(Press-News.org) Peking University, November 15, 2024: A research team led by Prof. Li Mingsong at Peking University has provided new insights into the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) and its effects on ocean chemistry. This study, entitled “Coupled decline in ocean pH and carbonate saturation during the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum” published in Nature Geoscience reconstructs ocean acidification during this ancient climate event, offering parallels with current trends linked to human-driven CO2 emissions.
Why It Matters:
The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), 56 million years ago, was a major carbon release event that resulted in rapid global warming and significant ocean acidification. This study highlights parallels with current climate change, emphasizing the need to understand past events to predict future impacts. The findings stress the urgency of addressing human-driven CO2 emissions to protect marine ecosystems, particularly in vulnerable regions like the Arctic.
Key Findings:
1. Ocean Acidification:
The team used paleoclimate data assimilation (DA), integrating proxy data and Earth system model simulations to reconstruct ocean carbonate chemistry.
Atmospheric CO2 rose dramatically from 890 ppm to 1980 ppm during the PETM.
Acidification was most severe in high-latitude regions, similar to current trends in the Arctic, where aragonite saturation is declining.
2. PETM Overview:
The PETM was triggered by a massive carbon release, causing rapid warming and disrupting ecosystems.
Ocean pH declined by 0.46 units, from 7.91 to 7.45, causing widespread disruptions to marine life.
3. Impact on Marine Life:
Ocean acidification led to the extinction of 30%-50% of benthic foraminifera and significant marine biodiversity loss.
4. Relevance to Modern Climate Change:
Current CO2 emissions are rising faster than during the PETM, threatening marine ecosystems and emphasizing the need for urgent climate action.
Written by: Akaash Babar
Edited by: Zhang Jiang
Source: School of Earth and Space Sciences
END
Coupled decline in ocean pH and carbonate saturation during the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
2024-12-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unlocking the Future of Superconductors in non-van-der Waals 2D Polymers
2024-12-26
Peking University, November 20, 2024: In a groundbreaking achievement, researchers from Peking University's School of Materials Science and Engineering, led by Professor Jin-Hu Dou, have synthesized a novel non-van-der-Waals two-dimensional (2D) coordination polymer with intrinsic superconducting properties. The findings, published in Nature Communications (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-53786-1) on October 29, 2024, introduce the first precise crystal structure of the Cu₃BHT coordination polymer, marking a significant leap in the ...
Starlight to sight: Breakthrough in short-wave infrared detection
2024-12-26
Peking University, December 3rd, 2024: Prof Zhang Zhiyong’s team developed a heterojunction-gated field-effect transistor (HGFET) that achieves high sensitivity in short-wave infrared detection, with a recorded specific detectivity above 1014 Jones at 1300 nm, making it capable of starlight detection. Their research was recently published in the journal Advanced Materials, titled “Opto-Electrical Decoupled Phototransistor for Starlight Detection”.
Why it matters: Highly sensitive shortwave infrared (SWIR) detectors are essential for detecting weak radiation (typically below 10−8 W·Sr−1·cm−2·µm−1) with high-end ...
Land use changes and China’s carbon sequestration potential
2024-12-26
Peking University, December 11, 2024: A team of researchers led by Professor Piao Shilong at the Institute of Carbon Neutrality of Peking University (PKU) has made significant advances in understanding how China’s land-use changes—such as forest planting—can contribute to the country’s efforts to reduce carbon emissions. Their study, published in Nature Communications, offers fresh insights into China’s carbon removal capacity through land-use, land-use change, and forestry (LULUCF), a key strategy for achieving carbon neutrality by 2060.
Why it matters: As part of its commitment under the Paris Agreement, China has pledged to become carbon ...
PKU scientists reveals phenological divergence between plants and animals under climate change
2024-12-26
Peking University, December 19, 2024: A collaborative study led by Piao Shilong’s team and Zhang Yao’s team from the Institute of Carbon Neutrality at Peking University reveals the distinct mechanisms by which plants and animals respond to climate change in their life-cycle phenology. This research provides comprehensive global-scale evidence on the asynchronous phenological changes between plants and animals.
Why it matters:
Climate change has altered the timing of recurring biological cycles in both plants and animals. ...
Aerobic exercise and weight loss in adults
2024-12-26
About The Study: In this meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, engaging in 30 minutes of aerobic exercise per week was associated with modest reductions in body weight, waist circumference, and body fat measures among adults with overweight or obesity. However, aerobic training exceeding 150 minutes per week at moderate intensity or greater may be needed to achieve clinically important reductions.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ahmad Jayedi, PhD, email a.jayedi@imperial.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed ...
Persistent short sleep duration from pregnancy to 2 to 7 years after delivery and metabolic health
2024-12-26
About The Study: In this study, short sleep duration that persisted from pregnancy to 2 to 7 years after delivery was associated with a greater risk for adverse cardiometabolic outcomes. Future studies should explore whether sleep-targeted interventions during and after pregnancy are associated with improved cardiometabolic health outcomes, particularly among populations at increased risk.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Minjee Kim, MD, email minjee.kim@northwestern.edu.
To ...
Kidney function decline after COVID-19 infection
2024-12-26
About The Study: This cohort study found an association between COVID-19 and accelerated decline in kidney function, particularly after hospitalization, compared with pneumonia. People who were hospitalized for COVID-19 should receive closer monitoring of kidney function to ensure early diagnosis and optimized management of chronic kidney disease to effectively prevent complications and further decline.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Viyaasan Mahalingasivam, MPhil, email viyaasan.mahalingasivam@nhs.net.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Investigation uncovers poor quality of dental coverage under Medicare Advantage
2024-12-26
Medicare Advantage—the privatized form of Medicare that offers benefits beyond traditional Medicare, such as dental insurance—is gaining in popularity, but a new analysis reveals that the quality of dental coverage offered by Medicare Advantage is poor, with only 8.4 percent of plans offering a dental benefit that met the study’s quality standards. The research led by a team from Mass General Brigham is published in JAMA.
“Our study suggests that many Medicare Advantage beneficiaries may not have access to the dental care they need, even if they are enrolled in a plan that nominally ...
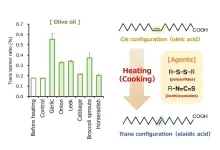
Cooking sulfur-containing vegetables can promote the formation of trans-fatty acids
2024-12-26
Trans-fatty acids (TFA) are a major cause of cardiovascular diseases. These harmful fats can accumulate along artery walls, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attacks. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), TFAs are responsible for over 278,000 annual deaths worldwide, and it recommends that TFA consumption should be limited to less than 1% of daily energy intake. Common sources of TFAs include fried (junk) foods and processed foods such as margarine, ghee, biscuits, cakes, etc. In processed foods, TFAs are produced through the hydrogenation of vegetable oil, a chemical process that saturates the oil with hydrogen. While the formation process of TFAs in ...
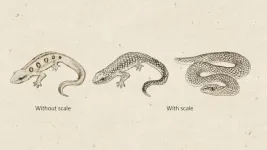
How do monkeys recognize snakes so fast?
2024-12-26
Dr. Nobuyuki Kawai from Nagoya University in Japan has found that the rapid detection of snakes by monkeys is because of the presence of snake scales as a visual cue. His findings highlight an evolutionary adaptation of primates to identify snakes based on specific visual characteristics. Understanding these mechanisms provides insight into the evolution of visual processing related to threat detection. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
Rapid detection of dangers and threats is important for personal ...