(Press-News.org)
A new study has shown that employees are experiencing mental and physical techno-strain due to being ‘hyperconnected’ to digital technology making it difficult for people to switch off from work.
Researchers from the University of Nottingham’s Schools of Psychology and Medicine conducted detailed interviews with employees from a range of professions and found that the cognitive and affective effort associated with constant connectivity and high work pace driven by the digital workplace is detrimental to employee wellbeing. The results have been published today in Frontiers in Organizational Psychology.
This new paper is the final part of a research project exploring the ‘dark side effects’ of digital working which include stress, overload, anxiety and fear of missing out. The results highlight an overarching theme of ‘digital workplace technology intensity’ as a result of digital workplace job demands.
The findings in this latest paper indicate a sense of burden associated with working digitally which surfaced for most participants in perceptions of overload and feelings of being overwhelmed by the proliferation of messages, applications and meetings in the digital workplace. Fear of missing out on important information and contact with colleagues also contributed to stress and strain for digital workers, as did hassles encountered when using digital technologies.
Elizabeth Marsh, ESRC PhD student from the School of Psychology led the qualitative study and said: “Digital workplaces benefit both organisations and employees, for example by enabling collaborative and flexible work. However, what we have found in our research is that there is a potential dark side to digital working, where employees can feel fatigue and strain due to being overburdened by the demands and intensity of the digital work environment. A sense of pressure to be constantly connected and keeping up with messages can make it hard to
psychologically detach from work.”
Fourteen employees were interviewed in detail and asked about their perceptions and experiences of digital workplace job demands and impacts to their health. In the analysis, the researchers explore potential underlying psychological, technological and organisational factors that may influence ways in which employees experience the digital workplace job demands.
Participants' dark side experiences were particularly shaped by a pervasive and constant state of connectivity in the digital workplace, termed "hyperconnectivity." These experiences contributed to a sense of pressure to be available and the erosion of work-life boundaries. The evidence also indicates that this hyperconnectivity has become the norm among workers post-pandemic.
Comments from interviewees included:
“[It’s] just more difficult to leave it behind when it's all online and you can kind of jump on and do work at any time of the day or night.”
“You kind of feel like you have to be there all the time. You have to be a little green light.”
“It's that pressure to respond [...] I've received an e-mail, I've gotta do this quickly because if not, someone might think “What is she doing from home?”
Elizabeth adds: “The findings underline the need for both researchers and professionals to identify, understand and mitigate the digital workplace job demands to protect the well-being of digital workers.”
The research makes practical suggestions for employers which include helping workers improve their digital skills and empowering them to manage boundaries in the digital workplace. The findings could also be used by technology departments to consider how to improve usability and accessibility of the digital workplace, as well as reining in the proliferation of applications. Understanding employees’ needs and preferences for digital working is important to inform such work.
Dr Alexa Spence, Professor of Psychology adds: “This research extends the Job Demands-Resources literature by clarifying digital workplace job demands including hyperconnectivity and overload. It also contributes a novel construct of digital workplace technology intensity which adds new insight on the causes of technostress in the digital workplace. In doing so, it highlights the potential health impacts, both mental and physical, of digital work.”
The research was funded by ESRC-MGS (Economic and Social Research Council - Midland Graduate School).
ENDS
END
Image
Adolescent drug use continued to drop in 2024, building on and extending the historically large decreases that occurred during the pandemic onset in 2020.
"I expected adolescent drug use would rebound at least partially after the large declines that took place during the pandemic onset in 2020, which were among the largest ever recorded," said Richard Miech, team lead of the Monitoring the Future study at U-M's Institute for Social Research.
"Many experts in the field had anticipated that drug use would resurge ...
NEW YORK CITY and ORLANDO— The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) and the McKnight Brain Research Foundation (MBRF) are pleased to announce the 2024 recipients of The McKnight Brain Research Foundation Innovator Awards in Cognitive Aging and Memory Loss: Janine Kwapis, PhD, of Pennsylvania State University, and Sanaz Sedaghat, PhD, of the University of Minnesota.
Now in its fourth year, the Innovator Awards provide funding to research scientists pursuing groundbreaking studies in the field of cognitive aging.
Janine Kwapis, PhD, is an Assistant Professor and Paul Berg Early Career Professor ...
Despite national medical guidelines supporting the use of antiviral medications in young children diagnosed with influenza, a recent study reports an underuse of the treatment.
“Antiviral Use Among Children Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Influenza Illness: A Prospective, Multicenter Surveillance Study” was published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, the flagship journal of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Flu illness accounts for up to 10% of all pediatric hospitalizations during ...
Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1), a member of the Ste20 serine/threonine kinases family, negatively regulates T cell function and is considered a promising target for immunotherapy. Despite the promising efficacy demonstrated in preclinical models, no HPK1 inhibitors are currently approved for clinical use, due to challenges including balance between kinase selectivity and pharmacokinetic properties.
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Dec 17, 2024 --- Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, is proud to announce its latest AI-powered ...
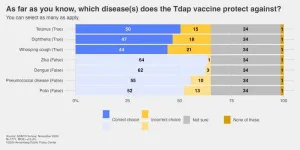
PHILADELPHIA – Following a several-year lull during the pandemic, cases of whooping cough are increasing across the United States. As of Nov. 30, early U.S. data show over 28,000 cases reported this year, or six times as many as in the same period in 2023, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Whooping cough or pertussis, a highly contagious bacterial infection of the respiratory tract, was one of the most common childhood diseases in the 20th century and a major cause ...
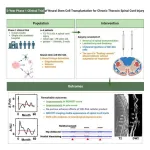
A Phase I clinical trial led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine has demonstrated the long-term safety and feasibility of neural stem cell transplantation for treating chronic spinal cord injuries. These devastating injuries often result in partial or full paralysis and are currently incurable. The study, which followed four patients with chronic spinal cord injuries for five years, found that two patients showed durable evidence of neurological improvement after treatment with neural stem cell implantation, including increased ...
The domestication of plants and animals has played a key role in the development of human societies. And microbes, too, have been tamed: a study by UNIL, published in the journal Nature Communications, shows that the bacteria used to produce Gruyère, Emmental and Sbrinz cheese show signs of ancient domestication.
The domestication of livestock and plants marked an important stage in the settlement of human populations in the Neolithic period, as they moved from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a subsistence model based on animal husbandry and agriculture. Because of the microscopic size and virtual absence of fossils ...
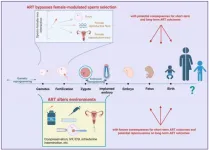
A Perspective summarizes the risks of bypassing natural selection when using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in humans and livestock. The authors call for dialogue between the fields of assisted reproduction and evolutionary biology.
Jonathan P. Evans and Francisco Garcia-Gonzalez detail how techniques used in ART, including in vitro fertilization, artificial insemination, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection, can stress and damage gametes and embryos and lead to deleterious epigenetic changes in offspring. Some ART techniques also bypass a system of filters in the female reproductive tract that select healthy sperm and may lead to better genetic matches with ...
Almost three quarters of adolescents in Australia experience clinically significant depression or anxiety symptoms, with most being chronic, according to a new study. And preventive strategies outside our clinics are urgently required to address this considerable public health problem facing the nation.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Lancet Psychiatry, found mental health problems were frequently chronic with 64 per cent reporting symptoms three or more times across their adolescent years.
MCRI Dr Ellie Robson said the rate and ...
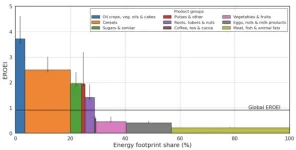
A primary output of agriculture is food, an energy source for the human body. But agriculture also requires energy inputs. Kajwan Rasul and colleagues calculated the global energy return on investment for agriculture over time from 1995 to 2019. The authors constructed a model using two existing models, one that captures the energy use of agriculture and food processing and another that captures flows of agricultural commodities. The authors find that the return on energy investment for global agriculture has increased from .68 to .91 over ...