(Press-News.org) Key takeaways
Hydroclimate whiplash – rapid swings between intensely wet and dangerously dry weather – has already increased globally due to climate change, with further large increases expected as warming continues, according to a team of researchers led by UCLA’s Daniel Swain.
The “expanding atmospheric sponge,” or the atmosphere’s ability to evaporate, absorb and release 7% more water for every degree Celsius the planet warms, is a key driver of the whiplash.
Co-management of extreme rainfall or extreme droughts, rather than approaching each in isolation, is necessary to find interventions and solutions, researchers said.
Los Angeles is burning, and accelerating hydroclimate whiplash is the key climate connection.
After years of severe drought, dozens of atmospheric rivers deluged California with record-breaking precipitation in the winter of 2022-23, burying mountain towns in snow, flooding valleys with rain and snow melt, and setting off hundreds of landslides.
Following a second extremely wet winter in southern parts of the state, resulting in abundant grass and brush, 2024 brought a record-hot summer and now a record-dry start to the 2025 rainy season, along with tinder-dry vegetation that has since burned in a series of damaging wildfires.
This is just the most recent example of the kind of “hydroclimate whiplash” – rapid swings between intensely wet and dangerously dry weather – that is increasing worldwide, according to a paper published today in Nature Reviews.
“The evidence shows that hydroclimate whiplash has already increased due to global warming, and further warming will bring about even larger increases,” said lead author Daniel Swain, a climate scientist with UCLA and UC Agriculture and Natural Resources. “This whiplash sequence in California has increased fire risk twofold: first, by greatly increasing the growth of flammable grass and brush in the months leading up to fire season, and then by drying it out to exceptionally high levels with the extreme dryness and warmth that followed.”
Global weather records show hydroclimate whiplash has swelled globally by 31% to 66% since the mid-20th century, the international team of climate researchers found – even more than climate models suggest should have happened. Climate change means the rate of increase is speeding up. The same potentially conservative climate models project that the whiplash will more than double if global temperatures rise 3 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The world is already poised to blast past the Paris Agreement’s targeted limit of 1.5 C. The researchers synthesized hundreds of previous scientific papers for the review, layering their own analysis on top.
Anthropogenic climate change is the culprit behind the accelerating whiplash, and a key driver is the “expanding atmospheric sponge” – the growing ability of the atmosphere to evaporate, absorb and release 7% more water for every degree Celsius the planet warms, researchers said.
“The problem is that the sponge grows exponentially, like compound interest in a bank,” Swain said. “The rate of expansion increases with each fraction of a degree of warming.”
The global consequences of hydroclimate whiplash include not only floods and droughts, but the heightened danger of whipsawing between the two, including the bloom-and-burn cycle of overwatered then overdried brush, and landslides on oversaturated hillsides where recent fires removed plants with roots to knit the soil and slurp up rainfall. Every fraction of a degree of warming speeds the growing destructive power of the transitions, Swain said.
Many previous studies of climate whiplash have only considered the precipitation side of the equation, and not the growing evaporative demand. The thirstier atmosphere pulls more water out of plants and soil, exacerbating drought conditions beyond simple lack of rainfall.
“The expanding atmospheric sponge effect may offer a unifying explanation for some of the most visible, visceral impacts of climate change that recently seem to have accelerated,” Swain said. “The planet is warming at an essentially linear pace, but in the last 5 or 10 years there has been much discussion around accelerating climate impacts. This increase in hydroclimate whiplash, via the exponentially expanding atmospheric sponge, offers a potentially compelling explanation.”
That acceleration, and the anticipated increase in boom-and-bust water cycles, has important implications for water management.
“We can’t look at just extreme rainfall or extreme droughts alone, because we have to safely manage these increasingly enormous influxes of water, while also preparing for progressively drier interludes,” Swain said. “That's why ‘co-management’ is an important paradigm. It leads you to more holistic conclusions about which interventions and solutions are most appropriate, compared to considering drought and flood risk in isolation.”
In many regions, traditional management designs include shunting flood waters to flow quickly into the ocean, or slower solutions like allowing rain to percolate into the water table. However, taken alone, each option leaves cities vulnerable to the other side of climate whiplash, the researchers noted.
“Hydroclimate in California is reliably unreliable,” said co-author John Abatzoglou, a UC Merced climate scientist. “However, swings like we saw a couple years ago, going from one of the driest three-year periods in a century to the once-in-a-lifetime spring 2023 snowpack, both tested our water-infrastructure systems and furthered conversations about floodwater management to ensure future water security in an increasingly variable hydroclimate.”
Hydroclimate whiplash is projected to increase most across northern Africa, the Middle East, South Asia, northern Eurasia, the tropical Pacific and the tropical Atlantic, but most other regions will also feel the shift.
“Increasing hydroclimate whiplash may turn out to be one of the more universal global changes on a warming Earth,” Swain said.
In California this week, although winds are fanning the extreme fires, it’s the whiplash-driven lack of rain that suspended Southern California in fire season.
“There's not really much evidence that climate change has increased or decreased the magnitude or likelihood of the wind events themselves in Southern California,” Swain said. “But climate change is increasing the overlap between extremely dry vegetation conditions later in the season and the occurrence of these wind events. This, ultimately, is the key climate change connection to Southern California wildfires.”
Under a high warming scenario, California will see an increase in both the wettest and driest years and seasons by later this century.
“The less warming there is, the less of an increase in hydroclimate whiplash we're going to see,” Swain said. “So anything that would reduce the amount of warming from climate change will directly slow or reduce the increase in whiplash. Yet we are currently still on a path to experience between 2 degrees and 3 degrees Celsius of global warming this century — so substantial further increases in whiplash are likely in our future, and we really need to be accounting for this in risk assessments and adaptation activities.”
The research was supported with funding from The Nature Conservancy of California and the Swiss National Science Foundation.
END
Floods, droughts, then fires: Hydroclimate whiplash is speeding up globally
New research links intensifying wet and dry swings to the atmosphere’s sponge-like ability to drop and absorb water
2025-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists fuel sustainable future with catalyst for hydrogen from ammonia
2025-01-09
Scientists have created a catalyst for hydrogen generation from ammonia that becomes more active with time, and by counting atoms revealed changes that boost the catalyst’s performance.
A research team from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry, in collaboration with the University of Birmingham and Cardiff University, has developed a novel material consisting of nanosized ruthenium (Ru) clusters anchored on graphitized carbon. These Ru nanoclusters react with ammonia molecules, catalysing splitting ammonia into ...
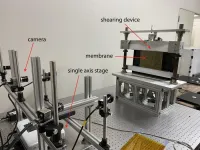
Discovering hidden wrinkles in spacecraft membrane with a single camera
2025-01-09
Exiting Earth’s gravity takes an enormous amount of fuel and power. Due to this, spacecraft strapped to rockets are limited in their carry capacity and every gram must be accounted for. To lighten the load, thin membranes are being researched as alternative materials, but their plastic wrap property causes wrinkling that can affect operational performance. For this reason, there is a need to develop measurement technology that can accurately detect deformations.
Professor Takashi Iwasa at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Engineering led a team in developing a method for measuring the size of wrinkles ...
Women are less likely to get a lung transplant than men and they spend six weeks longer on the waiting list
2025-01-09
Women are less likely to receive a lung transplant and spend an average of six weeks longer on the waiting list, according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, women who receive a lung transplant are more likely than men to live for five years post-transplant. Based on their findings, the researchers encourage changes in regulation and clinical guidelines to address this inequality.
Lung transplantation is the only treatment for people with end-stage respiratory failure and patients on the waiting list have a high risk ...
Study sheds more light on life expectancy after a dementia diagnosis
2025-01-09
The average life expectancy of people diagnosed with dementia ranges from 9 years at age 60 to 4.5 years at age 85 for women and from 6.5 to just over 2 years, respectively, in men, finds a systematic review of the latest evidence in The BMJ today.
The results also suggest that one third of people with dementia are admitted to a nursing home within three years of diagnosis.
Nearly 10 million people worldwide receive a diagnosis of dementia every year, but survival estimates vary widely, and few ...
Tesco urged to drop an “unethical” in-store infant feeding advice service pilot
2025-01-09
UK supermarket giant Tesco is being urged to drop an “unethical” pilot of an in-store infant feeding advice service in which Danone-funded midwives are expected to wear branded uniforms and undergo training by the formula company, reveals an exclusive news report published by The BMJ today.
Critics say that the initiative, running in Tesco’s flagship store and set to be rolled out shortly, is a backward step and reminiscent of the “milk nurses” scandal of the 1970s, where formula industry salespeople dressed as nurses and promoted formula milk to parents.
One midwife hired by Danone quit ...
Unraveling the events leading to multiple sex chromosomes using an echidna genome sequence
2025-01-09
Unraveling the Events Leading to Multiple Sex Chromosomes Using an Echidna Genome Sequence
A nearly gapless genome sequence of the echidna, an egg-laying mammal with multiple sex chromosomes, helps researchers to track genomic reorganization events that gave rise to a highly unusual sex determination system.
The short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) is one of Australia’s most iconic animals. Belonging to a unique group of mammals called “monotremes” (with the platypus as the other prominent member). Echidnas may at first glance be mistaken for a weird-looking hedgehog, ...
New AI platform identifies which patients are likely to benefit most from a clinical trial
2025-01-08
A new study led by Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University and Abramson Cancer Center of University of Pennsylvania researchers demonstrates that a first-of-its-kind platform using artificial intelligence (AI) could help clinicians and patients assess whether and how much an individual patient may benefit from a particular therapy being tested in a clinical trial. This AI platform can help with making informed treatment decisions, understanding the expected benefits of novel therapies and planning ...
Unique Stanford Medicine-designed AI predicts cancer prognoses, responses to treatment
2025-01-08
The melding of visual information (microscopic and X-ray images, CT and MRI scans, for example) with text (exam notes, communications between physicians of varying specialties) is a key component of cancer care. But while artificial intelligence helps doctors review images and home in on disease-associated anomalies like abnormally shaped cells, it’s been difficult to develop computerized models that can incorporate multiple types of data.
Now researchers at Stanford Medicine have developed an AI model able to incorporate visual ...
A new ultrathin conductor for nanoelectronics
2025-01-08
As computer chips continue to get smaller and more complex, the ultrathin metallic wires that carry electrical signals within these chips have become a weak link. Standard metal wires get worse at conducting electricity as they get thinner, ultimately limiting the size, efficiency, and performance of nanoscale electronics.
In a paper published Jan. 3 in Science, Stanford researchers show that niobium phosphide can conduct electricity better than copper in films that are only a few atoms thick. Moreover, these films can be created and deposited at sufficiently low temperatures to be compatible with modern computer ...
Synthetic chemicals and chemical products require a new regulatory and legal approach to safeguard children’s health
2025-01-08
Chestnut Hill, Mass (01/08/2025) – Nations must start testing and regulating chemicals and chemical products as closely as the current systems that safeguard prescription drugs or risk rising rates of chronic illnesses among children, according to a New England Journal of Medicine report by a group of experts writing as the Consortium for Children’s Environmental Health.
Global chemical inventories contain an estimated 350,000 products – such as manufactured chemicals, chemical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
[Press-News.org] Floods, droughts, then fires: Hydroclimate whiplash is speeding up globallyNew research links intensifying wet and dry swings to the atmosphere’s sponge-like ability to drop and absorb water