(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study identifies growing healthspan (years lived in good health)-lifespan gaps around the globe, threatening healthy longevity across worldwide populations. Women globally exhibited a larger healthspan-lifespan gap than men.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Andre Terzic, MD, PhD, email terzic.andre@mayo.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.50241)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.50241?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=121124
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Global healthspan-lifespan gaps among 183 WHO member states
JAMA Network Open
2024-12-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stanford scientists transform ubiquitous skin bacterium into a topical vaccine
2024-12-11
Imagine a world in which a vaccine is a cream you rub onto your skin instead of a needle a health care worker pushes into your one of your muscles. Even better, it’s entirely pain-free and not followed by fever, swelling, redness or a sore arm. No standing in a long line to get it. Plus, it’s cheap.
Thanks to Stanford University researchers’ domestication of a bacterial species that hangs out on the skin of close to everyone on Earth, that vision could become a reality.
“We all hate needles — everybody does,” said Michael Fischbach, PhD, the Liu (Liao) Family Professor and a professor of bioengineering. “I haven’t found a single person ...
Biological diversity is not just the result of genes
2024-12-11
How can we explain the morphological diversity of living organisms? Although genetics is the answer that typically springs to mind, it is not the only explanation. By combining observations of embryonic development, advanced microscopy, and cutting-edge computer modelling, a multi-disciplinary team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) demonstrate that the crocodile head scales emerge from the mechanics of growing tissues, rather than molecular genetics. The diversity of these head scales observed in different crocodilian species therefore arises from the evolution of mechanical parameters, such as the growth ...
Analysis reveals an additional mechanism behind statin therapy’s heart-related benefits in people with HIV
2024-12-11
Investigators who previously found that a daily statin pill helps prevent heart attacks and strokes in people with HIV have now discovered a potential mechanism that may help to stabilize plaques and prevent their rupture in blood vessels. The research led by a team from Mass General Brigham is published in JAMA Cardiology.
“Individuals with HIV tend to have an excess of noncalcified plaques that are vulnerable to rupture at a younger age, putting them at high risk for strokes, heart attacks, and sudden cardiac death,” said senior author Steven Grinspoon, MD, chief of the Metabolism Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare ...
Understanding how the immune system switches between rest and action
2024-12-11
SAN FRANCISCO—Cells in the immune system don’t always fight; they often rest and wait for threats, like viruses or bacteria. When such threats emerge, the cells activate to defend the body. This delicate balance between rest and activation is crucial to our health—immune cells must be poised for activation to protect against threats, but if they’re overly active, autoimmune diseases can result.
But what controls this important balance?
In a new study published in Nature, scientists from Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco ...
Wiley expands its KnowItAll solutions with new tools for LC-MS analysis, enterprise data management, and additional spectral advances
2024-12-11
HOBOKEN, N.J.—Wiley, one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in research and learning, today announced the release of the new version of its KnowItAll software, with numerous advances to accelerate spectral analysis and optimize workflows.
KnowItAll 2025, the latest version of Wiley’s comprehensive software suite for spectral analysis and analytical data management, introduces a groundbreaking new tool to automate LC-MS analysis, enhanced data management, and numerous other features to streamline analysis across multiple ...
A new class of antivirals could help prevent future pandemics
2024-12-11
The arrival of Paxlovid in December 2021 marked another turning point in the COVID-19 pandemic—an effective antiviral that has since successfully treated millions. But like many antivirals before it, scientists know that at some point, Paxlovid is likely to lose some efficacy due to drug resistance. Researchers working to stay ahead of such emerging threats have now identified a wholly new way to treat SARS-CoV-2 infections—work that may have even broader implications.
In fact, a new study by the Tuschl ...
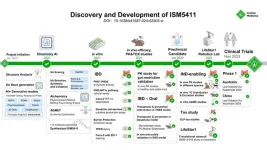
Nature Biotechnology | Generative chemistry enables Insilico to develop gut-restricted PhD inhibitors promising for intestinal mucosal barrier repair and immunomodulation
2024-12-11
The study presents the journey of designing and optimizing novel gut-restricted PHD inhibitors using the comprehensive generative chemistry engine Chemistry42.
From initiation to preclinical candidate nomination, the program spanned only 12 months, during which approximately 115 molecules were synthesized and screened.
Preclinical studies demonstrate ISM5411 to be gut-restricted and PHD-specific, thus reducing cardiovascular and systematical tumorigenic risks.
Two Phase 1 clinical trials of ISM5411 for IBD are currently being conducted in parallel in Australia and China, with the last subject out in both ...
2 U-M faculty members elected to National Academy of Inventors
2024-12-11
ANN ARBOR—Two University of Michigan faculty members have been elected to the National Academy of Inventors, the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors.
Robert Bartlett, professor emeritus of surgery at the Medical School, and Zhen Xu, professor of biomedical engineering at the College of Engineering and professor of radiology and neurosurgery at the Medical School, were elected this month to the academy.
Bartlett and Xu were nominated for being innovative researchers with extensive work translating discoveries into ...
Breakthroughs in cell-penetrating monoclonal antibody therapies
2024-12-11
“Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) have emerged as a promising tool in advancing personalized medicine.”
BUFFALO, NY – December 11, 2024 – A news feature on the research paper “Next-generation cell-penetrating antibodies for tumor targeting and RAD51 inhibition” by Rackear et al. was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on November 22, 2024, titled “Advancements in cell-penetrating monoclonal antibody treatment.“
This new publication by Sai Pallavi Pradeep and Raman Bahal from the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of Connecticut highlights significant advancements in ...
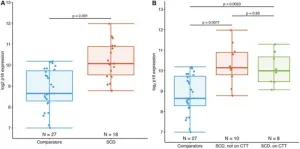
Accelerated aging in young sickle cell patients linked to elevated T-cell p16INK4a
2024-12-11
“These initial results suggest that individuals with SCD have a significantly higher cellular senescence burden which may contribute to premature aging, physiological decline, and excess morbidities.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 11, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 14, 2024, entitled, “Adolescents and young adults with sickle cell disease exhibit accelerated aging with elevated T-cell p16INK4a expression.”
Researchers Samuel R. Wilson, Natalia Mitin, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] Global healthspan-lifespan gaps among 183 WHO member statesJAMA Network Open