(Press-News.org) Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have discovered sophisticated behavioral strategies that enable parasitic crickets to survive within ant colonies. Led by Ryoya Tanaka, the team documented how these insects successfully navigate life among potentially lethal hosts through precise evasion tactics. Their findings, published in Communications Biology, reveal remarkable adaptations that allow these cricket species to thrive in a hostile environment.
Animals that live in ant colonies, known as “ant guests”, exploit their hosts’ resources. However, this behavior carries a significant risk because ants ruthlessly exterminate intruders upon detection.
Myrmecophilus ant crickets employ specialized escape behaviors to avoid ant attacks. Tanaka and colleagues studied this behavior in Myrmecophilus tetramorii, a "brood parasite" that sustains itself within host colonies by consuming dead insects and ant larvae. The researchers studied the behaviors that allow crickets to escape from their hosts.
They found that most behaviors could be classified into two types: “distancing,” where the crickets move directly away from the ants and “dodging,” where the crickets fled from the ants in a circular movement that positioned them behind the ants to avoid their mandibles. They noticed that when the cricket initiated dodging behavior, it stayed farther from its host and moved at a slower pace than during distancing.
The researchers concluded that crickets employ dodging behavior to methodically evade perceived threats under low-risk conditions, while they utilize distancing behavior as a rapid defensive response when facing imminent attack.
“While distancing behaviour can quickly get crickets away from the approaching ant, such quick movements may alert surrounding potential enemies to the crickets’ presence, triggering an aggressive chase by another ant. Ant crickets benefit from a slow and precise reaction to dodging, which reduces the probability of being attacked by ants,” Tanaka explained. “In most cases, the ant cricket used dodging to escape from its host ants. Distancing incidents were comparatively rare.”
When they observed the behavior of crickets that were already integrated into the host ant colony, the researchers found that the crickets did not move uniformly around the colony but tended to stay close to certain locations, such as those with accumulated debris, areas with wet paper, and corners.
“Dodging behaviour is advantageous for staying in attractive areas while avoiding ants,” Tanaka explained. “The unique trait of dodging behaviour might be a way of effectively staying in a safe location while avoiding a succession of incoming ants, allowing them to reduce the risk of being attacked.”
By staying in advantageous locations and carefully employing the two strategies, crickets can survive in the hostile environment of the host colony. Tanaka hopes that his research will open people’s eyes to the fascinating world of insects. “I often stroll around the Nagoya University campus to see insects. I still remember when I saw an ant cricket skillfully evading ants despite being surrounded by them,” he said. “From that moment on, I was utterly enthralled by this behavior.”
END
How crickets co-exist with hostile ant hosts
2025-01-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tapered polymer fibers enhance light delivery for neuroscience research
2025-01-15
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a reliable and reproducible way to fabricate tapered polymer optical fibers that can be used to deliver light to the brain. These fibers could be used in animal studies to help scientists better understand treatments and interventions for various neurological conditions.
The tapered fibers are optimized for neuroscience research techniques, such as optogenetic experiments and fiber photometry, which rely on the interaction between genetically modified neurons and visible light delivered to and/or collected from the brain.
“Unlike standard optical fibers, which are cylindrical, the tapered fibers we developed have a conical shape, which ...
Syracuse University’s Fran Brown named Paul “Bear” Bryant Newcomer Coach of the Year Award recipient
2025-01-15
HOUSTON, January 15, 2025 — The American Heart Association has named Syracuse University’s Fran Brown as the recipient of the 2024 Paul “Bear” Bryant Newcomer Coach of the Year Award. This award celebrates the achievements of an individual who has not had any previous head coaching experience at the NCAA Division I football sub-division (FBS) level.
Coach Brown will be recognized with the honor during the 2025 Bear Bryant Awards on January 22.
After being named Syracuse’s 31st head coach on November 28, 2023, Brown immediately instilled a culture of ...
DARPA-ABC program supports Wyss Institute-led collaboration toward deeper understanding of anesthesia and safe drugs enabling anesthesia without the need for extensive monitoring
2025-01-15
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Currently, no anesthetic compound or cocktail can be used safely outside of a hospital facility. This is because current drugs impair the brain and central nervous system’s ability to regulate a number of vital processes, including respiration, body temperature, and heart rate in addition to creating a state of unconsciousness or sedation, making the strict monitoring of patients with the help of sophisticated instruments and highly-trained clinical personnel an absolute necessity. To reduce trauma associated with injuries and improve combat casualty outcomes, under a new DARPA-ABC contract ...
The Offshore Wind Innovation Hub 2025 call for innovators opens today
2025-01-15
The Offshore Wind Innovation Hub today announced the opening of its 2025 application process, designed to identify and support entrepreneurial and innovative companies that will help unleash the potential of the dynamic emerging offshore wind industry.
Winners take on a six-month mentoring and business development program residency designed to prepare them for strategic partnerships with major offshore wind developers and to be part of the larger offshore wind value chain. The program aims to enable innovators to overcome barriers ...
Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) launches a new funding opportunity to join the Collaborative Research Network
2025-01-15
The Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) initiative opened applications for members of the research community to apply to join the Collaborative Research Network (CRN) 2025 Scientific Track. The new Scientific Track grants will support collaborative research teams focused on dissecting the mechanisms that contribute to Parkinson’s disease (PD) heterogeneity across one of six focus areas listed below, offering funding of up to $3 million per year over three years.
Examining PD in the context of aging
Understanding how co-pathologies can influence PD pathogenesis and progression
Dissecting ...
State-of-the-art fusion simulation leads three scientists to the 2024 Kaul Foundation Prize
2025-01-15
Three scientists were awarded the 2024 Kaul Foundation Prize for Excellence in Plasma Physics Research and Technology Development based on their decades of groundbreaking research about how plasma behaves in fusion reactors.
Choongseok (CS) Chang, Seung-Hoe Ku and Robert Hager of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) were recognized “for experimentally validated simulations of turbulence-broadened divertor heat flux widths using the X-Point Included Gyrokinetic Code (XGC),” following decades of research developing comprehensive simulations to model the fusion plasma edge.
Recently, ...
Davos Alzheimer's Collaborative launches innovative brain health navigator program for intuitive coordination between patients and providers
2025-01-15
The Davos Alzheimer’s Collaborative (DAC), a pioneering worldwide initiative seeking to cure Alzheimer’s disease and improve brain health, today announced the launch of its Brain Health Navigator program. The initiative led by the DAC Healthcare System Preparedness (DAC-SP) team will provide resources for patients and providers at six sites across the U.S.
Despite Alzheimer’s status as a growing worldwide epidemic, pathways for accurate diagnosis and evidence based interventions including new therapies are either underdeveloped or non-existent. ...
Media registration now open: ATS 2025 in San Francisco
2025-01-15
New York, NY – Jan. 15, 2025 –We are excited to welcome you to San Francisco for the ATS 2025 International Conference! Journalists will have access to leaders, as well as emerging scientists and clinicians, who are at the forefront of medical breakthroughs and clinical innovation in pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine.
Join us beginning Sunday, May 18* through Wednesday, May 21. Register now and check out our Program at a Glance.
As always, you are welcome to contact the ATS communications and marketing director about scientific sessions and expert interviews whether you are joining us in person or from your (home) office. Registered ...
New study shows that corn-soybean crop rotation benefits are extremely sensitive to climate
2025-01-15
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (01/15/2024) — A study by researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities offers new insights into how alternating corn and soybean crops can help increase crop yield in a changing climate.
The research is published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Global Change Biology.
Rising temperatures and weather extremes are threatening global food security, making it crucial to understand how sustainable practices like crop rotation can help improve agricultural yields and resilience.
The study found that the benefits to corn-soybean rotation, compared to continuous corn year after year, are extremely sensitive to ...
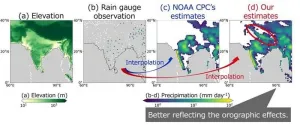
From drops to data: Advancing global precipitation estimates with the LETKF algorithm
2025-01-15
With the increase in climate change, global precipitation estimates have become a necessity for predicting water-related disasters like floods and droughts, as well as for managing water resources. The most accurate data that can be used for these predictions are ground rain gauge observations, but it is often challenging due to limited locations and sparse rain gauge data. To solve this problem, Assistant Professor Yuka Muto from the Center for Environmental Remote Sensing, Japan, and Professor Shunji Kotsuki of the Institute for Advanced Academic Research, Center for Environmental Remote Sensing, ...