(Press-News.org) A new study led by researchers at the American Museum of Natural History presents the oldest known example in the fossil record of an evolutionary arms race. These 517-million-year-old predator-prey interactions occurred in the ocean covering what is now South Australia between a small, shelled animal distantly related to brachiopods and an unknown marine animal capable of piercing its shell. Described today in the journal Current Biology, the study provides the first demonstrable record of an evolutionary arms race in the Cambrian.
“Predator-prey interactions are often touted as a major driver of the Cambrian explosion, especially with regard to the rapid increase in diversity and abundance of biomineralizing organisms at this time. Yet, there has been a paucity of empirical evidence showing that prey directly responded to predation, and vice versa,” said Russell Bicknell, a postdoctoral researcher in the Museum’s Division of Paleontology and lead author of the study.
An evolutionary arms race is a process where predators and prey continuously adapt and evolve in response to each other. This dynamic is often described as an arms race because one species’ improved abilities lead to the other species improving its abilities in response.
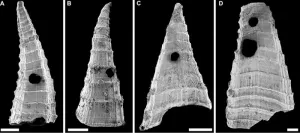
Bicknell and colleagues from the University of New England and Macquarie University—both in Australia—studied a large sample of fossilized shells of an early Cambrian tommotiid species, Lapworthella fasciculata, from South Australia. More than 200 of these extremely small specimens, ranging in size from slightly larger than a grain of sand to just smaller than an apple seed, have holes that were likely made by a hole-punching predator—most likely a kind of soft-bodied mollusk or worm. The researchers analyzed these specimens in relation to their geologic ages, finding an increase in shell wall thickness that coincides with an increase in the number of perforated shells in a short amount of time. This suggests that a microevolutionary arms race was in place, with L. fasciculata finding a way to fortify its shell against predation and the predator, in turn, investing in the ability to puncture its prey despite its ever-bulkier armor.
“This critically important evolutionary record demonstrates, for the first time, that predation played a pivotal role in the proliferation of early animal ecosystems and shows the rapid speed at which such phenotypic modifications arose during the Cambrian Explosion event,” Bicknell says.
This research was funded in part by the University of New England, the American Museum of Natural History, and the Australian Research Council (grant #s DP200102005 and DE190101423).
Study DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.12.007
ABOUT THE AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY (AMNH)
The American Museum of Natural History, founded in 1869 with a dual mission of scientific research and science education, is one of the world’s preeminent scientific, educational, and cultural institutions. The Museum encompasses more than 40 permanent exhibition halls, galleries for temporary exhibitions, the Rose Center for Earth and Space including the Hayden Planetarium, and the Richard Gilder Center for Science, Education, and Innovation. The Museum’s scientists draw on a world-class permanent collection of more than 30 million specimens and artifacts, some of which are billions of years old, and on one of the largest natural history libraries in the world. Through its Richard Gilder Graduate School, the Museum offers two of the only free-standing, degree-granting programs of their kind at any museum in the U.S.: the Ph.D. program in Comparative Biology and the Master of Arts in Teaching (MAT) Earth Science residency program. Visit amnh.org for more information.
END
Study reveals oldest-known evolutionary “arms race”
Hundreds of punctured shells from the Cambrian illuminate unique predator-prey interactions in the ocean 517 million years ago
2025-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
People find medical test results hard to understand, increasing overall worry
2025-01-03
In April 2021, a provision in the 21st Century Cures act took effect which required that all medical test results be released to a patient’s electronic medical record as soon as they become available.
As a result of this newer law, many patients are seeing and reading their test results even before their doctor has.
The problem is that many medical reports aren’t written with patients in mind.
For example, “a standard pathology report is written by a pathologist for a clinical specialist like a surgeon or ...
Mizzou researchers aim to reduce avoidable hospitalizations for nursing home residents with dementia
2025-01-03
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- For many nursing home residents, a trip to the hospital can be a jarring experience — one that leaves them confused and stressed. Yet avoidable transfers happen far too often, not only disrupting a resident’s routine but also costing the U.S. healthcare system $2.6 billion annually.
When researchers at the University of Missouri recently looked at the decision-making process for whether or not to transfer nursing home residents to the hospital, they quickly discovered that it’s complicated — particularly for residents with cognitive impairment who may not ...
National Diabetes Prevention Program saves costs for enrollees
2025-01-03
About 1 in 3 adults in the United States have prediabetes, a condition where blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
Affecting 98 million adults, prediabetes can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes.
While it can be reversed, 8 in 10 adults are unaware that they even have prediabetes.
To counter this growing problem, the National Diabetes Prevention Program was created by the Centers for Disease Control and ...
Research team to study critical aspects of Alzheimer’s and dementia healthcare delivery
2025-01-03
Kosali Simon, PhD, M.A., a professor with the Paul H. O’Neill School of Public and Environmental Affairs and a Regenstrief Institute research scientist; and Katherine Baicker, PhD, University of Chicago provost, will co-lead an expected nearly $16 million National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Aging (NIA) program to explore critical aspects of healthcare delivery for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD).
This five-year research initiative aims to identify and address barriers to equitable and effective healthcare for this growing patient population. The ...
Major breakthrough for ‘smart cell’ design
2025-01-03
HOUSTON – (Jan. 3, 2025) – Rice University bioengineers have developed a new construction kit for building custom sense-and-respond circuits in human cells. The research, published in the journal Science, represents a major breakthrough in the field of synthetic biology that could revolutionize therapies for complex conditions like autoimmune disease and cancer.
“Imagine tiny processors inside cells made of proteins that can ‘decide’ how to respond to specific signals like inflammation, tumor growth markers or blood sugar levels,” said Xiaoyu Yang, a graduate ...
From CO2 to acetaldehyde: Towards greener industrial chemistry
2025-01-03
Acetaldehyde is a vital chemical used in making everything from perfumes to plastics. Today, its production largely relies on ethylene, a petrochemical. But increasing environmental concerns are pushing the chemical industry to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels, so scientists have been searching for greener ways to produce acetaldehyde.
Currently, acetaldehyde is produced through the so-called “Wacker process”, a chemical synthesis method that uses ethylene from oil and natural gas with other chemicals such as strong acids, i.e. hydrochloric acid. The Wacker process not only has a large carbon footprint ...
Unlocking proteostasis: A new frontier in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's
2025-01-03
Scientists have uncovered a powerful ally in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases: a nucleolar complex that plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular health through protein homeostasis (proteostasis), by which cells maintain the balance and proper functioning of their proteins. By suppressing this complex, researchers have shown it’s possible to dramatically reduce the toxic effects of Alzheimer’s-causing proteins, boosting the cell’s natural defenses through enhanced degradation of hazardous proteins. This mechanism regulates proteostasis across tissues by modulating TGF-β signaling, a pathway involved in cell growth, differentiation, ...
New nanocrystal material a key step toward faster, more energy-efficient computing
2025-01-03
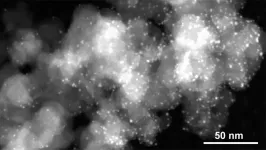
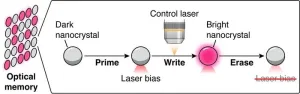
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists including an Oregon State University chemistry researcher have taken a key step toward faster, more energy-efficient artificial intelligence, and data processing in general, with the discovery of luminescent nanocrystals that can be quickly toggled from light to dark and back again.
“The extraordinary switching and memory capabilities of these nanocrystals may one day become integral to optical computing – a way to rapidly process and store information using light particles, which travel faster than anything in the ...
One of the world’s largest social programs greatly reduced tuberculosis among the most vulnerable
2025-01-03
Brazil’s Bolsa Família Program (BFP), one of the world’s largest conditional cash transfer programmes, was responsible for the reduction of more than half the number of tuberculosis cases and deaths among those living in extreme poverty and indigenous groups, shows a large study coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, the Institute of Collective Health, and the CIDACS-FIOCRUZ in Bahia, Brazil. The findings, published in Nature ...
Surprising ‘two-faced’ cancer gene role supports paradigm shift in predicting disease
2025-01-03
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10AM (UK TIME) FRIDAY 3 JANUARY 2025.
Peer reviewed | Observational study | Cells
A genetic fault long believed to drive the development of oesophageal cancer may in fact play a protective role early in the disease, according to new research published in Nature Cancer. This unexpected discovery could help doctors identify which individuals are at greater risk of developing cancer, potentially leading to more personalised and effective preventive strategies.
“We ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] Study reveals oldest-known evolutionary “arms race”Hundreds of punctured shells from the Cambrian illuminate unique predator-prey interactions in the ocean 517 million years ago