(Press-News.org) Atlantic and Baltic herring are typical plankton-eating fish of central importance for the northern Atlantic Ocean and Baltic Sea ecosystems. A new study published in Nature Communications led by scientists from Uppsala University (Sweden) documents the discovery of the evolution of genetically distinct, fish-eating herring in the Baltic Sea, a young water body that has only existed since the end of the last glaciation.
Atlantic and Baltic herring have a key role in the ecosystem, acting as a critical link between plankton production and other organisms, like predatory fish, sea birds, sea mammals, and humans. Previous research from the Uppsala group has documented that herring is subdivided into a number of ecotypes that show genetic adaptation related to, for instance, climate conditions, salinity, and preferred spawning season.
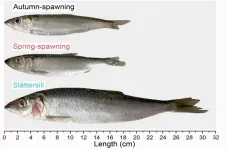
Larger than the common plankton-eating Baltic herring
Linnaeus, the founder of taxonomy and professor in Uppsala in the 18th century, defined the Baltic herring as a subspecies of the Atlantic herring adapted to the brackish water in the Baltic Sea. The Baltic herring is much smaller and has less fat than the Atlantic herring. The current project was initiated when the principal investigator was informed by a local fisherman at the coast northeast of Uppsala that there is a special type of herring “that always spawns just before midsummer and which is as big as the Atlantic herring,” thus much larger than the common plankton-eating Baltic herring.
“When I learned that the locals are aware of a specific population of very large Baltic herring that always spawns in the same area year after year, I decided to sample and explore their genetic constitution. Now we know that this is a genetically unique population that must have evolved over hundreds, if not thousands, of years in the Baltic Sea,” says Leif Andersson, Professor at the Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology at Uppsala University, who led the study.
The researchers carried out a careful analysis of morphology, growth pattern, fat content, and presence of environmental pollutants. A striking finding was that the large herring exhibited damaged gill rakers. The plankton-eating Baltic herring uses the gill rakers to sieve plankton, while the observed gill damage in large herring likely reflects a switch to a fish diet, probably including the common stickleback, which has sharp spines for predation protection.
Another interesting finding was that the large herring had a significantly higher fat content and significantly reduced level of dioxin, a problematic chloro-organic pollutant in the Baltic Sea. Both these observations and the much faster growth rate are consistent with a switch to a fish diet. The relatively low dioxin content makes this fish-eating Baltic herring interesting for human consumption.
Two distinct subpopulations of fish-eating herring
After finding that the large fish-eating herring is genetically unique, the researchers decided to perform whole genome sequencing of the large herring together with previously collected large herring from different parts of the Baltic Sea. The stomach content of this second set of large herring showed that these individuals were feeding on small fish.
“Our genetic analysis demonstrates that there are at least two distinct subpopulations of fish-eating herring in the Baltic Sea; one occurs north of Stockholm, and the other occurs south of Stockholm,” says Jake Goodall, researcher at Uppsala University and first author on the publication.
One interesting question is why fish-eating herring have evolved in the Baltic Sea, when there is no evidence for such herring in the Atlantic Ocean. The Baltic Sea is a very young water body that has only existed for about 8,000 years, after the end of the last glaciation period. Only a limited number of marine fish have been able to colonise the brackish Baltic Sea, where salinity is in the range of 2-10‰ compared with about 35‰ in the Atlantic Ocean.
“We hypothesise that fish-eating Baltic herring have evolved due to a lack of competition from other predatory fish, for instance, mackerel and tuna, which do not occur where we find fish-eating herring. Thus, these herring take advantage of an underutilised food resource in the Baltic Sea,” says Leif Andersson.
END
Evolution of fast-growing fish-eating herring in the Baltic Sea
2024-12-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
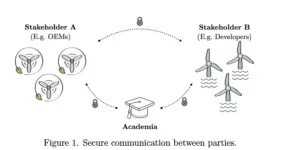
Cryptographic protocol enables secure data sharing in the floating wind energy sector
2024-12-23
Floating wind power offers enormous potential for deepwater offshore energy development. However, the management and secure exchange of data between stakeholders represents a key challenge for its evolution. A new cryptographic framework, proposed by researchers Claudia Bartoli (IMDEA Software) and Irene Rivera-Arreba (Norwegian University of Science and Technology, NTNU), presented at WindTech 2024 Conference, tries to solve this problem with a data sharing scheme that guarantees data integrity without compromising privacy. This breakthrough seeks to foster collaboration between industries and academia, driving innovation in floating wind technologies.
Context
Floating wind power ...
Can drinking coffee or tea help prevent head and neck cancer?
2024-12-23
In a recent analysis of data from more than a dozen studies, coffee and tea consumption was linked with lower risks of developing head and neck cancer, including cancers of the mouth and throat. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Head and neck cancer is the seventh most common cancer worldwide, and rates are rising in low- and middle-income countries. Many studies have assessed whether drinking coffee or tea is associated with head and neck cancer, with inconsistent results.
To provide additional insight, investigators examined data from 14 studies by different scientists associated with the International Head and ...
Development of a global innovative drug in eye drop form for treating dry age-related macular degeneration
2024-12-23
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of vision loss in individuals over 65, characterized by abnormal changes in the macular, resulting in reduced vision and distorted objects. Dry AMD accounts for 90% of all AMD cases, with relatively mild vision impairment; however, approximately 30% progress to the severe vision loss associated with wet AMD within 10 years. The only FDA-approved treatments for dry AMD as of 2023 are two injectable drugs, which are limited by concerns over complications from intravitreal injections and modest ...
Scientists unlock secrets behind flowering of the king of fruits
2024-12-21
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered that around 15 days of dry weather can trigger the flowering of durian. Observations of 110 durian plants revealed that flowering occurred around 50 days after an approximately 15-day dry spell, independent of whether the plant was grafted or grown from a seed. The team’s work might not only impact the production of a valuable agricultural asset but deepen our understanding of tropical ecosystems.
Known in many countries as the “king of fruits,” the durian is known for its distinctive strong odor, large size, ...
Texas A&M researchers illuminate the mysteries of icy ocean worlds
2024-12-21
As NASA’s Europa Clipper embarks on its historic journey to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, Dr. Matt Powell-Palm, a faculty member at Texas A&M University’s J. Mike Walker ‘66 Department of Mechanical Engineering, has unveiled groundbreaking research that could transform our understanding of icy ocean worlds across the solar system. The study published in Nature Communications, co-authored with planetary scientist Dr. Baptiste Journaux of the University of Washington, introduces a novel thermodynamic concept called the “centotectic” and investigates the stability of liquids in extreme conditions - critical ...
Prosthetic material could help reduce infections from intravenous catheters
2024-12-21
In the holiday movie The Grinch, makeup artists are reported to have spent several hours each day encasing Jim Carrey’s face with prosthetics to create the iconic grumpy, green-furred creature. Such elaborate prosthetics, often made possible by materials like silicone rubbers, may have now found an unexpected yet beneficial biomedical engineering application, according to a new study from Texas A&M University.
Published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers have created realistic, skin-like replicas made of Ecoflex, a type of silicone rubber that can potentially serve as a platform to evaluate risks of bacterial infections from ...
Can the heart heal itself? New study says it can
2024-12-20
A research team co-led by a physician-scientist at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson’s Sarver Heart Center found that a subset of artificial heart patients can regenerate heart muscle, which may open the door to new ways to treat and perhaps someday cure heart failure. The results were published in the journal Circulation.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, heart failure affects nearly 7 million U.S. adults and is responsible for 14% of deaths per ...
Microscopic discovery in cancer cells could have a big impact
2024-12-20
In 2022 alone, over 20 million people were diagnosed with cancer, and nearly 10 million died from the disease, according to the World Health Organization. While the reaches of cancer are massive, the answer to more effective treatments may be hidden within a microscopic cell.
Led by Texas A&M University graduate students Samere Zade of the biomedical engineering department and Ting-Ching Wang of the chemical engineering department, an article released by the Lele Lab has uncovered new details about the mechanism behind cancer progression.
Published in Nature Communications, the article ...
Rice researchers take ‘significant leap forward’ with quantum simulation of molecular electron transfer
2024-12-20
Researchers at Rice University have made a meaningful advance in the simulation of molecular electron transfer — a fundamental process underpinning countless physical, chemical and biological processes. The study, published in Science Advances, details the use of a trapped-ion quantum simulator to model electron transfer dynamics with unprecedented tunability, unlocking new opportunities for scientific exploration in fields ranging from molecular electronics to photosynthesis.
Electron transfer, critical to processes such as cellular respiration and energy harvesting ...
Breakthrough new material brings affordable, sustainable future within grasp
2024-12-20
HOUSTON, Dec. 20, 2024 –While lithium-ion batteries have been the go-to technology for everything from smartphones and laptops to electric cars, there are growing concerns about the future because lithium is relatively scarce, expensive and difficult to source, and may soon be at risk due to geopolitical considerations. Scientists around the world are working to create viable alternatives.
An international team of interdisciplinary researchers, including the Canepa Research Laboratory at the University of Houston, has developed a new type of material for sodium-ion batteries that could ...