(Press-News.org) A new method of scanning lungs is able to show the effects of treatment on lung function in real time and enable experts to see the functioning of transplanted lungs.
This could enable medics to identify sooner any decline in lung function.
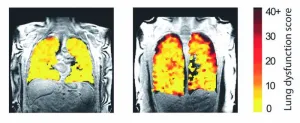
The scan method has enabled the team, led by researchers at Newcastle University, UK, to see how air moves in and out of the lungs as people take a breath in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and patients who have received a lung transplant.
Publishing two complementary papers in Radiology and JHLT Open, the team explain how they use a special gas, called perfluoropropane, that can be seen on an MRI scanner. The gas can be safely breathed in and out by patients, and then scans taken to look at where in the lungs the gas has reached.
The project lead, Professor Pete Thelwall is Professor of Magnetic Resonance Physics and Director of the Centre for In Vivo Imaging at Newcastle University. He said; “Our scans show where there is patchy ventilation in patients with lung disease, and show us which parts of the lung improve with treatment. For example, when we scan a patient as they use their asthma medication, we can see how much of their lungs and which parts of their lung are better able to move air in and out with each breath.”
Using the new scanning method, the team are able to reveal the parts of the lung that air doesn’t reach properly during breathing. By measuring how much of the lung is well-ventilated and how much is poorly ventilated, experts can make an assessment of the effects of a patient’s respiratory disease, and they can locate and visualise the lung regions with ventilation defects.
Demonstrating that the scans work in patients with asthma or COPD, the team comprising experts from across Universities and NHS Trusts in Newcastle and Sheffield publish the first paper in Radiology.
The new scanning technique allows the team to quantify the degree of improvement in ventilation when patients have a treatment, in this case a widely used inhaler, the bronchodilator, salbutamol. This shows that the imaging methods could be valuable in clinical trials of new treatments of lung disease.
Use in lung transplants
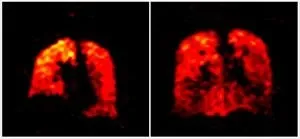
A further study, published in JHLT Open, examined patients who had previously received a lung transplant for very severe lung disease at the Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It demonstrates how the team further developed the imaging method to provide lung function measurements which could be used to better support lung transplant recipients in the future. The sensitivity of the measurement means medics can spot early changes in lung function allowing them to identify lung problems earlier and so provide better care for patients.
In research studies, the team scanned transplant recipients’ lungs over multiple breaths in and out, collecting MRI pictures that show how the air containing the gas reached different areas of the lung. The team scanned those who either had normal lung function or who were experiencing chronic rejection after lung transplant, which is a common issue in lung transplant recipients as their immune system attacks the donor lungs. In those with chronic rejection, the scans showed poorer movement of air to the edges of the lungs, most likely due to damage in the very small breathing tubes (airways) in the lung, a feature typical of chronic rejection also known as chronic lung allograft dysfunction.
Professor Andrew Fisher, Professor of Respiratory Transplant Medicine at Newcastle Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and Newcastle University, UK, co-author of the study said; “We hope this new type of scan might allow us to see changes in the transplant lungs earlier and before signs of damage are present in the usual blowing tests. This would allow any treatment to be started earlier and help protect the transplanted lungs from further damage.”
The team say there is potential for this scan method to be used in the clinical management of lung transplant recipients and other lung diseases in the future, bringing a sensitive measurement that may spot early changes in lung function that enable better management of these conditions.
This work on lung imaging has been funded by the Medical Research Council and by The Rosetrees Trust.
References:
Assessing Lung Ventilation and Bronchodilator Response in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with Fluorine 19 MRI. Pippard BJ, Neal MA, Holland CW, Maunder AM, Forrest I, Lawson RA, Fisher HF, Matthews JNS, Wild JM, Simpson AJ, Thelwall, PE. Radiology. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.240949 (n.b. live date 24th Dec)
Dynamic 19F-MRI of pulmonary ventilation in lung transplant recipients with and without chronic lung allograft dysfunction. Neal MA, Bos S, Holland CW, Hollingsworth KG, Meachery G, Nair A, Lordan JL, Fisher AJ, Thelwall, PE. JHLT Open. Doi: https://www.jhltopen.org/article/S2950-1334(24)00116-2/fulltext
END
New scan method unveils lung function secrets
2024-12-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Searching for hidden medieval stories from the island of the Sagas
2024-12-24
Iceland has a long and rich literary tradition. With its 380,000 inhabitants, Iceland has produced many great writers, and it is said that one in two Icelanders writes books. The literary tradition stretches all the way back to the Middle Ages.
“Previously, the theory was that Iceland was so dark and barren that the Icelanders had to fill their lives with storytelling and poetry to compensate for this. But Icelanders were certainly part of Europe and had a lot of contact with Britain, Germany, Denmark and ...
Breakthrough study reveals bumetanide treatment restores early social communication in fragile X syndrome mouse model
2024-12-24
SAN ANTONIO, Texas, USA, 17 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, researchers from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and Hirosaki University have uncovered critical new insights into the developmental trajectory of social behaviors in fragile X syndrome, the leading genetic cause of autism spectrum disorder.
The study, published in Genomic Psychiatry, demonstrates that treating pregnant mice with bumetanide - a drug that regulates chloride levels ...
Neuroscience leader reveals oxytocin's crucial role beyond the 'love hormone' label
2024-12-24
REGENSBURG, Bavaria, Germany, 24 December 2024 – In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Professor Inga Neumann, Chair of the Department of Behavioural and Molecular Neurobiology at the University of Regensburg, reveals groundbreaking insights into how oxytocin shapes social behavior and emotional responses in the brain.
The interview, published in Brain Medicine (DOI: 10.61373/bm024k.0139), showcases Professor Neumann's pioneering research on neuropeptides, particularly oxytocin, which has evolved far beyond its popular characterization ...
Twelve questions to ask your doctor for better brain health in the new year
2024-12-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE ON MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Improving your brain health in the new year can start with a simple step, talking with your neurologist or primary care physician about 12 factors to protect your brain. The factors are outlined in an Emerging Issues in Neurology article developed by the American Academy of Neurology and published in the December 16, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Neurologists are the experts in brain health, with the training and insight needed to help you ...
Microelectronics Science Research Centers to lead charge on next-generation designs and prototypes
2024-12-23
RICHLAND, Wash.—Microelectronics run the modern world. Staying ahead of the development curve requires an investment that doesn’t just keep pace but sets new standards for the next generation of technological advances. Today, the Department of Energy announced the creation of three Microelectronics Science Research Centers to address the nation’s specific needs for microelectronics designed to operate in extreme environments such as high radiation, extreme cold, and high magnetic field—situations where robust and reliable operating environments are crucial. The new MSRCs not only focus on the next generation ...
Study identifies genetic cause for yellow nail syndrome
2024-12-23
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 23 December 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
New drug to prevent migraine may start working right away
2024-12-23
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A drug recently approved to prevent migraine may start working right away, according to a study published in the December 23, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study looked at the drug atogepant, which is a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist taken by mouth.
“With many current drugs to prevent migraine, it takes time to find the right dosage for the individual ...
Good news for people with MS: COVID-19 infection not tied to worsening symptoms
2024-12-23
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – For people with multiple sclerosis (MS), having a COVID-19 infection is not associated with worsening MS symptoms or disability, according to a study published in the December 23, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Infections may be associated with more disability among people with MS,” said study author Amber Salter, PhD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, ...
Department of Energy announces $179 million for Microelectronics Science Research Centers
2024-12-23
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $179 million in funding for three Microelectronics Science Research Centers (MSRCs). These three MSRCs will perform basic research in microelectronics materials, device and system design, and manufacturing science to transform future microelectronics technologies. The MSRCs were authorized by the Micro Act, passed in the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, and complement the activities appropriated under the CHIPS and Science Act at the Department of Commerce, the Department of Defense, and other agencies.
For decades, DOE has been at ...
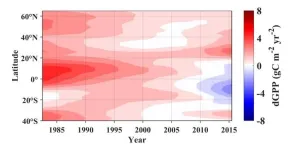
Human-related activities continue to threaten global climate and productivity
2024-12-23
The pace at which anthropogenic climate change has altered the terrestrial carbon stores is making our current climate-change mitigation efforts seem fruitless, unless behaviors are quickly changed.
Climate change induced by human behaviors, or anthropogenic climate change, has been a hot topic for decades and is not going away. As with any problem, reviewing datasets from the past to analyze trends and garner information is one of the first steps towards a solution. Gross primary productivity, or GPP, is a key indicator of the overall health of an ecosystem and is the amount of CO2 fixed by plants per unit of time and area. Researchers ...