Cooking sulfur-containing vegetables can promote the formation of trans-fatty acids
New study reveal that garlic and onions contain chemicals that can transform into trans fats when cooked at high temperatures
2024-12-26
(Press-News.org)
Trans-fatty acids (TFA) are a major cause of cardiovascular diseases. These harmful fats can accumulate along artery walls, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attacks. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), TFAs are responsible for over 278,000 annual deaths worldwide, and it recommends that TFA consumption should be limited to less than 1% of daily energy intake. Common sources of TFAs include fried (junk) foods and processed foods such as margarine, ghee, biscuits, cakes, etc. In processed foods, TFAs are produced through the hydrogenation of vegetable oil, a chemical process that saturates the oil with hydrogen. While the formation process of TFAs in processed foods is well-known, evidence suggests that they can also be created at home during cooking.
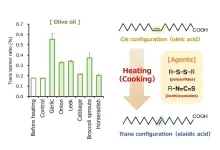
Studies indicate that unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs) can undergo trans-isomerization, a molecular reconfiguration that transform them into TFAs when heated at 150 °C or higher. On the other hand, sulfur-containing compounds, such as isothiocyanates and polysulfides, which are found in many vegetables, are known to promote geometrical isomerization of carotenoids (e.g., lycopene in tomato) —natural pigments that give vegetables their red, orange, or yellow color. This raises the question that whether these sulfur compounds also promote the trans-isomerization of UFAs in everyday cooking. Understanding the impact of natural sulfur compounds on the cooking process can help regulate TFA intake, particularly for those who avoid processed foods.
To explore this, a Japanese research team led by by Mr. Junji Obi of Nissui Corporation and Dr. Masaki Honda of Meijo University assessed the role of isothiocyanates and polysulfides in promoting the trans-isomerization of vegetable UFAs during cooking. The research was published online on November 27, 2024, in the journal Food Research International.
The researchers first evaluated the effects of sulfur compounds in triacylglycerols (TAGs) in a model system using reagents. Then, tests were conducted using ingredients (garlic, onion, leek, cabbage, horseradish, and broccoli sprouts) and vegetable oils (soybean and olive oils) to simulate actual cooking processes.
“We wanted to understand the principal characteristics of UFA isomerization in TAGs promoted by sulfur compounds through a model system using reagent-grade sulfur compounds and triglycerides,” explains Junji Obi, the first author of this paper. “We were interested in the effects of temperature, reaction time, sulfur compound concentration, the type of sulfur compounds, and addition of antioxidants on UFA isomerization.”
The team also assessed the role of antioxidants such as α-tocopherol in reducing the isomerization of UFAs in triglycerides like triolein and trilinolein.
The study revealed that sulfur compounds significantly promote heat-induced trans-isomerization of UFAs in vegetable oils, especially when cooking temperatures is above 140°C. The addition of antioxidants significantly reduced the promotion of UFAs isomerization by isothiocyanates, whereas they did little to inhibit the promotion of isomerization by polysulfides. This explains that cooking polysulfide-rich vegetables such as garlic and onions in vegetable oil at high temperatures can generate TFAs. In fact, this study demonstrated that garlic and onions significantly promote the trans-isomerization of UFAs.
Under normal cooking conditions, the corresponding increase in the trans isomer ratio is expected to be minimal, at most a few percentages. Therefore, while excessive caution is not necessary, it is important to recognize that cooking with ingredients rich in sulfur compounds may increase the risk of TFA intake.
“Release of TFAs under normal cooking conditions is expected to be minimal. Therefore, excessive caution is unnecessary,” concludes Dr. Honda, the corresponding author of this paper. “However, it is important to understand that cooking with ingredients rich in natural sulfur compounds may increase the risk of TFA intake.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-26
Dr. Nobuyuki Kawai from Nagoya University in Japan has found that the rapid detection of snakes by monkeys is because of the presence of snake scales as a visual cue. His findings highlight an evolutionary adaptation of primates to identify snakes based on specific visual characteristics. Understanding these mechanisms provides insight into the evolution of visual processing related to threat detection. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
Rapid detection of dangers and threats is important for personal ...
2024-12-26
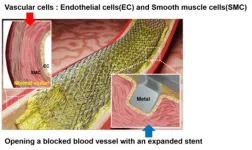
The research team led by Dr. Hojeong Jeon and Dr. Hyung-Seop Han of the Biomaterials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Oh Sang-Rok), along with Dr. Indong Jun from KIST Europe, has developed a novel stent surface treatment technology using laser patterning. This technology promotes endothelial cell growth while inhibiting smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation in blood vessels. By controlling cellular responses to nanostructured patterns, the technique holds promise for enhancing ...
2024-12-26
Can we examine the teeth of living fish and other vertebrates in detail, repeatedly over time, without harming them?
Previously, small animals often had to be euthanized to obtain precise information, but now scientists have found a new way to humanely study detailed dental characteristics of vertebrates. This customizable method can be used for both living animals and museum specimens and has been published in the Journal of Morphology.
Customizable trays for precise impressions
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and their collaborators applied human dental impression techniques to study fish teeth in a species called Polypterus ...
2024-12-24
Theme
"Emerging Transportation Solutions for Building Efficient, Sustainable, Reliable, and Inclusive Transport Systems"
We are pleased to announce the call for papers for the 14th Asia-Pacific Conference on Transportation and the Environment (APTE 2025), hosted by the School of Vehicle and Mobility, Tsinghua University, co-organized by Communications in Transportation Research, Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, and ETS-Data. The conference will be held from 9 to 11 August 2025, in Hangzhou, China.
Objective
The APTE 2025 conference provides a platform for scholars, professionals, and practitioners to share cutting-edge research, foster international ...
2024-12-24
Powered descent guidance (PDG) is a key technology for reusable rockets to accomplish high-precision landing on Earth. Different from the well-established PDG for lunar landing and planetary landing, endoatmospheric powered descent guidance is required to accommodate nonlinear dynamics and more disturbing flight conditions, including engine thrust fluctuation, aerodynamic uncertainty, and winds. For example, the winds can produce a persistent aerodynamic force disturbance on the rocket, resulting in ...
2024-12-24
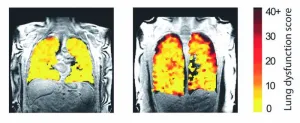
A new method of scanning lungs is able to show the effects of treatment on lung function in real time and enable experts to see the functioning of transplanted lungs.
This could enable medics to identify sooner any decline in lung function.
The scan method has enabled the team, led by researchers at Newcastle University, UK, to see how air moves in and out of the lungs as people take a breath in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and patients who have received a lung transplant.
Publishing two complementary papers in Radiology and JHLT Open, the team explain how they ...
2024-12-24
Iceland has a long and rich literary tradition. With its 380,000 inhabitants, Iceland has produced many great writers, and it is said that one in two Icelanders writes books. The literary tradition stretches all the way back to the Middle Ages.
“Previously, the theory was that Iceland was so dark and barren that the Icelanders had to fill their lives with storytelling and poetry to compensate for this. But Icelanders were certainly part of Europe and had a lot of contact with Britain, Germany, Denmark and ...
2024-12-24
SAN ANTONIO, Texas, USA, 17 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, researchers from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and Hirosaki University have uncovered critical new insights into the developmental trajectory of social behaviors in fragile X syndrome, the leading genetic cause of autism spectrum disorder.
The study, published in Genomic Psychiatry, demonstrates that treating pregnant mice with bumetanide - a drug that regulates chloride levels ...
2024-12-24
REGENSBURG, Bavaria, Germany, 24 December 2024 – In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Professor Inga Neumann, Chair of the Department of Behavioural and Molecular Neurobiology at the University of Regensburg, reveals groundbreaking insights into how oxytocin shapes social behavior and emotional responses in the brain.
The interview, published in Brain Medicine (DOI: 10.61373/bm024k.0139), showcases Professor Neumann's pioneering research on neuropeptides, particularly oxytocin, which has evolved far beyond its popular characterization ...
2024-12-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE ON MONDAY, DECEMBER 23, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Improving your brain health in the new year can start with a simple step, talking with your neurologist or primary care physician about 12 factors to protect your brain. The factors are outlined in an Emerging Issues in Neurology article developed by the American Academy of Neurology and published in the December 16, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Neurologists are the experts in brain health, with the training and insight needed to help you ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cooking sulfur-containing vegetables can promote the formation of trans-fatty acids
New study reveal that garlic and onions contain chemicals that can transform into trans fats when cooked at high temperatures