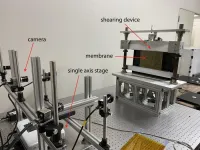
Discovering hidden wrinkles in spacecraft membrane with a single camera
Deformation in thin membrane can be measured using simple method
2025-01-09
(Press-News.org)
Exiting Earth’s gravity takes an enormous amount of fuel and power. Due to this, spacecraft strapped to rockets are limited in their carry capacity and every gram must be accounted for. To lighten the load, thin membranes are being researched as alternative materials, but their plastic wrap property causes wrinkling that can affect operational performance. For this reason, there is a need to develop measurement technology that can accurately detect deformations.
Professor Takashi Iwasa at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Engineering led a team in developing a method for measuring the size of wrinkles that have formed across thin membrane using photogrammetry and a single camera. By examining photographs taken of the surface before and after putting stress on the material, the amplitude and wavelength of wrinkles can be detected. Measurement points are printed on the membrane and changes in their position indicate deformation.
“In the past, multiple cameras were required, but in this research, the size of the wrinkles can be easily detected by applying tension-field theory for the measurement result of a single-camera photogrammetry,” stated Professor Iwasa. “We are conducting this research on large thin membrane spacecraft and expect this method to be used where there is limited space for installing cameras.”
The findings were published in Measurement.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-09
Women are less likely to receive a lung transplant and spend an average of six weeks longer on the waiting list, according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, women who receive a lung transplant are more likely than men to live for five years post-transplant. Based on their findings, the researchers encourage changes in regulation and clinical guidelines to address this inequality.
Lung transplantation is the only treatment for people with end-stage respiratory failure and patients on the waiting list have a high risk ...
2025-01-09
The average life expectancy of people diagnosed with dementia ranges from 9 years at age 60 to 4.5 years at age 85 for women and from 6.5 to just over 2 years, respectively, in men, finds a systematic review of the latest evidence in The BMJ today.
The results also suggest that one third of people with dementia are admitted to a nursing home within three years of diagnosis.
Nearly 10 million people worldwide receive a diagnosis of dementia every year, but survival estimates vary widely, and few ...
2025-01-09
UK supermarket giant Tesco is being urged to drop an “unethical” pilot of an in-store infant feeding advice service in which Danone-funded midwives are expected to wear branded uniforms and undergo training by the formula company, reveals an exclusive news report published by The BMJ today.
Critics say that the initiative, running in Tesco’s flagship store and set to be rolled out shortly, is a backward step and reminiscent of the “milk nurses” scandal of the 1970s, where formula industry salespeople dressed as nurses and promoted formula milk to parents.
One midwife hired by Danone quit ...
2025-01-09
Unraveling the Events Leading to Multiple Sex Chromosomes Using an Echidna Genome Sequence
A nearly gapless genome sequence of the echidna, an egg-laying mammal with multiple sex chromosomes, helps researchers to track genomic reorganization events that gave rise to a highly unusual sex determination system.
The short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) is one of Australia’s most iconic animals. Belonging to a unique group of mammals called “monotremes” (with the platypus as the other prominent member). Echidnas may at first glance be mistaken for a weird-looking hedgehog, ...
2025-01-08
A new study led by Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University and Abramson Cancer Center of University of Pennsylvania researchers demonstrates that a first-of-its-kind platform using artificial intelligence (AI) could help clinicians and patients assess whether and how much an individual patient may benefit from a particular therapy being tested in a clinical trial. This AI platform can help with making informed treatment decisions, understanding the expected benefits of novel therapies and planning ...
2025-01-08
The melding of visual information (microscopic and X-ray images, CT and MRI scans, for example) with text (exam notes, communications between physicians of varying specialties) is a key component of cancer care. But while artificial intelligence helps doctors review images and home in on disease-associated anomalies like abnormally shaped cells, it’s been difficult to develop computerized models that can incorporate multiple types of data.
Now researchers at Stanford Medicine have developed an AI model able to incorporate visual ...
2025-01-08
As computer chips continue to get smaller and more complex, the ultrathin metallic wires that carry electrical signals within these chips have become a weak link. Standard metal wires get worse at conducting electricity as they get thinner, ultimately limiting the size, efficiency, and performance of nanoscale electronics.
In a paper published Jan. 3 in Science, Stanford researchers show that niobium phosphide can conduct electricity better than copper in films that are only a few atoms thick. Moreover, these films can be created and deposited at sufficiently low temperatures to be compatible with modern computer ...
2025-01-08
Chestnut Hill, Mass (01/08/2025) – Nations must start testing and regulating chemicals and chemical products as closely as the current systems that safeguard prescription drugs or risk rising rates of chronic illnesses among children, according to a New England Journal of Medicine report by a group of experts writing as the Consortium for Children’s Environmental Health.
Global chemical inventories contain an estimated 350,000 products – such as manufactured chemicals, chemical ...
2025-01-08
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact: Levi.Gadye@ucsf.edu, (415) 502-6397
Subscribe to UCSF News
The discovery of a new type of stem cell in the brain could usher in better treatments for the deadliest brain tumor.
UCSF scientists have discovered a stem cell in the young brain that’s capable of forming the cells found in tumors. The breakthrough could explain how adult brain cells take advantage of developmental processes to instigate the explosive growth seen in deadly brain cancers like glioblastoma.
They made the discovery while taking a broad genomic survey of human brain ...
2025-01-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. – If you like the smell of spring roses, the sounds of summer birdsong and the colors of fall foliage, you have the stabilization of the ozone layer to thank for it. Located in the stratosphere where it shields the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, the ozone layer plays a key role in preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
Now, we may have a better idea of why that took more than 2 billion years to happen.
Michigan State University researcher Dalton Hardisty contributed to a new Yale University-led study finding that Earth’s early atmosphere hosted a battle royal between ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Discovering hidden wrinkles in spacecraft membrane with a single camera
Deformation in thin membrane can be measured using simple method