicals, large sections of the population are still exposed to them. UNICEF reports that about 800 million children globally, nearly half of whom live in South Asia, are still exposed to unsafe levels of lead resulting from the hazardous ...
2024-12-05
Control systems are ubiquitous in modern day technology. In industrial contexts, these systems ensure that relevant variables remain within a desirable range to keep processes running safely and efficiently. A vast array of control strategies exists, and it is not uncommon to combine different types of controllers to improve performance. For instance, high-level controllers based on mathematical modeling of a given process are routinely combined with low-level controllers, such as the widely used ...
2024-12-05
The Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons (HWE) reaction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry, widely used to create conjugated carbonyl compounds. Conjugated carbonyl compounds are used in many industries for synthesizing perfumes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals and are also involved in biological processes. Consequently, methods for improving HWE reactions are an active area of research.
One potential application of HWE reactions is to develop (E)-isomers of conjugated carbonyl compounds that are useful for synthesizing chemicals called hynapene analogues with promising anti-cancer ...
2024-12-05
Patients and families affected by food allergy worry when they fly and often make travel decisions with food allergy management top-of-mind
Airlines don’t always honor buffer zones, allergen-free food or cabin announcements that were promised to travelers during the booking process
Simple steps to help ensure the safety of travelers with food allergy can go a long way
CHICAGO ---The skies aren’t always so friendly for patients and families affected by food allergies, who may often experience worry and anxiety regarding airline travel, according to a new study from the Center for Food Allergy and Asthma Research at Northwestern University ...
2024-12-05
More images and video available- see link in the Notes section.
A new study suggests that the fundamental abilities underlying human language and technological culture may have evolved before humans and apes diverged millions of years ago. The findings will be published 5th December 2024 in the journal PeerJ.
Many human behaviours are more complex than those of other animals, involving the production of elaborate sequences (such as spoken language, or tool manufacturing). These sequences include the ability to organise behaviours by hierarchical chunks, and to understand relationships between distantly separated elements.
For example, even relatively simple human behaviours like making ...
2024-12-05
PULLMAN, Wash. – Analysis of cheek swabs taken from pregnant women revealed a potential epigenetic biomarker for preeclampsia, a potentially life-threatening condition that often leads to preterm births.
While a clinical trial is needed to confirm the results, a study published in the journal Environmental Epigenetics offers hope that a simple test can be developed to identify preeclampsia earlier in pregnancy. Currently preeclampsia is usually identified by symptoms, such as abnormally high blood pressure, which only appear in the second trimester of pregnancy. Sometimes the condition can go undetected ...
2024-12-05
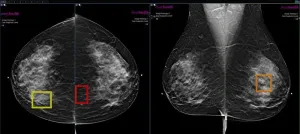
CHICAGO – More than a third of women across 10 health care practices chose to enroll in a self-pay, artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced breast cancer screening program, and the women who enrolled were 21% more likely to have cancer detected, according to research being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
AI has shown great promise in mammography as a “second set of eyes” for radiologists providing decision support, risk prediction and other benefits. Despite its promise, AI is not yet reimbursed by insurance, which likely is slowing its adoption ...
2024-12-05
We all need to eat, but the impact of the climate crisis on our crops is throwing the world’s food supply into question. Modern crops, domesticated for high food yields and ease of harvesting, lack the genetic resources to respond to the climate crisis. Significant environmental stresses are reducing the amount of food produced, driving supplies down and prices up. We can’t sustainably take over more land for agriculture, so we need to change our crops—this time to adapt them to the world we have altered.
“Agriculture is highly vulnerable to climate change, and the intensity and frequency of extreme events is only going to increase,” said Prof Sergey ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Durian helps rice plants thrive in salty soil