(Press-News.org) A cutting-edge article is paving the way for a transformation in cervical cancer screening, leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance detection accuracy and efficiency. This pioneering research explores the application of AI in medical image interpretation, marking a significant leap in cervical cancer management and prevention. With the aid of deep learning algorithms, the study seeks to address the critical need for more effective screening tests, especially in low- and middle-income countries where traditional methods often fall short. This innovative approach promises to alleviate the global burden of cervical cancer by improving early detection and treatment, offering a beacon of hope for millions of women worldwide.
Cervical cancer remains a major health threat for women globally, with the highest incidence in developing nations. Despite the availability of preventive measures, challenges such as limited healthcare resources and inadequate screening programs continue to undermine global efforts to eliminate the disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) has set an ambitious target to screen 70% of women aged 35 to 45 by 2030, a goal deemed essential to reduce mortality rates. However, achieving this requires innovative solutions that are both effective and scalable, particularly in regions where access to healthcare is restricted.
A team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, in collaboration with the International Agency for Research on Cancer, has recently published a comprehensive review (DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0198) in Cancer Biology & Medicine. The article examines the current and future applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in improving cervical cancer screening methods.
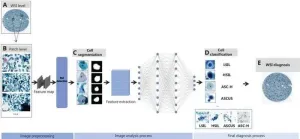
The review delves into AI’s transformative potential in cervical cancer screening, focusing on its role in medical image recognition to identify abnormal cytology and neoplastic lesions. By harnessing deep learning algorithms, AI is now able to replicate human-like interpretation of medical images, resulting in more accurate detection of cervical cancer. The study highlights how AI can automate the segmentation and classification of cytology images, which is vital for early diagnosis. Additionally, it explores AI’s potential to enhance colposcopy, a procedure traditionally hampered by subjective interpretation and reliance on highly skilled professionals. By integrating AI into this process, the review envisions more objective and efficient screenings. AI’s role in risk prediction models is also discussed, where clinical data is used to predict the progression of high-risk HPV infections and cervical cancer development. These models, powered by machine learning, offer a personalized approach to screening, reducing unnecessary referrals and allowing for better risk stratification.
Dr. Youlin Qiao, lead author of the study, emphasizes the transformative potential of AI in cervical cancer detection: “AI has the ability to revolutionize cervical cancer screening by offering automated, objective, and unbiased detection of both cancerous and precancerous conditions. This technology is particularly vital for bridging the healthcare gap in underserved regions.”
The implications of AI-powered cervical cancer screening are profound. Beyond improving detection rates and efficiency, this technology could also expand access to screening services in remote or resource-limited areas. If adopted globally, AI-assisted screening could significantly reduce misdiagnoses, improve healthcare delivery, and move the world closer to the goal of eliminating cervical cancer by the century’s end.
Despite its promise, several hurdles must be addressed for AI to achieve widespread clinical integration:
Data Standardization: Establishing global platforms for standardized and annotated datasets to ensure diverse and high-quality training data.
Ethical Integration: Addressing transparency, privacy, and accountability concerns to build trust among clinicians and patients.
Model Interpretability: Enhancing AI’s explainability to foster confidence and seamless adoption in clinical workflows.
Validation Across Contexts: Conducting robust external validation studies and equipping clinicians with the necessary training to use AI tools effectively.
By tackling these challenges, AI-driven cervical cancer screening could redefine global healthcare, offering a powerful tool in the fight against one of the most preventable cancers.
###
References
DOI
10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0198
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0198
Funding information
This study was supported by grants from CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (Grant No. CAMS 2021-I2M-1-004) and from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (Grant No. INV-031449).
About Cancer Biology & Medicine (CBM)
Cancer Biology & Medicine (CBM) is a peer-reviewed open-access journal sponsored by China Anti-cancer Association (CACA) and Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital. The journal monthly provides innovative and significant information on biological basis of cancer, cancer microenvironment, translational cancer research, and all aspects of clinical cancer research. The journal also publishes significant perspectives on indigenous cancer types in China. The journal is indexed in SCOPUS, MEDLINE and SCI (IF 5.6, 5-year IF 5.9), with all full texts freely visible to clinicians and researchers all over the world (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/journals/2000/).
END
Intelligent fight: AI enhances cervical cancer detection
2025-01-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breakthrough study reveals the secrets behind cordierite’s anomalous thermal expansion
2025-01-10
Cordierite, a remarkable mineral familiar to many as the material behind heat-resistant pizza stones, exhibits an unusual ability to resist changes in size despite significant temperature fluctuations. While widely used in diverse applications from automotive catalytic converters to high-temperature industrial processes, the fundamental reasons behind this anomalous thermal behaviour have remained largely unexplained. A new study, led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London and published in Matter, now provides the first comprehensive explanation, with profound implications for the design and development of advanced materials.
"Modern society demands materials that ...
Patient-reported influence of sociopolitical issues on post-Dobbs vasectomy decisions
2025-01-10
About The Study: Nearly one-third of survey participants indicated sociopolitical issues influenced their vasectomy decision, despite the fact these policies have targeted female reproductive policy. These patient-reported motivations are consistent with recent research using administrative data that found a rise in vasectomy procedure volume after the Dobbs decision.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kathleen Hwang, MD, email kathleen.hwang@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.54430)
Editor’s ...
Radon exposure and gestational diabetes
2025-01-10
About The Study: This cohort study suggests that higher radon exposure is associated with greater odds of gestational diabetes in nulliparous pregnant individuals. Further studies are needed to confirm the results and elucidate the underlying mechanisms, especially with individual-level residential radon exposure assessment.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ka Kahe, MD, ScD, email kk3399@columbia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
EMBARGOED UNTIL 1600 GMT, FRIDAY 10 JANUARY 2025: Northumbria space physicist honoured by Royal Astronomical Society
2025-01-10
Dr John Coxon, esteemed member of Northumbria University’s world-leading Solar and Space Physics research group, has been recognised by the Royal Astronomical Society for his work.
Dr Coxon is a Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Ernest Rutherford Fellow at Northumbria University who has garnered international recognition for his research into understanding the Sun's influence on Earth's space environment.
It has today been announced that he has been awarded the with the prestigious ...
Medicare rules may reduce prescription steering
2025-01-10
Weill Cornell Medicine researchers have found that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs)—organizations that negotiate access to medicines for most patients in the United States—steer patients to use their own pharmacies. However, these pharmacies appear less used in Medicare than in other market segments. These PBMs are part of integrated health care conglomerates that own insurance companies and pharmacies, which may create conflicts of interest.
The study, published Jan. 10 in JAMA Health Forum, found that in 2021 a third of all Medicare Part D pharmacy spending and almost 40% of specialty drug spending within Medicare Part D was through pharmacies owned by the four largest PBMs: ...
Red light linked to lowered risk of blood clots
2025-01-10
Humans and mice exposed to long-wavelength red light had lower rates of blood clots that can cause heart attacks, lung damage and strokes, according to research led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and UPMC surgeon-scientists and published today in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
The findings, which need to be verified through clinical trials, have the potential to reduce blood clots in veins and arteries, which are leading causes of preventable death worldwide.
“The light we’re exposed to can change our biological processes and change ...
Menarini Group and Insilico Medicine enter a second exclusive global license agreement for an AI discovered preclinical asset targeting high unmet needs in oncology
2025-01-10
This is the second asset Menarini Group has inlicensed from Insilico Medicine which was discovered through their generative AI platform, similar to the preclinical stage KAT6 inhibitor (MEN2312) licensed a year ago and which advanced rapidly into the clinical phase.
Under the agreement, Menarini Group will be granted global rights to develop and commercialize the asset. The deal includes a $20m upfront payment, and the combined value, including all development, regulatory, and commercial milestones, is over $550 million, followed by tiered royalties.
FLORENCE, Italy and CAMBRIDGE, Mass., January 10, 2025 : The Menarini Group ("Menarini"), ...
Climate fee on food could effectively cut greenhouse gas emissions in agriculture while ensuring a social balance
2025-01-10
Agriculture accounts for 8 percent of all greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in Germany. “However, emissions within this sector, could be reduced by 22.5 percent or over 15 million tonnes of GHG annually, if the social cost of carbon were reflected in food prices,” says Julian Schaper, guest scientist at PIK and lead author of the study published in the journal Food Policy. In the Federal Climate Change Act passed in 2019, the government set itself the goal of reducing annual emissions from the current 62 million tonnes to 56 Mt GHG by 2030.
The social cost of carbon is an estimate of the economic damages that would result from emitting one additional tonne of carbon into the ...
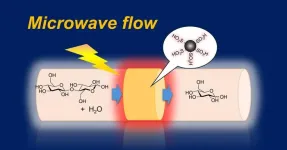
Harnessing microwave flow reaction to convert biomass into useful sugars
2025-01-10
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers at Kyushu University have developed a device that combines a catalyst and microwave flow reaction to efficiently convert complex polysaccharides into simple monosaccharides. The device utilizes a continuous-flow hydrolysis process, where cellobiose—a disaccharide made from two glucose molecules—is passed through a sulfonated carbon catalyst that is heated using microwaves. The subsequent chemical reaction breaks down cellobiose into glucose. Their results were published in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Converting biomass into ...
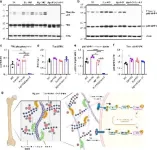
Unveiling the secrets of bone strength: the role of biglycan and decorin
2025-01-10
A recent study has uncovered the essential roles of two proteoglycans, biglycan and decorin, in maintaining bone mass, water retention, and bulk/in situ mechanical competence. Through the use of genetically modified mouse models, the research demonstrates that while biglycan plays a predominant role in preserving bone structure and toughness, decorin significantly contributes to the bone’s mechanical properties. These findings reveal how these proteins interact with water and other matrix components to regulate the mechanical ...