(Press-News.org) Investigators who previously found that a daily statin pill helps prevent heart attacks and strokes in people with HIV have now discovered a potential mechanism that may help to stabilize plaques and prevent their rupture in blood vessels. The research led by a team from Mass General Brigham is published in JAMA Cardiology.
“Individuals with HIV tend to have an excess of noncalcified plaques that are vulnerable to rupture at a younger age, putting them at high risk for strokes, heart attacks, and sudden cardiac death,” said senior author Steven Grinspoon, MD, chief of the Metabolism Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. “Understanding how statins benefit this population could lead to additional and more targeted therapies to protect their cardiovascular health.”
The work is a secondary analysis of the phase 3 Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV (REPRIEVE), which demonstrated that the cholesterol-lowering medication pitavastatin reduced the risk of adverse cardiovascular events by 36% over a median follow-up of 5.6 years in people with HIV. The effect was greater than what would be expected from cholesterol lowering alone.
In this latest research, Grinspoon and his colleagues measured the levels of 255 different proteins circulating in the blood of 558 REPRIEVE participants. Analyses revealed that pitavastatin treatment increases the levels of an enzyme called procollagen C-endopeptidases enhancer 1 (PCOLCE) that is involved in the production of collagen that may help to stabilize vulnerable plaques during atherosclerosis buildup. Additional experiments showed that an abundance of PCOLCE was associated with reduced noncalcified plaques and, simultaneously, with more fibrous stabilized plaques. These effects, occurring with simultaneous reduction in lipid content of blood vessel plaques, may help to keep the plaques from rupturing.
“By showing that statins raise PCOLCE, which is associated with favorable changes in plaques, our findings expand our knowledge about how the benefits of statins go beyond cholesterol lowering,” said Grinspoon. “Although additional research is needed, these findings are potentially generalizable to individuals without HIV.”
Authorship: In addition, to Grinspoon, Mass General Brigham authors include Márton Kolossváry, Samuel R. Schnittman, Markella V. Zanni, Kathleen V. Fitch, Marissa R. Diggs Murat Centinbas, Ruslan Sadreyev, Jana Taron, Borek Foldyna, Thomas Mayrhofer, Julia Karady, and Michael T. Lu.
Disclosures: Grinspoon reported receiving grants from the NIH, Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, Gilead Sciences, and ViiV Healthcare and advisory board fees from Theratechnologies, ViiV Healthcare, and Marathon Asset Management outside the submitted work. Additional author disclosures can be found in the paper.
Funding: National Institutes of Health (U01HL123336 and 1UG3HL164285, U01HL123339 1U24HL164284, T32 AI007387), Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, Gilead Sciences, ViiV Healthcare, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (UM1 AI068636, UM1 AI10670). Grinspoon reported receiving support from the Nutrition Obesity Research Center at Harvard (P30DK040561).
Paper cited: Kolossváry Met al. “Pitavastatin, Procollagen Pathways, and Plaque Stabilization in Patients With HIV” JAMA Cardiology DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2024.4115
###
About Mass General Brigham
Mass General Brigham is an integrated academic health care system, uniting great minds to solve the hardest problems in medicine for our communities and the world. Mass General Brigham connects a full continuum of care across a system of academic medical centers, community and specialty hospitals, a health insurance plan, physician networks, community health centers, home care, and long-term care services. Mass General Brigham is a nonprofit organization committed to patient care, research, teaching, and service to the community. In addition, Mass General Brigham is one of the nation’s leading biomedical research organizations with several Harvard Medical School teaching hospitals. For more information, please visit massgeneralbrigham.org.
END
SAN FRANCISCO—Cells in the immune system don’t always fight; they often rest and wait for threats, like viruses or bacteria. When such threats emerge, the cells activate to defend the body. This delicate balance between rest and activation is crucial to our health—immune cells must be poised for activation to protect against threats, but if they’re overly active, autoimmune diseases can result.
But what controls this important balance?
In a new study published in Nature, scientists from Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco ...
HOBOKEN, N.J.—Wiley, one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in research and learning, today announced the release of the new version of its KnowItAll software, with numerous advances to accelerate spectral analysis and optimize workflows.
KnowItAll 2025, the latest version of Wiley’s comprehensive software suite for spectral analysis and analytical data management, introduces a groundbreaking new tool to automate LC-MS analysis, enhanced data management, and numerous other features to streamline analysis across multiple ...
The arrival of Paxlovid in December 2021 marked another turning point in the COVID-19 pandemic—an effective antiviral that has since successfully treated millions. But like many antivirals before it, scientists know that at some point, Paxlovid is likely to lose some efficacy due to drug resistance. Researchers working to stay ahead of such emerging threats have now identified a wholly new way to treat SARS-CoV-2 infections—work that may have even broader implications.
In fact, a new study by the Tuschl ...
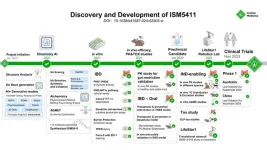
The study presents the journey of designing and optimizing novel gut-restricted PHD inhibitors using the comprehensive generative chemistry engine Chemistry42.
From initiation to preclinical candidate nomination, the program spanned only 12 months, during which approximately 115 molecules were synthesized and screened.
Preclinical studies demonstrate ISM5411 to be gut-restricted and PHD-specific, thus reducing cardiovascular and systematical tumorigenic risks.
Two Phase 1 clinical trials of ISM5411 for IBD are currently being conducted in parallel in Australia and China, with the last subject out in both ...
ANN ARBOR—Two University of Michigan faculty members have been elected to the National Academy of Inventors, the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors.
Robert Bartlett, professor emeritus of surgery at the Medical School, and Zhen Xu, professor of biomedical engineering at the College of Engineering and professor of radiology and neurosurgery at the Medical School, were elected this month to the academy.
Bartlett and Xu were nominated for being innovative researchers with extensive work translating discoveries into ...
“Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) have emerged as a promising tool in advancing personalized medicine.”
BUFFALO, NY – December 11, 2024 – A news feature on the research paper “Next-generation cell-penetrating antibodies for tumor targeting and RAD51 inhibition” by Rackear et al. was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on November 22, 2024, titled “Advancements in cell-penetrating monoclonal antibody treatment.“
This new publication by Sai Pallavi Pradeep and Raman Bahal from the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of Connecticut highlights significant advancements in ...
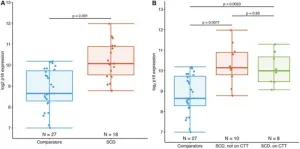
“These initial results suggest that individuals with SCD have a significantly higher cellular senescence burden which may contribute to premature aging, physiological decline, and excess morbidities.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 11, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 14, 2024, entitled, “Adolescents and young adults with sickle cell disease exhibit accelerated aging with elevated T-cell p16INK4a expression.”
Researchers Samuel R. Wilson, Natalia Mitin, ...
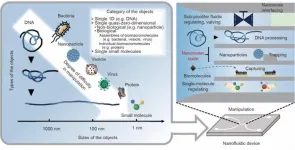
One of the great ambitions in the scientific world is to use tiny objects—such as molecules, viruses, and nanoparticles—as building blocks to construct essential macromolecules and materials, much like constructing intricate designs with LEGO bricks. However, achieving this requires overcoming significant challenges. Molecules in liquid environments move randomly and at extraordinary speeds—approximately many times faster than Usain Bolt at peak velocity—making precise manipulation extraordinarily challenging.
To ...
Advancing the energy transition requires more than just technological innovation – it demands a joint effort between public and private actors. Giovanna Pinilla De La Cruz’s doctoral dissertation at the University of Vaasa, Finland, explores the mechanisms that foster collaboration in the energy sector, highlighting the Vaasa region’s energy cluster as a successful example.
The transition to sustainable energy systems is one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Successfully navigating this transition requires coordinated ...
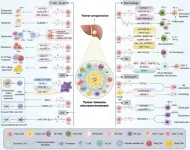
The TIME is a dynamic network composed of cancer cells, immune cells, and stromal components. During the early stages of tumorigenesis, the TIME attempts to eliminate abnormal cells through immune surveillance. However, as tumors evolve, they exploit the TIME to evade immune responses and promote tumor progression. Exosomes play a central role in this transformation by transporting bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, thereby influencing processes like immune escape, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
HCC is particularly adept ...