(Press-News.org) Throughout history, volcanic eruptions have had serious consequences for human societies such as cold weather, lack of sun, and low crop yields. In the year 43 BC when a volcano in Alaska spewed large quantities of sulphur into the stratosphere, harvests failed the following years in the countries around the Mediterranean, causing famine and disease. This is well-documented in written sources from ancient Greece and Rome.
We do not have written sources from the Neolithic. But climate scientists from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen have analysed ice cores from the Greenland ice sheet and can now document that around 2,900 BC a similar volcanic eruption took place. An eruption that must have had equally devastating consequences for the Neolithic peoples who lived in Northern Europe at the time and who were deeply dependent on agriculture.
This new insight into a climate episode in the Neolithic period has led archaeologists from the University of Copenhagen, the National Museum of Denmark and the Museum of Bornholm to view their findings of so-called "sun stones" from the Neolithic Vasagård site on Bornholm in a new light, and they have just published a scientific article on the phenomenon in the journal Antiquity:
"We have known for a long time that the sun was the focal point for the early agricultural cultures we know of in Northern Europe. They farmed the land and depended on the sun to bring home the harvest. If the sun almost disappeared due to mist in the stratosphere for longer periods of time, it would have been extremely frightening for them,” says archaeologist Rune Iversen from the University of Copenhagen, who has participated in the excavations at the site led by the Museum of Bornholm and the National Museum. He adds:
“One type of find that is completely unique to Bornholm is the so-called sun stones, which are flat shale pieces with engraved patterns and sun motifs. They symbolized fertility and were probably sacrificed to ensure sun and growth. Sun stones were found in large quantities at the Vasagård West site, where residents deposited them in ditches forming part of a causewayed enclosure together with the remains of ritual feasts in the form of animal bones, broken clay vessels, and flint objects around 2,900 BC. The ditches were subsequently closed.”
Rune Iversen and his colleagues believe that there is a very high probability that there is a connection between the volcanic eruption, the subsequent climate changes and the discovery of the ritual sun stone sacrifices.
“It is reasonable to believe that the Neolithic people on Bornholm wanted to protect themselves from further deterioration of the climate by sacrificing sun stones – or perhaps they wanted to show their gratitude that the sun had returned again.”
Major cultural changes
As if an acute climate deterioration around 2,900 BC was not enough, Northern European Neolithic cultures were also affected by other disasters; New DNA studies of human bones have shown that the plague was very widespread and fatal.
During the same period when the Neolithic people were affected by both climate change and disease, archaeologists can also document a shift in the traditions they had held on to for a long time. The so-called Funnel Beaker Culture, which had been dominant until about 5,000 years ago with its characteristic ceramics and passage graves, was gradually disappearing.
“At the causewayed enclosure we have excavated on Bornholm, we can also see that, after the sacrifice of the sun stones, the residents changed the structure of the site so that instead of sacrificial ditches it was provided with extensive rows of palisades and circular cult houses. We do not know why, but it is reasonable to believe that the dramatic climatic changes they had been exposed to would have played a role in some way, Rune Iversen concludes.
Sun stones to be exhibited in Copenhagen
Four of the sun stones from Vasagård on Bornholm can be experienced from 28 January in the prehistoric exhibition at The National Museum of Denmark in Copenhagen. They probably exemplify one of the earliest depositional practices connected to a Neolithic sun-cult in South Scandinavia, which are also known from the Nordic Bronze Age with objects like the sun chariot.
"The sunstones are completely unique, also in a European context. The closest we get to a similar sun-cult in the Neolithic is some passage graves in southern Scandinavia or henge structures like Stonehenge in England, which some researchers associate with the sun. With the sun stones, there is in my mind no doubt. It is quite simply an incredible discovery, which demonstrates that depositions honouring the sun is an ancient phenomenon, which we encounter again in South Scandinavia during the climate disaster caused by a volcanic eruption in the year 536 AD, where several large gold hoards were deposited as sacrifices,” says Lasse Vilien Sørensen, who is senior researcher at The National Museum of Denmark and co-author of the research paper.
Volcanic eruption 2,900 BC
The researchers can document reduced radiation from the sun and consequent cooling, which can be traced in both the United States and Europe around 2,900 BC.
Dendrochronological analyses of fossil wood show signs of frost in the spring and summer months both before and after 2,900 BC.
And ice cores from the Greenland ice cap and the Antarctica contain sulphur, which is a sign of the occurrence of a strong volcanic eruption.
END
Volcanic eruption caused Neolithic people to sacrifice unique "sun stones"
Archaeologists and climate scientists from the University of Copenhagen can now show that ritual sacrifices of sun stones coincided with a large volcanic eruption hat made the sun disappear throughout Northern Europe.
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug in clinical trials for breast cancer could also treat some blood cancers
2025-01-16
Two new studies led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a possible way to block the progression of several forms of blood cancer using a drug already in clinical trials against breast cancer.
The studies — both conducted in patient samples and animal models — found that inhibiting a protein called RSK1 reduces inflammation and stops the progression of blood cancers called myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) as well as an aggressive form of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). With the RSK1 inhibitor already in clinical testing, the path to expanded use as a treatment for blood ...
Study identifies mechanism underlying increased osteoarthritis risk in postmenopausal females
2025-01-16
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a condition that disproportionally affects postmenopausal women, and the millions affected can attest to the pain, reduced mobility and diminished quality of life that comes from this disease. While the hormonal changes associated with menopause have long been known to accelerate the development and progression of OA, a deeper understanding of the biological mechanisms that underlie this correlation is crucial for developing effective treatments.
A new study led by researchers at Spaulding Rehabilitation, a member of the Mass General Brigham ...
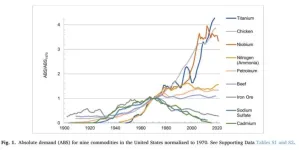
The material revolution: How USA’s commodity appetite evolved from 1900 to present
2025-01-16
A new study documents the dramatic change in America’s material diet from 1900 to 2020 – ongoing shifts in US commodity consumption patterns with profound environmental, economic, and geopolitical implications.
Published by Iddo K. Wernick of The Rockefeller University’s Program for the Human Environment in the Elsevier journal Resources Policy, the paper details the consumption of 100 key commodities used to build cities, power cars, produce everyday products, and connect people. It charts transformative changes since the start of the 20th century in both absolute ...
Asteroid impact sulfur release less lethal in dinosaur extinction
2025-01-16
Approximately 66 million years ago, the Chicxulub asteroid, estimated to be 10-15 kilometer in diameter, struck the Yucatán Peninsula (in current-day Mexico), creating a 200-kilometer-wide impact crater. This impact triggered a chain reaction of destructive events including a rapid climate change that eventually led to the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs and in total about 75% of species on Earth. The main culprit is most likely the “impact winter”, which was caused by massive release of dust, soot, and sulfur into the atmosphere, leading to extreme cold, darkness, and a collapse ...
Study shows seed impact mills clobber waterhemp seed viability
2025-01-16
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 16 January 2025 – Recently published research in the journal Weed Science shows promise for controlling herbicide-resistant weeds in soybean fields by using a seed impact mill at harvest. When installed on a combine, this harvest weed-seed control system (HWSC) mechanically damages weed seeds as they move through the mill to render them non-viable.
Iowa State University Researchers Alexis Meadows and Ram (Ramawatar) Yadav conducted seed impact mill field experiments ...
Study links rising suicidality among teen girls to increase in identifying as LGBQ
2025-01-16
Amid an increase in suicidal behavior among teen girls, new research links this phenomenon to the significant increase in the number of female students identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or questioning (LGBQ).
“This finding suggests that the overall increase in female suicidality is not due to all female students becoming more suicidal, but rather to a larger proportion of students being part of a group that has historically experienced higher rates of suicidal thoughts and behaviors due to social and structural pressures,” says lead author Joseph Cimpian, ...
Mind’s eye: Pineal gland photoreceptor’s 2 genes help fish detect color
2025-01-16
We see color because photoreceptor cones in our eyes detect light waves corresponding to red, green, and blue, while dimness or brightness is detected by photoreceptor rods. Many non-mammalian vertebrates like fish, however, are known to detect color and brightness with the pineal gland, which is part of the brain. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group has further elucidated on how the pineal organ of fish do so.
Previously, the research group led by Professor Akihisa Terakita and Professor Mitsumasa Koyanagi of the Graduate School of Science revealed that ...
Nipah virus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention
2025-01-16
Nipah virus (NiV), a zoonotic paramyxovirus with significant human health implications, has garnered considerable attention due to its high fatality rates and potential for human-to-human transmission, posing a global public health threat. Emerging in South and Southeast Asia, NiV is known for its recurrent outbreaks, with a particular focus on its genetic lineages, NiV-MY and NiV-BD, which differ in pathogenicity and transmissibility. The virus, initially isolated in Malaysia in 1998, has since caused outbreaks linked to contact with infected ...
FDA ban on Red Dye 3 and more are highlighted in Sylvester Cancer's January tip sheet
2025-01-16
FDA BANS RED DYE 3 IN FOOD AND INGESTED DRUGS
Citing two studies linking Red Dye 3 to cancer in laboratory male rats, the FDA today revoked authorization for the use of the dye in food and ingested drugs. The move came in response to a 2022 color additive petition. “This is long overdue,” said Tracy Crane, Ph.D., RDN., director of Lifestyle Medicine and Prevention at Sylvester. “Red Dye 3 has been banned for use in cosmetics and topical drugs for more than three decades,” she said. “Yet it gives more than 9,000 foods in the United States their red coloring. These colorful foods and drinks are particularly appealing to young children,” ...
Mapping gene regulation
2025-01-16
KYOTO – An international team of researchers has taken an important step toward understanding how gene expression is controlled across the human genome. A new study has comprehensively analyzed “cis-regulatory elements” (CREs), which are the DNA sequences that regulate gene transcription. This work sheds light on how these elements contribute to cell-specific gene expression and how mutations within them may influence health and disease.
CREs, including enhancers and promoters, are essential for controlling when and where genes are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
[Press-News.org] Volcanic eruption caused Neolithic people to sacrifice unique "sun stones"Archaeologists and climate scientists from the University of Copenhagen can now show that ritual sacrifices of sun stones coincided with a large volcanic eruption hat made the sun disappear throughout Northern Europe.