(Press-News.org) Online training that helps people recognise and understand new voices could be key to helping older adults improve communication in everyday environments, finds research by UCL experts.
The study, published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, tested whether learned voices were easier to understand than unfamiliar voices in 20 older (55-73 years) and 20 younger (18-34 years) adults.
Participants took part in some preparatory online training, where they were trained to understand three new voices by listening to them each say 10 meaningful sentences until they became “familiar”.
They then had to listen to one of these voices speak at the same time as two new “unfamiliar” voices (similar to in a social setting) to see if they could pick out a specific sentence and name which of the three “familiar” speakers they were listening to.
Participants completed this exercise 468 times each and the target “familiar” voice changed throughout the trial.
The researchers found that there was around a 30% improvement in understanding sentences spoken by new voices that participants had been trained to recognise, in both older and younger adults.
Lead author, Dr Emma Holmes (UCL Psychology & Language Sciences), said: “People often face the challenge of understanding speech in noisy environments: imagine a festive office party, a family gathering, or trying to hold a conversation in a busy café. This process becomes more challenging as people age.
“Yet, in these environments, we are better at understanding people who are familiar to us, such as our family members, friends and colleagues.
“In this paper we found people get as much benefit from being trained to understand newly familiarised voices, as for naturally familiar voices such as family members.”
Participants were able to complete the training on a computer in the comfort of their own homes and effective results were seen in less than one hour.
Based on their findings, the team believes that if a person practices listening to voices that they regularly encounter, it could improve their everyday communication.
Dr Holmes added: “This type of training may be particularly appealing to older adults, given that people often find it increasingly difficult to understand speech in noisy places as they age.”
The researchers now aim to personalise the training to voices that participants regularly encounter in their daily lives.
Eventually, after technical development, they hope the training will be publicly available via a smartphone app.
They also hope to explore how this type of training could help people who have hearing loss, who often find it difficult to communicate in noisy places.
The researchers recently published another study, funded by the Royal National Institute for Deaf People, on how people focus on a voice of interest amid multiple conversations. They found that both younger adults and older adults with excellent hearing use the location of the voice to understand speech. However, this ability decreases with age-related hearing loss.
Interestingly, this decline occurs even when the hearing loss is below the clinical diagnosis threshold. This suggests that changes in both peripheral and central auditory processes begin before clinical hearing loss is diagnosed, explaining why people with hearing loss struggle in noisy environments.
The new research was funded by Wellcome and the Experimental Psychology Society.
END
Online training could help older adults communicate in noisy environments
Peer-reviewed | Experimental study | People
2024-12-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Short-term cognitive boost from exercise may last for 24 hours
2024-12-10
Short-term cognitive boost from exercise may last for 24 hours
The short-term boost our brains get after we do exercise persists throughout the following day, suggests a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
Previous research in a laboratory setting has shown that people’s cognitive performance improves in the hours after exercise, but how long this benefit lasts is unknown.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, ...
Pulte Institute joins global consortium using research to end poverty
2024-12-09
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has awarded $75 million to a consortium of leading global institutions, including the Pulte Institute for Global Development at the University of Notre Dame’s Keough School of Global Affairs, to enhance the effectiveness of poverty alleviation programs through research.
The Promoting Impact and Learning with Cost-Effectiveness Evidence (PILCEE) partnership, led by the Center for Effective Global Action at the University of California, Berkeley, represents a historic ...
ASH: Monoclonal antibody therapy improves survival in cancer-associated hyper-inflammatory disorder
2024-12-09
ABSTRACT: 805
SAN DIEGO – Adult patients with newly diagnosed malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (mHLH) – a rare, aggressive hyperinflammatory condition – who were treated with the first-in-class monoclonal antibody, ELA026, experienced a 100% response rate and an improved survival rate at two months, according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Data from the Phase Ib trial were presented today at the 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition by Abhishek Maiti, M.D., assistant professor of Leukemia and the trial’s principal investigator. ...
Researchers ‘see’ vulnerability to gaming addiction in the adolescent brain
2024-12-09
Playing video games is a rite of passage for many adolescents, but for some, it could also be the first step to a gaming addiction.
“A number one concern for parents of children and teenagers is how much screen time and how much gaming is enough gaming and how to figure out where to draw the line,” said John Foxe, PhD, director of the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester and co-author of a study out today in the Journal of Behavioral Addictions that discovered a key marker in the brain of teens who develop gaming addiction symptoms. “These data begin to give us some answers.”
Researchers ...
Considering social and genetic factors in addition to clinical factors improves prediction of heart disease risk
2024-12-09
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 9 December 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Biomarker-guided antibiotic duration for hospitalized patients with suspected sepsis
2024-12-09
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/About The Study: In hospitalized adults, daily procalcitonin -guided protocol reduced antibiotic duration safely compared with standard care, but daily C-reactive protein -guided protocol does not. All-cause mortality for C-reactive protein was inconclusive.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paul Dark, MD, PhD, email adaptsepsistrial@warwick.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.26458)
Editor’s ...
American Meteorological Society announces Alan Sealls as 2025 President-Elect
2024-12-09
Members of the American Meteorological Society (AMS) have elected Alan Sealls to the position of AMS president-elect for 2025. Sealls is an AMS Fellow and Certified Broadcast Meteorologist who retired this year from a 37-year broadcast career, which included serving as chief meteorologist at WPMI-TV in Mobile, Alabama. He will be inducted as president-elect on Sunday, 12 January, 2025, during the 105th AMS Annual Meeting in New Orleans, Louisiana.
At the meeting, the AMS—the professional society for weather, water, and climate sciences ...
Dogs use two-word button combos to communicate
2024-12-09
A new study from UC San Diego’s Comparative Cognition Lab shows that dogs trained to use soundboards to “talk” are capable of making two-word button combinations that go beyond random behavior or simple imitation of their owners. Published in the journal Scientific Reports from Springer Nature, the study analyzed data from 152 dogs over 21 months, capturing more than 260,000 button presses – 195,000 of which were made by the dogs themselves.
“This is the first scientific study to analyze how dogs actually use soundboards,” said lead researcher Federico Rossano, associate professor of cognitive science at UC San Diego and director ...
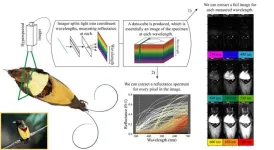
Researchers use a powerful imaging technique to illuminate the colorful plumage of birds
2024-12-09
Animals showcase a remarkable diversity of colors and patterns, from the shimmery appearance of a peacock’s tail to the distinctive rosettes on a jaguar’s fur. Quantifying animal color has been a longtime goal of evolutionary biologists, who aim to understand how color evolved over time—and the physical and genetic mechanisms involved. Ultimately, studying animal color is important because it can reveal how evolutionary forces, such as natural and sexual selection, favor certain traits over others. However, fully capturing animal color is challenging because researchers must choose between high spatial resolution (as in traditional ...
Jabuticaba peel improves nutritional characteristics of bread
2024-12-09
Researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state, Brazil, have developed a sourdough bread formulation enriched with jabuticaba peel that could be an alternative for people with diabetes and others who need to control blood sugar. An article describing their research and test results is published in the journal Foods.
As noted in the article, the high carbohydrate content of bread can sharply raise blood sugar levels, risking hyperglycemia. Given the high demand for healthier bread, which is widely consumed, artisanal bakers seek to diversify their products with formulations that add nutritional value while involving fermentation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Online training could help older adults communicate in noisy environmentsPeer-reviewed | Experimental study | People