(Press-News.org) Children and young people with high levels of mental health needs are struggling to receive the help they need, or to have their difficulties recognised, according to a new study.
The STADIA trial, which is published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, was led by experts from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, and was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
The large study, which spans different parts of England, involved 1,225 children and young people with emotional difficulties who had been referred to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) for help, and followed them up over 18 months to see how they got on.
The children and young people in this group were found to have high levels of mental health needs, with 67% scoring very high for at least one emotional disorder, most commonly depression or an anxiety disorder. Despite this, only 11% received a clinical diagnosis of an emotional disorder from CAMHS.
Only 44% of children and young people had their referral to CAMHS accepted, and 35% required a re-referral to CAMHS, suggesting that there were delays in receiving help.
One year after their referral, these children and young people did not seem to improve. Their mental health difficulties continued to remain at a severe level over this period, with high levels of self-reported and parent-reported mental health symptoms, functional impairment, and self-harm thoughts and behaviour, even at 12 months follow-up.
At 18 months follow-up, less than half (47%) had been offered any treatment or intervention from CAMHS.
Professor Kapil Sayal, from the School of Medicine and the STADIA Chief Investigator said: “We are very concerned that many children and young people with high levels of mental health needs, particularly conditions such as depression and anxiety disorders, for which NICE-recommended evidence-based interventions are available, are struggling to access help and have their difficulties appropriately recognised. One year is a very long time in a child's life - delays in accessing the right care mean that their difficulties and distress, and the associated impact on their day-to-day lives and activities, are being unnecessarily prolonged.”
The results of the study also found that:
The completion of an online standardised diagnostic assessment tool by young people and parents, soon after the referral had been received by CAMHS, did not impact on receiving a clinical diagnosis from CAMHS.
Online/digital approaches to diagnostic assessment are highly acceptable to families and young people who have been referred to CAMHS, which suggests a way forward for offering and optimising access to the right help and support - as long as there is sufficient investment in CAMHS to properly implement this.
Professor Sayal adds: “It needs to be kept in mind that the time period of the study (reflecting referrals to CAMHS between 2019 and 2021) spanned the COVID-19 pandemic, with associated national lockdown and school closures – a time when many children and young people experienced greater levels of uncertainty, stress and mental health difficulties. Over the past few years, referrals to CAMHS have gone up considerably, which unfortunately has meant that not everyone who could benefit from support has been able to receive timely help and support.”
Colleen Ewart, Parent and STADIA Co-investigator and Patient & Public Involvement lead said: “Sadly, the stories I hear from young people and their parents or carers still echo our family experience of 15 years ago. We can and must do better for this generation of children and young people and those to come. Reducing delays in accessing the right help and quickly is essential to save untold suffering (often life-long) for children, young people and their families."
The research was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), and led by Nottinghamshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust, the University of Nottingham and the Nottingham Clinical Trials Unit, in partnership with other NHS Trusts.
END
Many children and young people with diagnosable mental health disorders are not receiving timely help, says new research
2025-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dinosaurs roamed the northern hemisphere millions of years earlier than previously thought, according to new analysis of the oldest North American fossils
2025-01-08
MADISON — How and when did dinosaurs first emerge and spread across the planet more than 200 million years ago? That question has for decades been a source of debate among paleontologists faced with fragmented fossil records. The mainstream view has held that the reptiles emerged on the southern portion of the ancient supercontinent Pangea called Gondwana millions of years before spreading to the northern half named Laurasia.
But now, a newly described dinosaur whose fossils were uncovered by University of Wisconsin–Madison paleontologists is challenging ...
Breakthrough Durham University research offers new insights into quenching electrical waves in the heart
2025-01-08
-With images-
Scientists at Durham University have developed a theoretical framework to predict the efficacy of quenching of electrical pulses in excitable media, such as those found in the human heart.
This breakthrough could significantly accelerate the development of more efficient defibrillation techniques for treating cardiac arrhythmias.
The study, published in Physical Review E, addresses a longstanding challenge in understanding how stable excitation waves in systems like cardiac tissue can be effectively neutralised through small changes.
These electrical waves, when irregular, are thought to underly serious conditions such as fibrillation, ...
SLAC will play a key role in DOE’s new research centers for advancing next-generation microelectronics
2025-01-07
Around the globe day and night, the microelectronics behind much of modern technology help run computers, medical devices and state-of-the-art instruments that power scientific discoveries. But all of that technology consumes energy, and adding artificial intelligence to the mix increases our energy needs dramatically. Some experts caution that this pace of energy usage is unsustainable.
To tackle this challenge, the Department of Energy (DOE) has announced funding $179 million for three Microelectronics ...
Market researchers and online advertisers, are A-B tests leading you astray? A new study says they could be
2025-01-07
Researchers from Southern Methodist University and University of Michigan published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines platforms’ A-B testing of online ads and uncovers significant limitations that can create misleading conclusions about ad performance.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Where A-B Testing Goes Wrong: How Divergent Delivery Affects What Online Experiments Cannot (and Can) Tell You About How Customers Respond to Advertising” and is authored by Michael Braun and Eric M. Schwartz.
Consider a landscaping company whose designs focus ...
Research alert: Ketamine use on the rise in U.S. adults; new trends emerge
2025-01-07
A recent study analyzing data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) found that past-year recreational ketamine use among adults has increased dramatically since 2015, including significant shifts in associations with depression and sociodemographic characteristics such as race, age and education status. Ketamine use has shown promise in clinical trials therapy for several mental illnesses, including treatment-resistant depression, and the new research suggests that ongoing monitoring of recreational use trends is crucial to balancing these ...
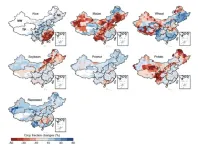
Crop switching for climate change in China
2025-01-07
A study of Chinese agriculture recommends planting areas currently growing maize and rapeseed with alternative crops to reduce environmental costs while maximizing food production as the climate changes.
Chinese food production has nearly doubled since the 1980s, mainly thanks to intensified nutrient usage and irrigation. Given that China’s demand for food is forecast to increase further, Qi Guan and colleagues modeled the country’s agricultural system under varying climate change scenarios in the 21st century, using a dynamic global vegetation model. The authors created scenarios ...
Cell-based therapy improves outcomes in a pig model of heart attacks
2025-01-07
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In a large-animal model study, researchers have found that heart attack recovery is aided by injection of heart muscle cell spheroids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells, or hiPSCs, that overexpress cyclin D2 and are knocked out for human leukocyte antigen classes I and II. This research, published in the journal Circulation Research, used a pig model of heart attacks. Pig hearts more closely resemble the human heart in size and physiology, and thus have a higher clinical relevance to human disease, compared to studies in mice.
University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers, led by Jianyi “Jay” ...
Researchers have a better understanding of how our cells dispose of waste while developing ways to control it
2025-01-07
Recycling takes place in our cells at all times: in a process called autophagy, cell components that are no longer needed are enclosed by membranes and broken down into their basic building blocks. This vital process prevents the formation of harmful aggregates and makes nutrients available again. A research team co-led by Prof. Dr. Claudine Kraft from the CIBSS Cluster of Excellence at the University of Freiburg and Dr. Florian Wilfling from the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt has now discovered the conditions necessary for autophagy to start. They were also able ...
Earth’s air war: Explaining the delayed rise of plants, animals on land
2025-01-07
New Haven, Conn. — If you like the smell of spring roses, the sounds of summer birdsong, and the colors of fall foliage, you have the stabilization of the ozone layer to thank for it. Located in the stratosphere, where it shields the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, the ozone layer plays a key role in preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
And now we may have a better idea of why that took so long — more than 2 billion years — to happen.
According to a new, Yale-led study, ...
More than half of college students report alcohol-related harms from others
2025-01-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Tuesday, January 7, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
More than half of US college students experienced alcohol-related harms caused by others, according to the first national probability-based survey of such harms conducted in 20 years. The findings, published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Review in December, shed light on how others’ drinking affects students’ health, academics, and safety.
“Our research ...