(Press-News.org) A new prediction model for infected pancreatic necrosis (IPN) in patients with acute pancreatitis (AP) offers a groundbreaking approach to improving patient outcomes. Developed by a team of researchers across eight Chinese hospitals, the model harnesses five early clinical indicators—respiratory rate, temperature, serum glucose, calcium, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)—to identify high-risk patients within 24 hours of hospital admission.
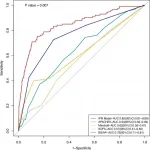
The study, recently published in eGastroenterology, analyzed data from over 3,000 patients diagnosed with AP between 2017 and 2023. Researchers employed advanced statistical methods, including LASSO regression and multivariate analysis, to develop and validate the model. In the development phase, it achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.85, significantly outperforming widely used scoring systems like BISAP (AUC 0.76) and SOFA (AUC 0.57).
“Infected pancreatic necrosis is a serious complication of acute pancreatitis that increases mortality risk and hospital stays,” said Dr Dong Wu, a senior researcher from Peking Union Medical College Hospital. “Our model represents a practical and highly accurate tool for early risk stratification, ensuring timely intervention and better resource allocation in healthcare systems.”
Why Early Detection Matters
IPN occurs in approximately 6% of AP cases, with a markedly higher prevalence in patients suffering from severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). Left untreated, the condition can lead to systemic infections, multiple organ failure, and increased mortality. Timely and accurate prediction is critical for initiating appropriate treatments, including antibiotics and minimally invasive procedures.
The model focuses on variables readily available in routine clinical settings, such as vital signs and basic laboratory tests. This approach ensures ease of implementation and minimizes reliance on expensive or specialized diagnostic tools. “By focusing on universally available clinical data, our model can be adopted across diverse healthcare settings, including those with limited resources,” noted Dr. Yin Zhu from The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The study underscores the model’s utility in guiding personalized care strategies for AP patients. For high-risk individuals identified by the model, clinicians can prioritize closer monitoring and early initiation of targeted therapies. This proactive approach has the potential to significantly reduce complications and associated healthcare costs.
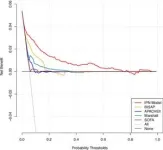
“Decision curve analysis revealed that the model offers a positive net benefit across a wide range of clinical thresholds,” explained Dr. Hongda Chen from Peking Union Medical College Hospital. “This means clinicians can confidently use it to balance the risks of overtreatment against the dangers of missed diagnoses.”
Global Reach and Future Directions
Although validated in a Chinese population, the researchers aim to expand the model’s application globally. Further studies are planned to adapt it for Western populations, where alcohol-related pancreatitis is predominant and other demographic factors may influence outcomes. The model also opens avenues for further research into preventive measures and early interventions for IPN.
“This innovation is a step forward in personalized medicine,” added Dr. Dong Wu. “We hope it will serve as a catalyst for future advancements in acute pancreatitis care, particularly in regions with high disease burden.”
See the article:
Song K, He W, Wu Z, et al. Early clinical predictors of infected pancreatic necrosis: a multicentre cohort study. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100095. doi:10.1136/egastro-2024-100095
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery). eGastroenterology is now indexed by DOAJ, Scopus, Dimensions, OpenAlex, ROAD, and COPE, with more to come!
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
Using an AI tool, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have analysed brain images from 70-year-olds and estimated their brains’ biological age. They found that factors detrimental to vascular health, such as inflammation and high glucose levels, are associated with an older-looking brain, while healthy lifestyles were linked to brains with a younger appearance. The results are presented in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
Every year, over 20,000 people in Sweden develop some form of dementia, with Alzheimer’s disease accounting for approximately two-thirds of cases. However, the speed at which ...
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a major cause of respiratory infections, particularly in infants, children under 5 years, and older adults. Its rapid spread makes RSV a serious public health concern. Currently, there are no effective medications for RSV, and current treatment focuses on providing supportive care and preventing its spread.
In a recent study, authors from the Chinese Academy of Medical Science and Peking Union Medical College, Nanjing Medical University, Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention of the Chinese Center ...
Scientists have discovered a way to remove toxic compounds from potatoes, making them safer to eat and easier to store. The breakthrough could cut food waste and enhance crop farming in space and other extreme environments.
Potato plants naturally produce chemicals that protect them from insects. The chemicals, called steroidal glycoalkaloids, or SGAs, are found in high quantities in the green parts of potato peels, and in the sprouting areas. They render the potatoes unsafe for insects as well as humans.
"These compounds are critical for plants to ward off insects, but they ...
The war in Ukraine is causing hunger thousands of miles from the battlefields, according to a study released today.
Nearly three years of war in the “breadbasket of the world” has left croplands destroyed and forced laborers who grow, harvest and process a bounty of wheat, barley and oats to flee. Combined with export bans from other countries, ripple effects resonated through global trade and upended food supply systems.
But understanding how far those disruptions reached, who suffered and who gained has been difficult. Researchers at Michigan State University’s Center for Systems Integration and Sustainability (CSIS) lead a unique effort, relying ...
TORONTO, December 20, 2024 — The unspoken rule for women of colour in academia is to be everything to everyone – mentor, diversity champion, tireless scholar, and silent workhorse, says York University equity studies Assistant Professor Yvonne Su in her recent paper published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
“We are expected to carry the banner of inclusion, but we are not truly included. Inclusion, as it’s currently defined, is about optics, not transformation,” observes Su in the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Professional Studies. “It’s about showing diversity on the surface ...
Leuven, 20 December 2024- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons. The average life span after diagnosis of this incurable disease is two to five years. In the relentless pursuit of understanding the cause of motor neuron death, scientists from KU Leuven and the VIB Center for Brain and Disease Research have identified an intriguing new lead: tiny, antenna-like structures 0n cells called primary cilia. Their study, published in Brain, could open a potential new avenue for therapeutic development.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s ...
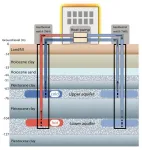
The aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) system, which uses geothermal heat as a renewable energy source, is one of the solutions to reducing fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emission. This system stores heat underground in aquifers, using groundwater as a heat medium. The heat is then extracted as needed according to the season to efficiently heat and cool buildings.
Its use is mainly expanding in Europe, and its widespread introduction is expected in Japan. However, regular inspection is required to utilize ...
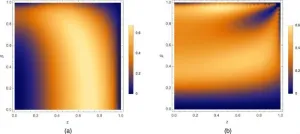
A brotherly research duo has discovered that when the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) produces top quarks – the heaviest known fundamental particles – it regularly creates a property known as magic.
This finding, published in Physical Review D, has implications for the progression of quantum computing, with magic being a measure that describes how difficult a quantum system is for a non-quantum computer to calculate.
“The higher the magic, the more we need quantum computers to describe the behaviour,” explains Professor Martin White, from the University ...
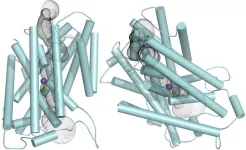
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have discovered that a protein which mediates the transport of alkali metal ions, such as potassium, and halides ions across plant membranes acts similarly to a protein found in animals.
The protein is a cation-chloride cotransporter (CCC), and these are present in all cellular life forms. Some CCCs are able to transport two types of ions, both potassium and halide chloride, while others can also transport a third – sodium.
The selectivity of plant CCCs has been controversial, and it was previously understood ...
Communities up and down the West Coast of the United States can expect the potent storms known as atmospheric rivers to evolve as the climate warms. But residents in Southern California will see much different changes than residents in more northerly locations like Seattle.
New research, led by scientists at the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR), found that warming conditions will increase evaporation of ocean waters and significantly alter atmospheric rivers to the south. Farther north, however, atmospheric rivers will be most influenced by rising temperatures in the ocean and atmosphere.
While ...