(Press-News.org) SPOKANE, Wash. – Adding strong evidence in support of “walkable” neighborhoods, a large national study found that the built environment can indeed increase how much people walk.
The study, published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, showed a strong connection between place and activity by studying about 11,000 twins, which helps control for family influences and genetic factors. The researchers found that each 1% increase in an area’s “walkability” resulted in 0.42% increase in neighborhood walking. When scaled up, that means a 55% increase in the walkability of the surrounding neighborhood would result in about 23% more walking—or about 19 minutes a week for every resident living in that area.
In terms of public health, that can add up to a big difference for the highly sedentary U.S. populace, according to study lead author Glen Duncan, a Washington State University nutrition and exercise physiology professor.
“We have so many people in the U.S. population who don't get sufficient activity. If we could shift the percentage of the population that just took on more plain old walking, we would see real health benefits,” said Duncan, who is also the director of the Washington State Twin Registry.
For the study, neighborhoods were deemed walkable based on an index that assesses the density of people, roads and desirable places to walk to, such as stores, parks, restaurants and coffee shops. The twin pairs in the study lived in all parts of the U.S., but the more walkable neighborhoods were typically found in urban areas.
Seattle’s Capitol Hill area is a good example of a walkable neighborhood, Duncan said, given its profusion of shops and restaurants, as well as access to public transportation such as buses and a light rail station. On the other side, more suburban or rural areas tend to be less walkable as they require driving to access things like grocery stores or other amenities.
The study analyzed data from surveys of 5,477 pairs of twins taken from 2009 to 2020 which included information about where they lived and number of minutes walked in a typical week, whether for recreation, exercise or simply to get from one place to the other. The analysis revealed that those who lived in areas considered more walkable actually did walk more.
The researchers also looked at whether an area’s walkability increased transit use, but few study participants used public transit. However, living in a walkable neighborhood reduced the chance of having no transit use at all by 32%.
Living in a walkable area didn’t appear to have an effect on more vigorous exercise, but the authors note that this kind of exercise, which includes running and lifting weights, isn’t limited to the neighborhood environment. For example, a person could go for a vigorous bike ride that would take them well outside the boundaries of their neighborhood.
Regardless, Duncan emphasized that walking is a great and easy way to improve health. It also counts toward the widely recommended 150 minutes a week of physical activity.
“You don't have to spend loads of money on fitness clothing and the best gear. Walking is a very natural thing. You just lace on some shoes and head out the door,” he said.
In addition to Duncan, co-authors on this study include researchers from the University of Washington, University of Southern California, University of Virginia, Columbia University and WSU.
END
More dense, populated neighborhoods inspire people to walk more
2024-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion
2024-12-12
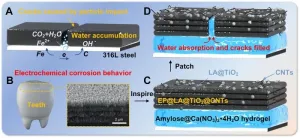
The long-term erosion and corrosion issues during the development of offshore oil and gas fields pose significant threats to the safe and efficient operation of these facilities. Superhydrophobic coatings, known for their ability to reduce interactions between corrosive substances and substrates, have garnered considerable attention. However, their poor mechanical properties often hinder their long-term application in practical working environments. To address this challenge, a research team led by Prof. Yuekun Lai from Fuzhou University and Prof. Xuewen Cao from China University of Petroleum (East China) has developed a biomimetic dental enamel coating with ...
New analytical approach revolutionizes reliability evaluation of power systems with renewable energy
2024-12-12
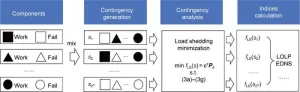
In a recent study published in Engineering, a team of researchers led by Bo Hu and Changzheng Shao from Chongqing University in China has introduced a novel method for evaluating the real-time dynamic reliability of composite power systems integrated with renewable energy sources (RES). The research addresses the challenges posed by the uncertainties associated with RES, which have been a significant obstacle in ensuring the stable and reliable operation of power grids.
The increasing integration of RES, such as wind and solar power, into the power grid has brought about concerns regarding power imbalance and load shedding due to their ...
Artificial intelligence improves mammography-based risk prediction
2024-12-12
The future of breast cancer screening and risk-reducing strategies is being shaped by artificial intelligence (AI), according to a review article published by Cell Press on December 12 in the journal Trends in Cancer.
“We discuss recent advances in AI-assisted breast cancer risk prediction, what this means for the future of breast cancer screening and prevention, and the key research needed to progress mammographic features from research into clinical practice,” says senior study author Erik Thompson of the Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia.
Breast tissue that appears white on ...
Brain tumors hijack circadian clock to grow
2024-12-12
Virtually every cell in the human body has an internal clock. These clocks take their cues from a central clock in the brain. In a normal, biological process called synchrony, the central clock coordinates daily rhythms around the body, so that every cell and tissue recognizes the same external time of day.
Knowing local time helps our bodies to regulate essential processes, including when to sleep and wake, when to eat and what temperature to maintain, among many other important functions.
But a deadly interloper is keeping time the same ...
Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for COVID-19 among children ages 5-17
2024-12-12
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that the BNT162b2 XBB vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) provided protection against COVID-19–associated hospitalization and emergency department or urgent care visits among children 5 to 17 years of age during the 2023-2024 season with estimated vaccine effectiveness point estimates ranging from 63% to 73%.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sara Y. Tartof, PhD, MPH, email Sara.Y.Tartof@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.49944)
Editor’s ...
Trends in school mental health and substance use education
2024-12-12
About The Study: From 2008-2020, teachers reported an increase in emotional/mental health and suicide prevention in schools, along with related teacher training. However, they reported a decrease in substance use prevention, particularly among middle schools, and no change in teacher training. Substance use during early adolescence is associated with risk for long-term addiction, and middle schools may be underused for prevention.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chloe Gao, BHSc, email chloe.gao@childrens.harvard.edu.
To ...
Genes that determine tooth shape identified
2024-12-12
Genetic variants that determine the shape of your teeth – including a gene inherited from Neanderthals – have been identified by a team co-led by UCL researchers.
In a new paper published in Current Biology, scientists found substantial tooth differences between ethnicities, potentially due in part to a gene inherited from Neanderthals that was only found in study participants of European origin.
Co-lead author Dr Kaustubh Adhikari (UCL Genetics, Evolution & Environment and The Open University) said: “Teeth ...
With a little help from their friends: Poll shows role of close friendships in older adults’ health
2024-12-12
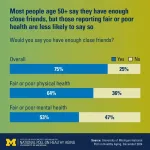
Whether they’re lifelong buddies or recently connected, close to home or miles away, a new poll shows the key role that friends play in the lives and wellbeing of adults aged 50 and older.
But it also reveals some challenges for those who have physical health or mental health issues – suggesting it may be important for them connect with existing friends or make new friends.
In all, 90% of people aged 50 and older say they have at least one close friend, and 75% say they have enough close friends, ...
Too much screen time can reduce sleep quality in preschool-age children, making behavioral problems worse
2024-12-12
Excessive screen use by preschool-age children can lead to reduced sleep quality, exacerbating problems such as poor attention, hyperactivity and unstable mood, a new study suggests.
Peer-reviewed findings published in Early Child Development and Care show how screen time is “significantly” correlated with increased hyperactive attention problems and emotional symptoms, and with decreased sleep quality.
Additionally, the research – carried out by experts in China and Canada – demonstrates how sleep quality is also extensively correlated with decreased hyperactive attention problems, emotional symptoms and peer problems.
The findings ...
Study reveals role of allele dosage in improving sweetpotato traits
2024-12-12
Sweetpotatoes are an agricultural powerhouse that feeds millions globally. However, their complex genetics make it challenging for breeders to understand and improve traits like yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content. A new study reveals insights into the significance of leveraging “allele dosages” in sweetpotato breeding practices.
“Sweetpotatoes are hexaploid, meaning they have six copies of each chromosome, unlike diploid crops like tomato or rice, which have two," explained Zhangjun Fei, a professor at the Boyce Thompson Institute and one of the study's lead authors. “This genetic ...