Science behind genetic testing for identifying risk of opioid misuse remains unproven
A new report from researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Crescenz VA Medical Center evaluated a genetic test for opioid use disorder that recently received pre-marketing approval by the FDA, finding that the genes co
2025-01-09
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA—Opioid misuse and specifically opioid use disorder (OUD), continues to represent a significant U.S. public health threat, with more than 6 million Americans aged 12 and older meeting the criteria for OUD in 2022. Efforts to ease the crisis have included the development of genetic testing to identify individuals most at risk for OUD. New research, out today in JAMA Network Open, questions the usefulness of 15 genetic variants from an algorithm meant to predict OUD risk that was recently granted pre-marketing approval by the Food and Drug Administration. It found that the testing could lead to both false positive and false negative results.
The study was led by Christal Davis, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Philadelphia-based Crescenz VA Medical Center and Henry Kranzler, MD, a professor of Psychiatry and the director of the Center for Studies of Addiction.
“These findings underscore the need for more robust and complete data, particularly given the complex nature of psychiatric conditions, including OUD,” Kranzler said. “The potential harms deriving from a faulty genetic test for OUD include both false negatives and false positives.”
For example, if the test wrongly identifies patients as being at low risk of OUD, they may have a false sense of security taking opioids, and providers may prescribe opioids to those who could become addicted. Patients who falsely test for a high risk of OUD may be denied an effective form of pain relief, in addition to potentially facing stigma.
The case-control study drew upon health record data from more than 450,000 participants with opioid exposure in the Million Veteran Program (MVP), including more than 33,000 individuals with OUD. It showed that the 15 single nucleotide variants (SNVs) purported to predict OUD risk were not useful in identifying OUD, as they had high rates of both false negative and false positive results. With 47 of 100 cases misidentified, the results are equivalent to a coin toss.
A related letter by a group of psychiatric geneticists, including Drs. Davis and Kranzler, was recently published in Lancet Psychiatry. It outlines key factors that regulators should consider for this and future proposed genetic testing for OUD and other psychiatric disorders. These considerations include the significant environmental contribution to psychiatric disorders and how differences in genetic ancestry and an individual’s life experiences need to be considered when predicting risk for OUD or other psychiatric disorders.
This study was supported principally by the Million Veteran Program, a research initiative of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs that studies how genes, lifestyle, military experiences, and other exposures impact health and wellness in veterans, with grant support provided by the awards I01 BX003341 and IK2 CX002336 from the VA; the VISN 4 Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center; grant K01 AA028292 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, and grant P30 DA046345 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
###
Penn Medicine is one of the world’s leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, excellence in patient care, and community service. The organization consists of the University of Pennsylvania Health System and Penn’s Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine, founded in 1765 as the nation’s first medical school.
The Perelman School of Medicine is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $550 million awarded in the 2022 fiscal year. Home to a proud history of “firsts” in medicine, Penn Medicine teams have pioneered discoveries and innovations that have shaped modern medicine, including recent breakthroughs such as CAR T cell therapy for cancer and the mRNA technology used in COVID-19 vaccines.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System’s patient care facilities stretch from the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania to the New Jersey shore. These include the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Penn Presbyterian Medical Center, Chester County Hospital, Lancaster General Health, Penn Medicine Princeton Health, and Pennsylvania Hospital—the nation’s first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional facilities and enterprises include GSPP Rehabilitation, Penn Medicine at Home, Lancaster Behavioral Health Hospital, and Princeton House Behavioral Health, among others.
Penn Medicine is an $11.1 billion enterprise powered by more than 49,000 talented faculty and staff.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-09
LA JOLLA (January 9, 2025)—Plants may burrow into the ground and stretch toward the sun, but they’re ultimately stuck where they sprout—at the mercy of environmental threats like temperature, drought, and microbial infection. To compensate for their inability to up and move when danger strikes, many plants have evolved ways to protect themselves by altering their physiology, such as building armor around parts of their body and roots called the periderm. However, since many plant biologists who study tissue development ...
2025-01-09
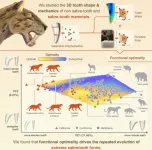
Sabre-toothed predators – best know from the infamous Smilodon – evolved multiple times across different mammal groups. A new study, published today in Current Biology reveals why: these teeth were ‘functionally optimal’ and highly effective at puncturing prey.
The study, led by scientists at the University of Bristol in collaboration with Monash University shows that long, sharp blade-like teeth gave sabre-tooth’s a real advantage as ...
2025-01-09
Russell W. Jenkins, MD, PhD, a physician investigator in the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at the Mass General Cancer Center and an assistant professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, is senior author of a new study in Cancer Immunology Research, “TBK1 is Identified as a Therapeutic Strategy to Enhance CAR T-Cell Efficacy Using Patient-Derived Organotypic Tumor Spheroids”.
The study was a collaboration with the late Soldano Ferrone, MD, PhD, and was carried across the finish line by his daughter Cristina Ferrone, MD, Moshe Sade-Feldman, PhD, and several other collaborators ...
2025-01-09
Which medicine is best when you are affected by cancer? This can vary from person to person. A new method can help people with a specific type of blood cancer get the best medicine for them.
“The new method can help those affected by chronic myelogenous leukemia,” says Jennifer Sheehan, a PhD research fellow from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Production at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). Sheehan was first author of a new publication in PLOS Computational Biology that describes ...
2025-01-09
Miami (January 9, 2025) – Additional research addressing the connection between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and metabolic syndrome is needed to improve holistic patient care, according to a new editorial. The editorial is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke ...
2025-01-09
A Mount Sinai-led team of researchers has enhanced an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered algorithm to analyze video recordings of clinical sleep tests, ultimately improving accurate diagnosis of a common sleep disorder affecting more than 80 million people worldwide. The study findings were published in the journal Annals of Neurology on January 9.
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a sleep condition that causes abnormal movements, or the physical acting out of dreams, during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep. RBD that occurs in otherwise healthy adults ...
2025-01-09
The Kinsey Institute at Indiana University has acquired remarkable archives from three pioneering figures in the study of human sexuality, relationships, and wellbeing: the legendary sex therapist Dr. Ruth Westheimer, renowned anthropologist Dr. Helen Fisher, and respected feminist historian Dr. Judith Allen. These invaluable collections represent decades of groundbreaking research, education, and cultural contributions that will advance future scholarship and research.
“For almost 80 ...
2025-01-09
An innovative project jointly funded by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) brings together a team of scientists from Florida Atlantic University and Lehigh University, along with a team from Japan that includes researchers from Kyoto University, University of Tokyo and Kumamoto University.
The project, titled “NSF-JST: An Inclusive Human-Centered Risk Management Modeling Framework for Flood Resilience,” is supported by a three-year, $1 million award split evenly between the U.S. and Japanese teams, with the U.S. team receiving $499,271. ...
2025-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Tracking coyote movement in metropolitan areas shows the animals spend lots of time in natural settings, but a new study suggests the human element of city life has a bigger impact than the environment on urban coyote survival.
Researchers monitoring coyotes in Chicago found that habitat – areas with relatively high levels of vegetation cover and low levels of human infrastructure – did not influence coyote survival in positive or negative ways. Instead, areas densely populated with humans were ...
2025-01-09
Given that today’s children will inherit the consequences of climate change, schools are instrumental in mobilizing a global response to the climate crisis, a science educator argues.
Climate literacy advocate Kelley T. Lê argues that climate change is the defining issue of our time, and in her new book, Teaching Climate Change for Grades 6–12: Activating Science Teachers to Take on the Climate Crisis Through NGSS, Lê provides teachers, administrators, and global leaders with practical tools to empower ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Science behind genetic testing for identifying risk of opioid misuse remains unproven
A new report from researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Crescenz VA Medical Center evaluated a genetic test for opioid use disorder that recently received pre-marketing approval by the FDA, finding that the genes co