(Press-News.org) HOBOKEN, N.J.—Wiley, one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in research and learning, today announced the release of the new version of its KnowItAll software, with numerous advances to accelerate spectral analysis and optimize workflows.
KnowItAll 2025, the latest version of Wiley’s comprehensive software suite for spectral analysis and analytical data management, introduces a groundbreaking new tool to automate LC-MS analysis, enhanced data management, and numerous other features to streamline analysis across multiple spectral techniques.
“Access to automated solutions and comprehensive datasets is critical to laboratories’ analytical success,” said Graeme Whitley, director of data science solutions at Wiley. “KnowItAll 2025 represents a major advancement in our mission to broaden these tools for the scientific community, with the introduction of a new tool that makes LC-MS analysis accessible to a broader audience of researchers.”
With KnowItAll’s new LC Expert users can now transform raw chromatograms into component identifications with a single click. Powered by Wiley’s comprehensive, high-quality database collections, LC Expert takes automated non-targeted and targeted spectral identification to the next level.
Additional benefits of KnowItAll 2025 include:
New comprehensive LC-MS libraries: Users can access up to 5M+ spectra depending on the databases they choose:
The new KnowItAll LC-MS Library collection provides access to over 2.7 million spectra.
Includes: Wiley Registry of Tandem Mass Spectral Data, as well as Class-Rule Based Lipids, PFAS, and Polymer Libraries
The following databases are also now available in KnowItAll format:
Maurer, Meyer, Helfer, Weber: LC-HR-MS/MS Library of Drugs, Poisons, and Their Metabolites (5K+ spectra)
Maurer, Wissenbach, Weber: LC-MSn Library of Drugs, Poisons, and Their Metabolites, 2nd Edition (13K+ spectra)
NIST MS/MS Library (2.3M+ spectra) – available in KnowItAll bundles
KnowItAll Data Control: Integrate access and version control into workflows to collaborate, develop, and secure shared analytical databases throughout an organization
Streamlined GC-MS workflow: Automatic deconvolution, peak picking, and manual analysis are now combined into one unified application
KnowItAll drug classification models: Designed to help forensics laboratories classify novel compounds, as drugs continue to be synthesized faster than reference data can be produced
New Raman processing algorithms: Fluorescence corrections and cosmic ray removal now available
Additional enhancements: NMR tools expanded to support X-NMR, easier chemical drawing using pre-defined substituents, and many more
KnowItAll provides a unified, vendor neutral software solution to identify, analyze, and manage analytical data (IR, GC-MS, LC-MS, NMR, Raman, and UV-Vis). Combined with Wiley’s comprehensive, high-quality spectral reference libraries, it provides an unparalleled solution for fast, reliable spectral analysis.
To learn more about Wiley Science Solutions, visit: www.sciencesolutions.wiley.com
About Wiley
Wiley (NYSE: WLY) is one of the world’s largest publishers and a trusted leader in research and learning. Our industry-leading content, services, platforms, and knowledge networks are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our customers and partners, including researchers, students, instructors, professionals, institutions, and corporations. We empower knowledge-seekers to transform today’s biggest obstacles into tomorrow’s brightest opportunities. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X (Twitter), LinkedIn and Instagram.
###
Contact: Ed Colby / edcolby@wiley.com
END
The arrival of Paxlovid in December 2021 marked another turning point in the COVID-19 pandemic—an effective antiviral that has since successfully treated millions. But like many antivirals before it, scientists know that at some point, Paxlovid is likely to lose some efficacy due to drug resistance. Researchers working to stay ahead of such emerging threats have now identified a wholly new way to treat SARS-CoV-2 infections—work that may have even broader implications.
In fact, a new study by the Tuschl ...
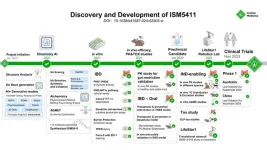
The study presents the journey of designing and optimizing novel gut-restricted PHD inhibitors using the comprehensive generative chemistry engine Chemistry42.
From initiation to preclinical candidate nomination, the program spanned only 12 months, during which approximately 115 molecules were synthesized and screened.
Preclinical studies demonstrate ISM5411 to be gut-restricted and PHD-specific, thus reducing cardiovascular and systematical tumorigenic risks.
Two Phase 1 clinical trials of ISM5411 for IBD are currently being conducted in parallel in Australia and China, with the last subject out in both ...
ANN ARBOR—Two University of Michigan faculty members have been elected to the National Academy of Inventors, the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors.
Robert Bartlett, professor emeritus of surgery at the Medical School, and Zhen Xu, professor of biomedical engineering at the College of Engineering and professor of radiology and neurosurgery at the Medical School, were elected this month to the academy.
Bartlett and Xu were nominated for being innovative researchers with extensive work translating discoveries into ...
“Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) have emerged as a promising tool in advancing personalized medicine.”
BUFFALO, NY – December 11, 2024 – A news feature on the research paper “Next-generation cell-penetrating antibodies for tumor targeting and RAD51 inhibition” by Rackear et al. was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on November 22, 2024, titled “Advancements in cell-penetrating monoclonal antibody treatment.“
This new publication by Sai Pallavi Pradeep and Raman Bahal from the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of Connecticut highlights significant advancements in ...
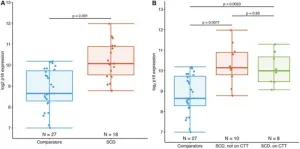
“These initial results suggest that individuals with SCD have a significantly higher cellular senescence burden which may contribute to premature aging, physiological decline, and excess morbidities.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 11, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 14, 2024, entitled, “Adolescents and young adults with sickle cell disease exhibit accelerated aging with elevated T-cell p16INK4a expression.”
Researchers Samuel R. Wilson, Natalia Mitin, ...
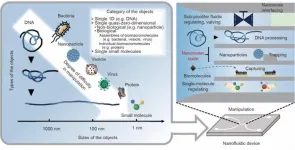
One of the great ambitions in the scientific world is to use tiny objects—such as molecules, viruses, and nanoparticles—as building blocks to construct essential macromolecules and materials, much like constructing intricate designs with LEGO bricks. However, achieving this requires overcoming significant challenges. Molecules in liquid environments move randomly and at extraordinary speeds—approximately many times faster than Usain Bolt at peak velocity—making precise manipulation extraordinarily challenging.
To ...
Advancing the energy transition requires more than just technological innovation – it demands a joint effort between public and private actors. Giovanna Pinilla De La Cruz’s doctoral dissertation at the University of Vaasa, Finland, explores the mechanisms that foster collaboration in the energy sector, highlighting the Vaasa region’s energy cluster as a successful example.
The transition to sustainable energy systems is one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Successfully navigating this transition requires coordinated ...
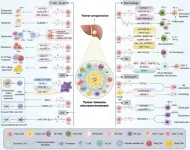
The TIME is a dynamic network composed of cancer cells, immune cells, and stromal components. During the early stages of tumorigenesis, the TIME attempts to eliminate abnormal cells through immune surveillance. However, as tumors evolve, they exploit the TIME to evade immune responses and promote tumor progression. Exosomes play a central role in this transformation by transporting bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, thereby influencing processes like immune escape, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
HCC is particularly adept ...
(Toronto, December 11, 2024) JMIR Publications is proud to announce that JMIR Aging has been accepted for inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) and the Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI).
This accomplishment follows a selective re-evaluation process, where a limited number of Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI) journals were considered for inclusion. To be eligible, journals needed to rank among the top three in their respective categories based on the latest Journal Citation Reports (JCR) data. JMIR Aging’s acceptance into SCIE and SSCI underscores its exceptional quality and impact, demonstrated by its outstanding performance ...
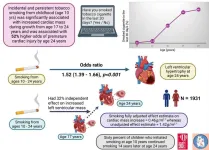
The majority of children who started smoking tobacco at age 10 years or in their later teens continued to smoke until their mid-twenties. Continuous smoking from childhood significantly increased the risk of premature heart damage, a new study shows. The study was conducted in collaboration between the Universities of Bristol and Exeter in the UK, and the University of Eastern Finland, and the results were published in the prestigious Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
In the present study, 1,931 children drawn from the University of Bristol’s Children of the 90s cohort were followed up from age 10 until 24 years. ...