(Press-News.org) Adding a new drug to standard care for stem cell transplant recipients may reduce a life-threatening side effect, according to an early-stage clinical trial conducted at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The trial showed that patients being treated for various blood cancers tolerated the investigational drug — called itacitinib —and experienced lower-than-expected rates of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), in which the donor’s stem cells attack the patient’s healthy tissues.
The study is online in the journal Blood.
“We have to be cautious about interpreting the results of a small study, but the rates of graft-versus-host disease were unexpectedly low,” said senior author John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, the Virginia E. & Sam J. Golman Endowed Professor of Medicine. “We saw no severe GvHD, and the rates of relapse were lower than expected in these high-risk patients. Low GvHD rates and low relapse resulted in very encouraging survival for the patients in this study. These early results are compelling, and we hope to conduct a bigger randomized controlled clinical trial to be able to evaluate efficacy.”
Conducted at Siteman Cancer Center, based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and WashU Medicine, this Phase I trial involved patients who received a particular stem cell transplant — called a “half-match” — in which half of the key proteins of a patient’s immune system matched those of the donor’s stem cells. Stem cell transplantation is standard care for multiple types of blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
A fully matched stem cell donor is preferred for stem cell transplant patients as it reduces the risk of graft-versus-host disease. But recruiting such a donor is often difficult and seeking one out can delay treatment. A patient’s parent or child is automatically a half-matched donor, and siblings are half-matched 50% of the time, making such donors far easier to find for most patients. Half-match stem cell transplants have become more common over the past decade as treatments to reduce graft-versus-host disease have improved, making such transplants safer.
“Half-matched transplants have increased dramatically in recent years, so improving the safety and effectiveness of this procedure is a big goal and has the potential to impact a lot of patients,” DiPersio said.
The trial included 42 patients, most of whom had been diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome, among other, rarer blood cancers. All patients in the study received itacitinib before transplantation and for 4-6 months after transplant, in addition to standard care for prevention of graft-versus-host disease.
None of the 42 patients developed severe (grade 3 or 4) graft-versus-host disease in the first 180 days after the transplant. There was no control group in this study, which was designed to assess the safety but not the efficacy of the treatment. Even so, historical data suggest 10 – 15% of patients would experience severe graft-versus-host disease with standard treatment, according to the investigators. Therefore, statistically, four to six patients in this sample size would be expected to develop severe forms of the disease.
After one year, 89% of patients had no chronic graft-versus-host disease. Two patients developed moderate or severe chronic graft-versus-host disease at that same timepoint, and they were treated with additional therapies. Overall survival at one year was 80%. This is on the high end of what is typically seen in such patients, whose survival can range from 60 – 80% at one year.
The investigational drug itacitinib is one of several JAK inhibitors under investigation for their potential to prevent graft-versus-host disease when given before a stem cell transplant, which would be a new use for this therapy. JAK inhibitors work by blocking the activity of specific enzymes that contributes to inflammation.
“Some other JAK inhibitors are already approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after it develops,” said first author Ramzi Abboud, MD, an assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Oncology at WashU Medicine. “We are interested in investigating these drugs as a possible way to prevent graft-versus-host disease by giving them before the transplant. We suspect that JAK inhibitors will have a place in prevention of this life-threatening side effect of stem cell transplants. We and other groups are evaluating these kinds of drugs in clinical trials using a variety of approaches. This study is encouraging, and we expect to know more about how best to use these prevention strategies in the coming years.”
###
Abboud R, Schroeder MA, Rettig MP, Jayasinghe RG, Gao F, Eisele J, Gehrs L, Ritchey J, Choi J, Abboud CN, Pusic I, Jacoby M, Westervelt P, Christopher M, Cashen A, Ghobadi A, Stockerl-Goldstein K, Uy GL, DiPersio JF. Itacitinib for prevention of graft-versus-host disease and cytokine release syndrome with T cell replete peripheral blood haploidentical transplantation. Blood. Nov. 22, 2024. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2024026497.
This work was supported by the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center, Biostatistics Core and Clinical Trials Core; the Bursky Center for Human Immunology and Immunotherapy, Immunomonitoring Laboratory; and the Tumor Procurement Core, funded via the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Comprehensive Cancer Center support grant P30 CA091842; and the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant UL1TR002345 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) of the NIH. Additional support was provided by the American Society of Hematology Clinical Research Training Institute; the American Society of Hematology Research Training Award for Fellows; and the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award number K12 CA167540; an NCI Outstanding Investigator Award, grant number R35 CA210084; the Leukemia SPORE, grant number P50 CA171963; and an NCI Research Specialist Award, grant number R50 CA211782. This content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Incyte Corporation provided itacitinib and funding to perform this investigator-initiated study. Incyte had no role in designing the trial, conducting the study or writing the manuscript.
About Washington University School of Medicine
WashU Medicine is a global leader in academic medicine, including biomedical research, patient care and educational programs with 2,900 faculty. Its National Institutes of Health (NIH) research funding portfolio is the second largest among U.S. medical schools and has grown 56% in the last seven years. Together with institutional investment, WashU Medicine commits well over $1 billion annually to basic and clinical research innovation and training. Its faculty practice is consistently within the top five in the country, with more than 1,900 faculty physicians practicing at 130 locations and who are also the medical staffs of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals of BJC HealthCare. WashU Medicine has a storied history in MD/PhD training, recently dedicated $100 million to scholarships and curriculum renewal for its medical students, and is home to top-notch training programs in every medical subspecialty as well as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and audiology and communications sciences.
END
New drug tested to reduce side effect of ‘half-matched’ stem cell transplants
Clinical trial indicates safety, fewer cases of life-threatening graft-versus-host disease than expected
2024-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
IGB researchers leverage team science to develop InSTAnT Toolkit
2024-12-05
In a new study published in Nature Communications, a team of researchers at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology report a new, robust computational toolset to extract biological relationships from large transcriptomics datasets. These efforts will help scientists better investigate cellular processes.
Living organisms are governed by their genome—an instruction manual written in the language of DNA that dictates how an organism grows, survives, and reproduces. By regulating the abundance of different RNA transcripts, cells control their protein expression level, thereby shaping their functions ...
AADOCR elects new Vice-president, Treasurer, and Representative to the IADR/AADOCR Publications Committee
2024-12-05
Alexandria, VA – Members of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) have elected Margherita R. Fontana, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, as Vice-president, Julie Frantsve-Hawley, Temple University Kornberg School of Dentistry, Philadelphia, PA, as Treasurer, and Ariadne Letra, University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine, PA, as Representative to the IADR/AADOCR Publications Committee. Their terms will commence at the conclusion of the 54th Annual Meeting ...
IADR elects Raul Garcia as Vice-president
2024-12-05
Alexandria, VA, USA – Members of the International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) have elected Raul I. Garcia, Boston University, USA, to serve as Vice-president. His term will commence at the conclusion of the 103rd General Session of the IADR, which will be held in conjunction with the 2025 IADR Pan European Regional Congress from June 25-28, 2025 in Barcelona, Spain.
Garcia is Professor and Chair of the Department of Health Policy and Health Services Research at the Henry M. Goldman School of Dental Medicine at Boston University. He received his DMD and MMedSc from the Harvard ...
Seven researchers named to Battelle Distinguished Inventor cadre
2024-12-05
Seven scientists affiliated with the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have been named Battelle Distinguished Inventors in recognition of being granted 14 or more United States patents. Since Battelle began managing ORNL in 2000, 104 ORNL researchers have reached this milestone.
“These innovators have not only developed cutting-edge technologies, but they have also prioritized taking the steps to move them out into the marketplace, which is critical for adoption and broad impact,” said Susan Hubbard, ORNL deputy for science and technology. “The innovators are working on a range of strategies important for our ...
Gene therapy fixes major cause of stillbirth, premature birth in guinea pig model
2024-12-05
The life of billions of people inhabiting Earth is owed to a temporary organ that supported and nourished them in a mother’s womb.
The placenta, or afterbirth, is considered sacred by some cultures, its pivotal role in pregnancy recognized as far back as the raising of Egypt’s pyramids. It provides nutrients and oxygen to the fetus via the umbilical cord, acting like a gut, kidney, liver, and lungs.
If the placenta fails, only one hazardous option remains — premature delivery through induced labor or cesarean delivery.
Now, the first therapy to potentially ...
From one gene switch, many possible outcomes
2024-12-05
Within all complex, multicellular living systems such as plants and humans, there exists a set of genetic elements that can be likened to the blueprints, tools, and specialized personnel at a construction site for an expanding development. Plant biologists like Aman Husbands at the University of Pennsylvania study a family of skilled subcontractors, known as the HD-ZIPIII transcription factors (TFs). These subcontractors are tasked with deciding which blueprints, or genes, to follow as they guide the ...
Visiting Fellows selected for inaugural cohort of the Africa-UBC Oceans and Fisheries Visiting Fellows Program
2024-12-05
The Africa-UBC Oceans and Fisheries Visiting Fellows Program is extremely pleased to announce the selection of its inaugural laureates: Dr. Cynthia A. Adinortey (Ghana) and Dr. Antony Otinga Oteng’o (Kenya).
“We had many excellent applicants from across Sub-Saharan Africa. Ultimately, our Selection Committee selected these two exemplary scholars, and we are most happy with the result,” said Dr. William Cheung, professor and Director of UBC’s Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries (IOF), which administers the Program. “These two exemplary scholars will now have the opportunity to collaborate ...
Innovative immunotherapy shows promise in early clinical trial for breast cancer
2024-12-05
A groundbreaking phase one clinical trial exploring a novel cell-based immunotherapy for breast cancer has been accepted for publication in JAMA Oncology. The technology tested in the trial was co-developed by Gary Koski, Ph.D., professor in Kent State University’s Department of Biological Sciences, and Brian J. Czerniecki, M.D., Ph.D., chair and senior member in the Moffitt Cancer Center’s Department of Breast Oncology. The study focuses on a new treatment approach that aims to harness the body’s immune system to enhance patient responses ...
Whiteness as a fundamental determinant of health in rural America
2024-12-05
WASHINGTON -- White people in rural America have unique factors that drive worse health outcomes than their urban counterparts, prompting a team of public health researchers to label whiteness as a fundamental determinant of health. They say while the health and well-being of racially minoritized populations should continue to be a research priority they urge researchers to consider factors that influence the health of majoritized populations.
In an analytic essay, "Whiteness: A Fundamental Determinant of the Health of Rural White Americans,” published Dec. 5 in the American Journal of Public Health, Caroline Efird, PhD, MPH, ...
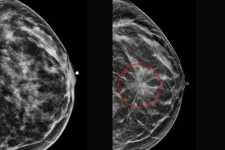
Analyzing multiple mammograms improves breast cancer risk prediction
2024-12-05
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis describes an innovative method of analyzing mammograms that significantly improves the accuracy of predicting the risk of breast cancer development over the following five years. Using up to three years of previous mammograms, the new method identified individuals at high risk of developing breast cancer 2.3 times more accurately than the standard method, which is based on questionnaires assessing clinical risk factors alone, such as age, race and family history of breast cancer.
The study is published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] New drug tested to reduce side effect of ‘half-matched’ stem cell transplantsClinical trial indicates safety, fewer cases of life-threatening graft-versus-host disease than expected