(Press-News.org) The research team led by Dr. Hojeong Jeon and Dr. Hyung-Seop Han of the Biomaterials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Oh Sang-Rok), along with Dr. Indong Jun from KIST Europe, has developed a novel stent surface treatment technology using laser patterning. This technology promotes endothelial cell growth while inhibiting smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation in blood vessels. By controlling cellular responses to nanostructured patterns, the technique holds promise for enhancing vascular recovery, especially when combined with chemical coating methods.
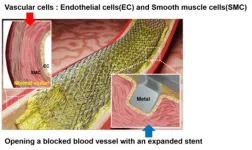
As South Korea approaches a super-aged society, the incidence of vascular diseases among the elderly population is rising, increasing the importance of therapeutic stents. These tubular medical devices maintain blood flow by expanding narrowed or blocked blood vessels. However, traditional metal stents may cause restenosis—a re-narrowing of the artery—due to excessive smooth muscle cell proliferation one month after implantation.
Drug-eluting stents are widely used to mitigate this issue but often inhibit vascular re-endothelialization, increasing the risk of thrombosis and necessitating the use of anticoagulants. To overcome these limitations, research into coating stent surfaces with bioactive molecules like proteins or nucleic acids is ongoing. However, these coatings often serve limited functions, falling short in accelerating endothelial cell proliferation.
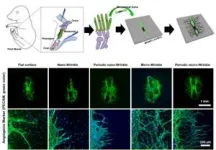
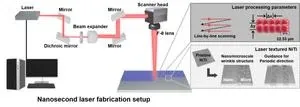
To address this issue, the research team applied nanosecond laser texturing technology to create nano- and micro-scale wrinkle patterns on nickel-titanium alloy surfaces. The wrinkle patterns inhibit the migration and morphological changes of smooth muscle cells caused by stent-induced vascular wall injury, preventing restenosis. The wrinkle patterns also enhance cellular adhesion, promoting re-endothelialization to restore the vascular lining.
The team validated the effectiveness of this technology through in vitro vascular cell studies and ex vivo angiogenesis assays using fetal animal bones. The laser-textured metal surfaces created favorable environments for endothelial cell proliferation while effectively suppressing smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation and excessive growth. Notably, smooth muscle cell growth on the wrinkled surfaces was reduced by approximately 75%, while angiogenesis increased more than twofold.
The surface patterning technology is expected to be applicable not only to metal stents but also to biodegradable stents. When applied to biodegradable stents, the patterns can prevent restenosis and enhance endothelialization before the stents dissolve, improving treatment outcomes and reducing complication risks. The research team is planning to conduct animal tests and clinical trials to verify the long-term safety and efficacy of this laser patterning technology.
Dr. Jeon stated, “This study demonstrates the potential of surface patterns to selectively control vascular cell responses without drugs. Using widely industrialized nanosecond lasers allows for precise and rapid stent surface processing, offering significant advantages for commercialization and process efficiency.”
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Sang Im Yoo) through KIST's major projectand the Future Promising Convergence Technology Pioneer Project (RS-2023-00302145). The findings were published in the international journal 「Bioactive Materials」 (IF: 18.0, JCR top 0.9%).
END
Revolutionizing stent surgery for cardiovascular diseases with laser patterning technology
Innovative stent surface technology to control vascular cell responses without drug side effects
2024-12-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fish-friendly dentistry: New method makes oral research non-lethal
2024-12-26
Can we examine the teeth of living fish and other vertebrates in detail, repeatedly over time, without harming them?
Previously, small animals often had to be euthanized to obtain precise information, but now scientists have found a new way to humanely study detailed dental characteristics of vertebrates. This customizable method can be used for both living animals and museum specimens and has been published in the Journal of Morphology.
Customizable trays for precise impressions
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and their collaborators applied human dental impression techniques to study fish teeth in a species called Polypterus ...
Call for papers: 14th Asia-Pacific Conference on Transportation and the Environment (APTE 2025)
2024-12-24
Theme
"Emerging Transportation Solutions for Building Efficient, Sustainable, Reliable, and Inclusive Transport Systems"
We are pleased to announce the call for papers for the 14th Asia-Pacific Conference on Transportation and the Environment (APTE 2025), hosted by the School of Vehicle and Mobility, Tsinghua University, co-organized by Communications in Transportation Research, Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, and ETS-Data. The conference will be held from 9 to 11 August 2025, in Hangzhou, China.
Objective
The APTE 2025 conference provides a platform for scholars, professionals, and practitioners to share cutting-edge research, foster international ...
A novel disturbance rejection optimal guidance method for enhancing precision landing performance of reusable rockets
2024-12-24
Powered descent guidance (PDG) is a key technology for reusable rockets to accomplish high-precision landing on Earth. Different from the well-established PDG for lunar landing and planetary landing, endoatmospheric powered descent guidance is required to accommodate nonlinear dynamics and more disturbing flight conditions, including engine thrust fluctuation, aerodynamic uncertainty, and winds. For example, the winds can produce a persistent aerodynamic force disturbance on the rocket, resulting in ...
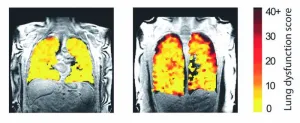
New scan method unveils lung function secrets
2024-12-24
A new method of scanning lungs is able to show the effects of treatment on lung function in real time and enable experts to see the functioning of transplanted lungs.
This could enable medics to identify sooner any decline in lung function.
The scan method has enabled the team, led by researchers at Newcastle University, UK, to see how air moves in and out of the lungs as people take a breath in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and patients who have received a lung transplant.
Publishing two complementary papers in Radiology and JHLT Open, the team explain how they ...
Searching for hidden medieval stories from the island of the Sagas
2024-12-24
Iceland has a long and rich literary tradition. With its 380,000 inhabitants, Iceland has produced many great writers, and it is said that one in two Icelanders writes books. The literary tradition stretches all the way back to the Middle Ages.
“Previously, the theory was that Iceland was so dark and barren that the Icelanders had to fill their lives with storytelling and poetry to compensate for this. But Icelanders were certainly part of Europe and had a lot of contact with Britain, Germany, Denmark and ...
Breakthrough study reveals bumetanide treatment restores early social communication in fragile X syndrome mouse model
2024-12-24
SAN ANTONIO, Texas, USA, 17 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, researchers from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and Hirosaki University have uncovered critical new insights into the developmental trajectory of social behaviors in fragile X syndrome, the leading genetic cause of autism spectrum disorder.
The study, published in Genomic Psychiatry, demonstrates that treating pregnant mice with bumetanide - a drug that regulates chloride levels ...
Neuroscience leader reveals oxytocin's crucial role beyond the 'love hormone' label
2024-12-24
REGENSBURG, Bavaria, Germany, 24 December 2024 – In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Professor Inga Neumann, Chair of the Department of Behavioural and Molecular Neurobiology at the University of Regensburg, reveals groundbreaking insights into how oxytocin shapes social behavior and emotional responses in the brain.
The interview, published in Brain Medicine (DOI: 10.61373/bm024k.0139), showcases Professor Neumann's pioneering research on neuropeptides, particularly oxytocin, which has evolved far beyond its popular characterization ...
Twelve questions to ask your doctor for better brain health in the new year
2024-12-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE ON MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Improving your brain health in the new year can start with a simple step, talking with your neurologist or primary care physician about 12 factors to protect your brain. The factors are outlined in an Emerging Issues in Neurology article developed by the American Academy of Neurology and published in the December 16, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Neurologists are the experts in brain health, with the training and insight needed to help you ...
Microelectronics Science Research Centers to lead charge on next-generation designs and prototypes
2024-12-23
RICHLAND, Wash.—Microelectronics run the modern world. Staying ahead of the development curve requires an investment that doesn’t just keep pace but sets new standards for the next generation of technological advances. Today, the Department of Energy announced the creation of three Microelectronics Science Research Centers to address the nation’s specific needs for microelectronics designed to operate in extreme environments such as high radiation, extreme cold, and high magnetic field—situations where robust and reliable operating environments are crucial. The new MSRCs not only focus on the next generation ...
Study identifies genetic cause for yellow nail syndrome
2024-12-23
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 23 December 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Revolutionizing stent surgery for cardiovascular diseases with laser patterning technologyInnovative stent surface technology to control vascular cell responses without drug side effects