(Press-News.org)
As the first line against microbial infections or endogenous cellular damage in our body, the innate immune system utilizes NLRs (NOD-like receptors) to sense the molecules triggering microbial infection and damage, thus ensuring the proper immune response function. In the NLRs family, NLRP3 is the most characterized member, and its overactivation can lead to excessive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, driving pathological processes in various inflammatory diseases.
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Dec 10, 2024 --- Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, today announced the nomination of ISM8969, an orally available NLRP3 inhibitor as pre-clinical candidate. Powered by Insilico’s proprietary Pharma.AI platform, the BBB (blood-brain barrier) penetrable molecule was designed as a potential treatment of various inflammation-related diseases, including gout flare, asthma, Crohn’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy.
NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3) is essential for identifying microbial infections and damage, which forms a multimolecular complex known as the inflammasome to trigger an innate immune cascade upon activation. By inhibiting NLRP3, it is possible to modulate the inflammatory response, so as to prevent tissue damage, leading to the suppression of IL-1β and IL-18 release, as well as a reduction in pyroptotic cell death. However, no current FDA-approved drugs specifically target NLRP3, calling for further research in the area.
“The need of patients has been driving our portfolio management decisions, and chronic diseases including inflammation-related disorders have attracted our attention with the massive population worldwide,” says Feng Ren, PhD, Co-CEO and Chief Scientific Officer of Insilico Medicine. “We are thrilled to take another step forward in the area of inflammation disease intervention. Leveraging our AI-driven platform has already demonstrated promising results, and we look forward to utilizing AI better for the benefit of patients.”
In preclinical evaluation studies, ISM8969 exhibited a balanced druggability profile, with promising in vitro activity and safety, favorable in vivo PK/PD (pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic) profile, as well as efficacy against inflammation in multiple mouse disease models, including acute inflammatory disease and chronic disease models.
Unlike certain peripheral-restricted candidates currently in the clinical stage also targeting NLRP3, ISM8969 has a desired BBB penetrable property, enabling the drug candidate to cross the natural protective membrane between CNS (central nervous system) and the blood stream, and providing the possibility to treat neuroinflammation-related diseases. The Insilico research and development team is working on the evaluation of ISM8969 in various neurological disease models.
“Chronic inflammation is closely linked to aging and a host of other serious health conditions, attaching even more importance to the fight against it,” says Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine. “It is exciting to see that AI has been accelerating the R&D process, giving more opportunities for a better shot at high-quality drugs. At Insilico, indication expansion research is ongoing for ISM8969, and we hope to see more proof-of-concept cases coming with the power of AI.”
In 2016, Insilico first described the concept of using generative AI for the design of novel molecules in a peer-reviewed journal, which laid the foundation for the commercially available Pharma.AI platform. Since then, Insilico keeps integrating technical breakthroughs into Pharma.AI platform, which is currently a generative AI-powered solution spanning across biology, chemistry, medicine development and science research. Powered by Pharma.AI, Insilico has nominated 21 preclinical candidates in its comprehensive portfolio of over 30 assets since 2021 and has received IND clearance for 10 molecules.
In early 2024, Insilico published a Nature Biotechnology paper presenting the entire R&D journey from AI algorithms to Phase II clinical trials of ISM001-055, the company's lead drug pipeline with AI-discovered target and AI-designed structure. Following that, Insilico has recently announced positive preliminary results from a Phase IIa trial (NCT05938920), where ISM001-055 showed favorable safety and tolerability across all dose levels, as well as dose-dependent response in forced vital capacity (FVC), after only 12 weeks of dosage.
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a global clinical stage biotechnology company powered by generative AI, is connecting biology, chemistry and clinical trials analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers and other modern machine learning techniques for novel target discovery and the generation of novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine is developing breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and aging-related diseases.
www.insilico.com
END
SAN FRANCISCO — FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
PLOS has been awarded a $3.3million grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, underscoring its commitment to pioneer a shift away from traditional publishing models. The 3-year funding package from the Gates Foundation will support PLOS’ transition towards APC-free publishing by enabling authors, funded by the foundation, to publish with PLOS without facing APC barriers, and to contribute to open access publishing options for authors who do not have access to funding. This 3-year grant offers support while PLOS is actively working on new publishing models grounded in open science starting with ...
Background and Aims
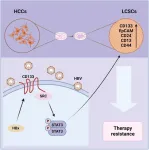
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumorigenesis, drug resistance, and recurrence, although the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Recent studies suggest that HBV infection may be associated with liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs), but the exact mechanisms are yet to be resolved. In this study, we aimed to analyze the role of HBV infection in regulating the stemness of HCCs, which is closely linked to drug resistance.
Methods
Sphere formation assay and real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction quantification were used to ...
Rockville, MD – December 10, 2024 –The American Society for Nutrition (ASN) applauds the release of the Scientific Report of the 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC). The Society is pleased to note that 19 of the 20 Committee members are ASN members, including the Chair, ASN President Sarah Booth, and Vice Chair, Angela Odoms-Young, a member of the ASN Board of Directors. The DGAC is an independent panel of nutrition science experts tasked to review the state of the evidence on nutrition-related topics and scientific questions identified by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) ...
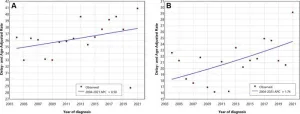
OAK BROOK, Ill. – The number of women with late-stage, invasive breast cancer at the time of diagnosis increased significantly among U.S. women across all ages and ethnicities between 2004 and 2021, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
In the study, researchers analyzed the latest available Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data on annual stage-specific breast cancer incidence rates between 2004 and 2021. SEER data is collected from 22 population-based ...
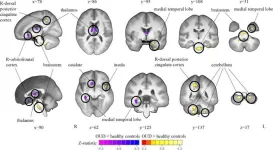
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers at the Yale School of Medicine found structural and functional alterations in specific brain regions of individuals with opioid use disorder. The study’s results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Opioids are a class of drugs that include synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, prescription pain relievers like oxycodone, and illegal narcotics, including heroin. Opioids have a high potential for misuse, and opioid use is a major contributor to drug overdoses in the ...
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
EMBARGOED FOR PUBLICATION UNTIL TUESDAY, DEC. 10, AT 10 A.M. ET
TAMPA, Fla. (Embargoed until Dec. 10, 2024) – Colorectal cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, may be fueled by the food on our plates. Researchers at the University of South Florida and Tampa General Hospital Cancer Institute have uncovered a potential link between the Western diet – dominated by ultra-processed foods and unhealthy oils – and the chronic inflammation that drives ...
Polymer scientist Gary E. Wnek and stem-cell biologist Arnold Caplan have been named Fellows of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors.
The two Case Western Reserve University faculty members will be inducted June 26 at the NAI’s 14th annual conference in Atlanta. Caplan, who was nominated in 2023, died in January. The NAI said his family will be invited to accept the medal in his honor.
The NAI Fellows Program was established “to highlight academic ...
UCSF scientists combine a precision drug therapy with an antibody and radiation to eliminate tumors without causing side effects.
Radiation is one of the most effective ways to kill a tumor. But these therapies are indiscriminate, and they can damage healthy tissues.
Now, UC San Francisco scientists have developed a way to deliver radiation just to cancerous cells. The therapy combines a drug to mark the cancer cells for destruction and a radioactive antibody to kill them.
It wiped out bladder and lung tumors in mice ...
A massive cleanup of derelict fishing gear in U.S. coastal waters is set to begin now that William & Mary’s Batten School & VIMS has awarded $1.4 million to fund 11 projects under the National Fishing Trap Removal, Assessment, and Prevention (TRAP) Program. From diving in waters up to 130 feet deep to retrieve lobster and crab traps in protected ecosystems to the removal of debris in tribal fishing grounds, this initial round of projects facilitates removal efforts in California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, ...
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL Dec. 10, 2024, AT 10AM EST) – New research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine suggests that one’s biological age, which can be higher than his or her chronological age – a concept called accelerated aging – may predict who’s at risk for developing colon polyps, a known risk factor for colorectal cancer.
The findings, published in Cancer Prevention Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, link accelerated aging to increased early colorectal cancer ...