(Press-News.org) Weill Cornell Medicine has received a $1.4 million, four-year grant from the U.S. Department of Defense to investigate a new therapeutic approach for the most common form of kidney cancer.
The grant is one of 10 Idea Awards the department funded this year to support innovative, high-risk, high-reward science that could lead to a paradigm shift in cancer care. The funding will enable principal investigators Dr. Lorraine Gudas and Dr. David Nanus to explore a cellular reprogramming strategy that may improve how patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) respond to a form of immunotherapy, called checkpoint inhibitors. Checkpoint inhibitors remove the brakes on T cells, which are a part of the immune system that help fight infection. This allows the T cells to attack cancer cells much like they attack bacteria and viruses.
Kidney cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers, striking nearly 82,000 Americans each year, according to the National Cancer Institute, and killing more than 14,000. Roughly 8 in 10 of those diagnoses is for clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
“We believe this work could completely change the way kidney cancer is treated,” said Dr. Nanus, the Mark W. Pasmantier Professor of Hematology and Oncology in Medicine and associate director of network integration at the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine. “Today, while checkpoint inhibitors are showing significant treatment benefits for a wide variety of cancers including kidney cancer, most patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma will become treatment resistant and ultimately die of their disease.”
One current treatment approach for many cancer types is an immunotherapy called chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T cell) therapy, which works by removing immune T cells from the body and genetically engineering them to recognize cancer cells based on the antigens they express. The T cells are then infused back into the patient to trigger an anti-tumor response. This approach has not been successful in patients with kidney cancer.
With this grant, the investigators will study an alternative approach: Rather than infusing patients with CAR-T cells, Dr. Gudas and Dr. Nanus will work to reprogram kidney cancer cells to become like immune cells called dendritic cells. These antigen-presenting cells can then train the immune system to target and kill the cancer. They hope that reprogramming the cells, combined with checkpoint inhibitors, can lead to a more effective immune response than what CAR T cell therapy can generate.
“These dendritic-like reprogrammed tumor cells will help to kill the other tumor cells around them, in part by bringing to the tumor T cells that are already in the patient,” said Dr. Gudas, chair of the Department of Pharmacology and the Revlon Pharmaceutical Professor of Pharmacology and Toxicology at Weill Cornell Medicine. “We only need to reprogram a tiny portion of the tumor cell population into dendritic cells to make this treatment strategy successful. “
The researchers plan to use a harmless adenovirus to deliver three genes encoding the proteins necessary to turn the tumor cells into dendritic-like cells. The makeshift dendritic cells can then capture proteins from tumor cells and present them to T cells, which are activated to kill tumor cells. These include cytotoxic T cells or “killer T cells” that destroy tumor cells and memory T cells that act as long-term immune surveillance, staying within the tumor site to recognize and attack future cancer cells.
“It's years away from being in patients, but I think that the concept will be fairly easy to test pre-clinically,” said Dr. Nanus, who is an oncologist and director of the NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center Healthcare Systems Cancer Program. “And since other people are doing similar work on other tumor types, it's something that could be the beginning of a whole new approach to immunotherapy in cancer.”
END
Finding innovative ways to address kidney cancer leads to DoD grant
2024-12-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Americans are uninformed about and undervaccinated for HPV
2024-12-10
LOS ANGELES — The human papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted infection, accounts for 70% of all throat cancers, according to the National Cancer Institute. While commonly associated with cervical cancer, throat cancer is now the most common type of HPV-related cancer.
However, the majority of American adults are unaware that HPV can cause throat cancer and are not taking advantage of the one proven method for prevention — the HPV vaccine.
These are the conclusions of two recent studies from the USC Head and Neck Center, part of Keck Medicine of USC and the USC Caruso Department of Otolaryngology – ...
KTU scientists developed a nanolaser: silver nanocubes enable light generation
2024-12-10
Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania researchers and scientists from Japan have developed a unique nanolaser. Although the dimensions of this laser are so small that its structure can only be seen through a powerful microscope, its potential is vast. With applications in early medical diagnostics, data communication, and security technologies, this invention could also become a key tool for the study of light and matter interactions.
Depending on the application, lasers differ in the way light is amplified and produced, which determines the colour of the radiation and the quality of the laser ...
Insilico Medicine nominates orally available pre-clinical candidate targeting NLRP3 to treat inflammation and central nervous system diseases
2024-12-10
As the first line against microbial infections or endogenous cellular damage in our body, the innate immune system utilizes NLRs (NOD-like receptors) to sense the molecules triggering microbial infection and damage, thus ensuring the proper immune response function. In the NLRs family, NLRP3 is the most characterized member, and its overactivation can lead to excessive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, driving pathological processes in various inflammatory diseases.
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Dec 10, 2024 --- Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery ...
PLOS receives $3.3 million grant to support Open Access publishing & business model transformation
2024-12-10
SAN FRANCISCO — FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
PLOS has been awarded a $3.3million grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, underscoring its commitment to pioneer a shift away from traditional publishing models. The 3-year funding package from the Gates Foundation will support PLOS’ transition towards APC-free publishing by enabling authors, funded by the foundation, to publish with PLOS without facing APC barriers, and to contribute to open access publishing options for authors who do not have access to funding. This 3-year grant offers support while PLOS is actively working on new publishing models grounded in open science starting with ...
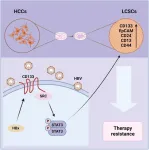
HBx facilitates drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via CD133-regulated self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells
2024-12-10
Background and Aims
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumorigenesis, drug resistance, and recurrence, although the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Recent studies suggest that HBV infection may be associated with liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs), but the exact mechanisms are yet to be resolved. In this study, we aimed to analyze the role of HBV infection in regulating the stemness of HCCs, which is closely linked to drug resistance.
Methods
Sphere formation assay and real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction quantification were used to ...
ASN congratulates members for their role in the development of the Scientific Report of the 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee
2024-12-10
Rockville, MD – December 10, 2024 –The American Society for Nutrition (ASN) applauds the release of the Scientific Report of the 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC). The Society is pleased to note that 19 of the 20 Committee members are ASN members, including the Chair, ASN President Sarah Booth, and Vice Chair, Angela Odoms-Young, a member of the ASN Board of Directors. The DGAC is an independent panel of nutrition science experts tasked to review the state of the evidence on nutrition-related topics and scientific questions identified by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) ...
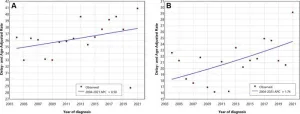
Late-stage breast cancer diagnosis on the rise in US
2024-12-10
OAK BROOK, Ill. – The number of women with late-stage, invasive breast cancer at the time of diagnosis increased significantly among U.S. women across all ages and ethnicities between 2004 and 2021, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
In the study, researchers analyzed the latest available Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data on annual stage-specific breast cancer incidence rates between 2004 and 2021. SEER data is collected from 22 population-based ...
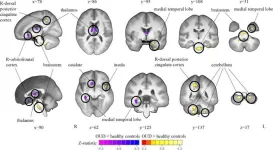
Brain volume changes seen in opioid users
2024-12-10
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers at the Yale School of Medicine found structural and functional alterations in specific brain regions of individuals with opioid use disorder. The study’s results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Opioids are a class of drugs that include synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, prescription pain relievers like oxycodone, and illegal narcotics, including heroin. Opioids have a high potential for misuse, and opioid use is a major contributor to drug overdoses in the ...
Ultra-processed foods may drive colorectal cancer risk, USF-TGH study finds
2024-12-10
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
EMBARGOED FOR PUBLICATION UNTIL TUESDAY, DEC. 10, AT 10 A.M. ET
TAMPA, Fla. (Embargoed until Dec. 10, 2024) – Colorectal cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, may be fueled by the food on our plates. Researchers at the University of South Florida and Tampa General Hospital Cancer Institute have uncovered a potential link between the Western diet – dominated by ultra-processed foods and unhealthy oils – and the chronic inflammation that drives ...
Two Case Western Reserve University faculty members honored as Fellows of the National Academy of Inventors
2024-12-10
Polymer scientist Gary E. Wnek and stem-cell biologist Arnold Caplan have been named Fellows of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors.
The two Case Western Reserve University faculty members will be inducted June 26 at the NAI’s 14th annual conference in Atlanta. Caplan, who was nominated in 2023, died in January. The NAI said his family will be invited to accept the medal in his honor.
The NAI Fellows Program was established “to highlight academic ...