(Press-News.org) Analyzing the sequence of proteins in cohort studies is done by comparing participant data against protein sequences predicted from the human genome.
– Today, the same reference proteins are used for all participants, says associate professor Marc Vaudel at the department of Clinical Science of the University of Bergen – but we are all different! We found that the small genetic changes that make us who we are create a bias: for those who differ from the reference, current informatic methods are blind to parts of their proteins.
To solve this problem, the researchers in Bergen developed new models to build sequences from large genetic panels. Their new method captures the protein sequences that are most likely to be observed in the population.
– Accounting for a greater diversity among cohort participants is key to refine medical research to individual profiles, adds PhD candidate Jakub Vašíček who designed the method.
However, many groups of people are not well represented in genetic panels and diversity is challenging to integrate in current data models.
– The road is still long before we can treat all patients fairly, but we are making good progress, Vašíček adds.
The new method has just been published in the prestigious journal Nature Methods: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-024-02506-0
END
New method enables protein analysis accounting for population diversity
2024-12-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breaking new ground in health care: Setting the standard for XR clinical research with the RATE-XR guideline
2024-12-09
(Toronto, December 9, 2024) In a pivotal step toward improving research standards in health care technologies, the Journal of Medical Internet Research has published the RATE-XR guideline. This new tool aims to standardize reporting for early-phase clinical studies involving extended reality (XR) technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality. Developed through a robust, expert-driven process, RATE-XR addresses critical gaps in transparency, safety, and ethical reporting, ensuring XR applications meet the needs of patients and researchers alike.
Led by a multidisciplinary team of international experts, RATE-XR offers a checklist comprising 17 XR-specific ...
Unlocking worm strategies: A path to innovative vaccines and therapies
2024-12-09
A research team led by Prof. Julia Esser-von Bieren from the Center of Allergy and Environment (ZAUM) at Helmholtz Munich and the Technical University of Munich, as well as the University of Lausanne (UNIL) has uncovered a molecular strategy employed by worm parasites (helminths) to evade host immune defenses. This discovery opens new avenues for the development of innovative vaccines and therapies. Published in Science Immunology, the study offers promising solutions for addressing major infectious diseases, allergies, and asthma by leveraging ...
Students are less likely to feel safe at their schools, compared to staff and parents
2024-12-09
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 9, 2024 – School shooting incidents have doubled in the last three years, according to the K-12 School Shooting Database, which tracks each time a firearm is discharged on school property. Many schools have taken measures to improve safety, including metal detectors, interior door locks, emergency drills, and undercover security. But do students and staff feel any safer?
Researchers at the University of Southern California (USC) conducted a nationwide study of K-12 parents, K-12 teachers, and recently graduated high school students to test their responses ...
SwRI announces joint industry program aimed at advancing heavy-duty hydrogen refueling infrastructure
2024-12-09
SAN ANTONIO — December 9, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute has announced a groundbreaking joint industry project (JIP) to help spur the growth and innovation of fueling technologies and infrastructure for hydrogen-powered heavy-duty vehicles.
SwRI’s H2HD REFUEL (Hydrogen Heavy Duty Refueling Equipment and Facilities Utilization Evaluation Laboratory) JIP aims to strengthen the acceptance of hydrogen fuel use by heavy-duty vehicles to help the mobility industry meet its decarbonization and zero-emissions goals by advancing hydrogen refueling station (HRS) technologies. Over the next four years, SwRI researchers will use hands-on ...
Webb telescope’s largest study of universe expansion confirms challenge to cosmic theory
2024-12-09
New observations from the James Webb Space Telescope suggest that a new feature in the universe—not a flaw in telescope measurements—may be behind the decadelong mystery of why the universe is expanding faster today than it did in its infancy billions of years ago.
The new data confirms Hubble Space Telescope measurements of distances between nearby stars and galaxies, offering a crucial cross-check to address the mismatch in measurements of the universe’s mysterious expansion. Known as the Hubble tension, the discrepancy remains unexplained even by the best cosmology models.
“The ...
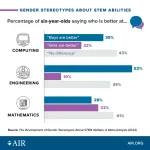
By age six, children think boys are better than girls at computing and engineering, new American Institutes for Research study shows
2024-12-09
Arlington, Va. – Children as young as age 6 develop gender stereotypes about computer science and engineering, viewing boys as more capable than girls, according to new results from an American Institutes for Research (AIR) study. However, math stereotypes are far less gendered, showing that young children do not view all science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields as the same.
These new findings come from the largest-ever study on children’s gender stereotypes about STEM and verbal abilities, based on data from 145,000 children across 33 nations, synthesizing more than 40 years of ...
Hair growth drug safe at low doses for breast cancer patients
2024-12-09
Hair loss during chemotherapy can cause enough distress for some women to lose self-confidence, which experts say may discourage them from seeking chemotherapy in the first place.
Oral minoxidil is a commonly prescribed treatment for hair loss. The drug is also the active ingredient in over-the-counter Rogaine. The prescription treatment is known, however, to dilate blood vessels, and experts worry that this could increase the heart-related side effects of chemotherapy and lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, or fluid buildup.
Now, a study in women with breast cancer suggests that low oral doses of minoxidil, taken during ...
Giving a gift? Better late than never, study finds
2024-12-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – If you feel terrible about giving a late gift to a friend for Christmas or their birthday, a new study has good news for you.
Researchers found that recipients aren’t nearly as upset about getting a late gift as givers assume they will be.
“Go ahead and send that late gift, because it doesn’t seem to bother most people as much as givers fear,” said Cory Haltman, lead author of the study and doctoral student in marketing at The Ohio State University’s Fisher College of Business.
In a series of six studies, Haltman and his colleagues explored the mismatch between givers’ ...
Judging knots throws people for a loop
2024-12-09
We tie our shoes, we put on neckties, we wrestle with power cords. Yet despite deep familiarity with knots, most people cannot tell a weak knot from a strong one by looking at them, new Johns Hopkins University research finds.
Researchers showed people pictures of two knots and asked them to point to the strongest one. They couldn’t.
They showed people videos of each knot, where the knots spin slowly so they could get a good long look. They still failed.
People couldn’t even manage it ...
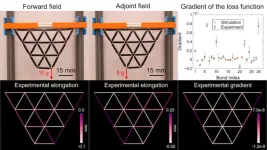
Not so simple machines: Cracking the code for materials that can learn
2024-12-09
It's easy to think that machine learning is a completely digital phenomenon, made possible by computers and algorithms that can mimic brain-like behaviors.
But the first machines were analog and now, a small but growing body of research is showing that mechanical systems are capable of learning, too. Physicists at the University of Michigan have provided the latest entry into that field of work.
The U-M team of Shuaifeng Li and Xiaoming Mao devised an algorithm that provides a mathematical framework for how learning works in lattices called ...