(Press-News.org) About 1 in 3 adults in the United States have prediabetes, a condition where blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
Affecting 98 million adults, prediabetes can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes.
While it can be reversed, 8 in 10 adults are unaware that they even have prediabetes.
To counter this growing problem, the National Diabetes Prevention Program was created by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2010 to offer an effective way to help prevent type 2 diabetes.
This national effort brought together private insurers, health care organizations, employers, community organizations, and government agencies.
Although cost-effectiveness evaluations of the program have been conducted previously, those studies focused on clinical trials and therefore provided limited information about diabetes prevention in real-world settings.
In a paper, published in Diabetes Care, researchers at the University of Michigan evaluated the uptake and outcomes of the National DPP using surveys from 5,948 university employees, dependents and retirees with prediabetes over two years.
Beginning in 2015, the University of Michigan offered the National DPP at no out-of-pocket cost to university employees, dependents,and retirees who were 18 years or older with prediabetes and belonged to the university’s health insurance program.
“We realized that there was finally an opportunity to evaluate the real-world economic impact of the National DPP,” said Shihchen Kuo, associate research scientist at the Caswell Diabetes Institute.
“Our results can inform policy decisions about the program’s scalability and sustainability.”
National DPP helps enrollees make key lifestyle changes
The year-long program focuses on teaching participants to make lasting changes: eating healthier, adding physical activity into their daily routines, and improving coping skills.
To do so, the participating organizations follow a CDC-approved curriculum, facilitate sessions with trained Lifestyle Coaches, and submit data on the efficacy of the program to the CDC.
“In the first six months, participants meet weekly to learn skills that help them improve their overall health. After that, they meet monthly to build on the skills they learned to maintain their positive changes,” Kuo said.
“An important component of the program is that it can be delivered in person, through online learning, or as a combination of the two.”
Enrollees saved over $5,000 in direct medical costs
Among the participants, 575 enrolled in the National DPP.
Over two years, they saved ~$5,000 in medical costs primarily due to lower costs of hospitalizations, outpatient visits, and emergency room visits.
The researchers also evaluated participants’ quality-of-life using a system called the EuroQol 5-Dimension 5-Level questionnaire, which assesses mobility, self-care, usual activities, discomfort and anxiety across five levels of how problematic each dimension is to the individual.
“We found that although the quality-of-life was unchanged, those in the National DPP had a lower probability of developing diabetes,” Kuo said.
The researchers are expanding the study to include a longer follow-up period.
The current work included data from the one-year intervention and one-year observational follow-up period, which is a relatively short time frame.
Many of the previous studies adopted a three-year time frame, which allowed them to detect longer-term changes in costs and quality-of-life.
“We also need to include more people in our study. Unfortunately, only 9.6% of the eligible population participated in the National DPP and, therefore, we couldn’t draw any conclusions on which mode of delivery worked the best, whether different patient populations showed similar results, and if the reduced medical costs were due to lower rates of hospitalization or shorter hospital stays,” Kuo said.
Additional authors: Wen Ye, Di Wang, Laura McEwen, Claudia Villatoro Santos, and William H. Herman.
Funding/disclosures: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases under R01DK109995 and P30DK092926 and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through grant U18DP006712.
Paper cited: “Cost-Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Prevention Program: A Real-World, 2-Year Prospective Study,” Diabetes Care. DOI: 10.2337/dc24-1110.
END
National Diabetes Prevention Program saves costs for enrollees
Participants also reduced their risk of developing diabetes over two years
2025-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research team to study critical aspects of Alzheimer’s and dementia healthcare delivery
2025-01-03
Kosali Simon, PhD, M.A., a professor with the Paul H. O’Neill School of Public and Environmental Affairs and a Regenstrief Institute research scientist; and Katherine Baicker, PhD, University of Chicago provost, will co-lead an expected nearly $16 million National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Aging (NIA) program to explore critical aspects of healthcare delivery for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD).
This five-year research initiative aims to identify and address barriers to equitable and effective healthcare for this growing patient population. The ...
Major breakthrough for ‘smart cell’ design
2025-01-03
HOUSTON – (Jan. 3, 2025) – Rice University bioengineers have developed a new construction kit for building custom sense-and-respond circuits in human cells. The research, published in the journal Science, represents a major breakthrough in the field of synthetic biology that could revolutionize therapies for complex conditions like autoimmune disease and cancer.
“Imagine tiny processors inside cells made of proteins that can ‘decide’ how to respond to specific signals like inflammation, tumor growth markers or blood sugar levels,” said Xiaoyu Yang, a graduate ...
From CO2 to acetaldehyde: Towards greener industrial chemistry
2025-01-03
Acetaldehyde is a vital chemical used in making everything from perfumes to plastics. Today, its production largely relies on ethylene, a petrochemical. But increasing environmental concerns are pushing the chemical industry to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels, so scientists have been searching for greener ways to produce acetaldehyde.
Currently, acetaldehyde is produced through the so-called “Wacker process”, a chemical synthesis method that uses ethylene from oil and natural gas with other chemicals such as strong acids, i.e. hydrochloric acid. The Wacker process not only has a large carbon footprint ...
Unlocking proteostasis: A new frontier in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's
2025-01-03
Scientists have uncovered a powerful ally in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases: a nucleolar complex that plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular health through protein homeostasis (proteostasis), by which cells maintain the balance and proper functioning of their proteins. By suppressing this complex, researchers have shown it’s possible to dramatically reduce the toxic effects of Alzheimer’s-causing proteins, boosting the cell’s natural defenses through enhanced degradation of hazardous proteins. This mechanism regulates proteostasis across tissues by modulating TGF-β signaling, a pathway involved in cell growth, differentiation, ...
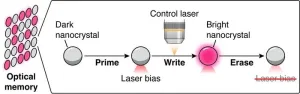
New nanocrystal material a key step toward faster, more energy-efficient computing
2025-01-03
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists including an Oregon State University chemistry researcher have taken a key step toward faster, more energy-efficient artificial intelligence, and data processing in general, with the discovery of luminescent nanocrystals that can be quickly toggled from light to dark and back again.
“The extraordinary switching and memory capabilities of these nanocrystals may one day become integral to optical computing – a way to rapidly process and store information using light particles, which travel faster than anything in the ...
One of the world’s largest social programs greatly reduced tuberculosis among the most vulnerable
2025-01-03
Brazil’s Bolsa Família Program (BFP), one of the world’s largest conditional cash transfer programmes, was responsible for the reduction of more than half the number of tuberculosis cases and deaths among those living in extreme poverty and indigenous groups, shows a large study coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, the Institute of Collective Health, and the CIDACS-FIOCRUZ in Bahia, Brazil. The findings, published in Nature ...
Surprising ‘two-faced’ cancer gene role supports paradigm shift in predicting disease
2025-01-03
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10AM (UK TIME) FRIDAY 3 JANUARY 2025.
Peer reviewed | Observational study | Cells
A genetic fault long believed to drive the development of oesophageal cancer may in fact play a protective role early in the disease, according to new research published in Nature Cancer. This unexpected discovery could help doctors identify which individuals are at greater risk of developing cancer, potentially leading to more personalised and effective preventive strategies.
“We ...
Growing divide: Agricultural climate policies affect food prices differently in poor and wealthy countries
2025-01-03
“In high-income countries like the U.S. or Germany, farmers receive less than a quarter of food spending, compared to over 70 percent in Sub-Saharan Africa, where farming costs make up a larger portion of food prices,” says David Meng-Chuen Chen, PIK scientist and lead author of the study published in Nature Food. “This gap underscores how differently food systems function across regions.” The researchers project that as economies develop and food systems industrialise, farmers will increasingly receive a smaller share of consumer spending, a measure known as the ‘farm ...
New approaches against metastatic breast cancer: mini-tumors from circulating cancer cells
2025-01-03
Tumor cells circulating in the blood are the “germ cells” of breast cancer metastases. They are very rare and could not be propagated in the culture dish until now, which made research into therapy resistance difficult. A team from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), the Heidelberg Stem Cell Institute HI-STEM* and the NCT Heidelberg** has now succeeded for the first time in cultivating stable tumor organoids directly from blood samples of breast cancer patients. Using these mini-tumors, the researchers ...
Loneliness linked to higher risk of heart disease and stroke and susceptibility to infection
2025-01-03
Interactions with friends and family may keep us healthy because they boost our immune system and reduce our risk of diseases such as heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes, new research suggests.
Researchers from the UK and China drew this conclusion after studying proteins from blood samples taken from over 42,000 adults recruited to the UK Biobank. Their findings are published today in the journal Nature Human Behaviour.
Social relationships play an important role in our wellbeing. Evidence increasingly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] National Diabetes Prevention Program saves costs for enrolleesParticipants also reduced their risk of developing diabetes over two years