(Press-News.org) The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has awarded $75 million to a consortium of leading global institutions, including the Pulte Institute for Global Development at the University of Notre Dame’s Keough School of Global Affairs, to enhance the effectiveness of poverty alleviation programs through research.
The Promoting Impact and Learning with Cost-Effectiveness Evidence (PILCEE) partnership, led by the Center for Effective Global Action at the University of California, Berkeley, represents a historic investment by USAID over five years to inform its activities and programs with detailed evidence linking investments in agriculture, global health and economic growth to improvements in human lives and community well-being.
“We’re proud that the Pulte Institute has been selected to identify the most efficient and impactful programs to fight poverty and improve lives,” Vice President for Research Jeffrey F. Rhoads said of the award, announced this week. “Through PILCEE, Notre Dame looks forward to deepening our partnerships with researchers around the globe with the shared goal of providing sustainable interventions to end poverty, part of our University’s strategic framework.”
Through PILCEE, a worldwide network of more than 1,500 researchers — including more than 250 from low- and middle-income countries — will collaborate to guide USAID’s work by evaluating the impact of agency-funded programs and synthesizing findings from the growing evidence base. In doing so, PILCEE will generate insights for the global development community about the most economical ways to improve lives and promote growth.
The Pulte Institute offers a unique ability to support the work of the PILCEE effort, as demonstrated by its experience synthesizing evidence for USAID in large-scale efforts, including the $40 million Supporting Holistic and Actionable Research in Education activity, focused on improving global education outcomes, and Expanding the Reach of Impact Evaluation, a $15.5 million multi-country effort to retrospectively assess the effectiveness of aid programming in areas from food security to peacebuilding.
“The Pulte Institute’s inclusion in this groundbreaking consortium underscores the Keough School’s and Notre Dame’s commitment to addressing global challenges through evidence-based solutions,” said Mary Gallagher, the Marilyn Keough Dean of the Keough School of Global Affairs. “Through this partnership, we will continue to advance research that directly informs practical solutions to poverty.”
In its work on behalf of the consortium, the Pulte Institute will connect USAID requests for research, evidence synthesis, evaluations and costing analyses with appropriate engagement opportunities and academic expertise from the Global North and South through an established network of local partnerships.
“Cost-effectiveness is a crucial area for USAID — and for all of us — to be investigating right now because there are limited resources that we can spend in international development and humanitarian aid,” said Danice Brown Guzmán, associate director of evidence and learning for the Pulte Institute and a lead researcher on the Expanding the Reach of Impact Evaluation project. “Being able to make strong, rigorous comparisons between different programs or ways of doing development work provides you with an understanding of which approaches are going to lead to the most impact with your investment.”
PILCEE will prioritize evidence from randomized controlled trials, an approach recognized by the Nobel Prize committee as transformational in understanding promising solutions to global poverty. The Center for Effective Global Action and other consortium partners — including the Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab, Innovations for Poverty Action and the Network of Impact Evaluation Researchers in Africa, among others — are experts in measuring program impact. Collectively, the consortium has produced, analyzed and translated more than 1,800 randomized controlled trials in nearly 100 countries over the past two decades, in addition to extensive research translation and dissemination work.
END
Pulte Institute joins global consortium using research to end poverty
2024-12-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASH: Monoclonal antibody therapy improves survival in cancer-associated hyper-inflammatory disorder
2024-12-09
ABSTRACT: 805
SAN DIEGO – Adult patients with newly diagnosed malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (mHLH) – a rare, aggressive hyperinflammatory condition – who were treated with the first-in-class monoclonal antibody, ELA026, experienced a 100% response rate and an improved survival rate at two months, according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Data from the Phase Ib trial were presented today at the 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition by Abhishek Maiti, M.D., assistant professor of Leukemia and the trial’s principal investigator. ...
Researchers ‘see’ vulnerability to gaming addiction in the adolescent brain
2024-12-09
Playing video games is a rite of passage for many adolescents, but for some, it could also be the first step to a gaming addiction.
“A number one concern for parents of children and teenagers is how much screen time and how much gaming is enough gaming and how to figure out where to draw the line,” said John Foxe, PhD, director of the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester and co-author of a study out today in the Journal of Behavioral Addictions that discovered a key marker in the brain of teens who develop gaming addiction symptoms. “These data begin to give us some answers.”
Researchers ...
Considering social and genetic factors in addition to clinical factors improves prediction of heart disease risk
2024-12-09
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 9 December 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Biomarker-guided antibiotic duration for hospitalized patients with suspected sepsis
2024-12-09
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/About The Study: In hospitalized adults, daily procalcitonin -guided protocol reduced antibiotic duration safely compared with standard care, but daily C-reactive protein -guided protocol does not. All-cause mortality for C-reactive protein was inconclusive.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paul Dark, MD, PhD, email adaptsepsistrial@warwick.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.26458)
Editor’s ...
American Meteorological Society announces Alan Sealls as 2025 President-Elect
2024-12-09
Members of the American Meteorological Society (AMS) have elected Alan Sealls to the position of AMS president-elect for 2025. Sealls is an AMS Fellow and Certified Broadcast Meteorologist who retired this year from a 37-year broadcast career, which included serving as chief meteorologist at WPMI-TV in Mobile, Alabama. He will be inducted as president-elect on Sunday, 12 January, 2025, during the 105th AMS Annual Meeting in New Orleans, Louisiana.
At the meeting, the AMS—the professional society for weather, water, and climate sciences ...
Dogs use two-word button combos to communicate
2024-12-09
A new study from UC San Diego’s Comparative Cognition Lab shows that dogs trained to use soundboards to “talk” are capable of making two-word button combinations that go beyond random behavior or simple imitation of their owners. Published in the journal Scientific Reports from Springer Nature, the study analyzed data from 152 dogs over 21 months, capturing more than 260,000 button presses – 195,000 of which were made by the dogs themselves.
“This is the first scientific study to analyze how dogs actually use soundboards,” said lead researcher Federico Rossano, associate professor of cognitive science at UC San Diego and director ...
Researchers use a powerful imaging technique to illuminate the colorful plumage of birds
2024-12-09
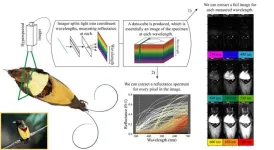
Animals showcase a remarkable diversity of colors and patterns, from the shimmery appearance of a peacock’s tail to the distinctive rosettes on a jaguar’s fur. Quantifying animal color has been a longtime goal of evolutionary biologists, who aim to understand how color evolved over time—and the physical and genetic mechanisms involved. Ultimately, studying animal color is important because it can reveal how evolutionary forces, such as natural and sexual selection, favor certain traits over others. However, fully capturing animal color is challenging because researchers must choose between high spatial resolution (as in traditional ...
Jabuticaba peel improves nutritional characteristics of bread
2024-12-09
Researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state, Brazil, have developed a sourdough bread formulation enriched with jabuticaba peel that could be an alternative for people with diabetes and others who need to control blood sugar. An article describing their research and test results is published in the journal Foods.
As noted in the article, the high carbohydrate content of bread can sharply raise blood sugar levels, risking hyperglycemia. Given the high demand for healthier bread, which is widely consumed, artisanal bakers seek to diversify their products with formulations that add nutritional value while involving fermentation ...
Department of Energy announces $36 million for student traineeships
2024-12-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced 29 projects totaling $36 million to 42 institutions in 16 states for traineeships for undergraduate students, graduate students, and postdoctoral researchers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). The funding, through the DOE Office of Science’s RENEW initiative, will support hands-on research experience, professional development activities to build or reinforce STEM identity, and mentorship to support personal and professional growth of trainees.
“The RENEW program provides new entry points to science for ...
Employee visits to adult or gambling sites doubles risk of infection by malware
2024-12-09
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 9, 2024 – Malware (malicious software) is a worldwide threat to network security for organizations. Individual users within those networks may inadvertently download or interact with malware like viruses and ransomware by browsing unsafe websites, downloading software, or clicking on phishing links in emails.
Cybersecurity researchers from the University of Trento and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam and the global cybersecurity firm Trend Micro wondered what behaviors bring the greatest risk of malware infection: working at night, browsing adult content, gambling, having a lot of software installed or just visiting strange places?
The ...