(Press-News.org)
Paper-thin optical lenses simple enough to mass produce like microchips could enable a new generation of compact optical devices. A team with researchers at the University of Tokyo and JSR Corp. fabricated and tested flat lenses called Fresnel zone plates (FZPs), but did so for the first time using only common semiconductor manufacturing equipment, the i-line stepper, for the first time. These flat lenses currently lack the efficiency of in-production lenses, but have the potential to reshape optics for industries ranging from astronomy to health care and consumer electronics.
Flat lenses, such as metalenses, exist, but they come with hefty price tags and a high degree of complexity, and only a small number of devices are available. In the race to increase the quality, performance and efficiency of devices whilst reducing costs, manufacturers, through the work of academic researchers, seek alternatives. FZPs have become a good candidate to improve optical devices where space is critical. And for the first time, researchers crafted sample lenses with just a few straightforward steps using industry standard machinery.
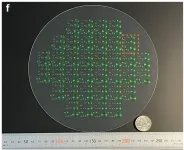
“We developed a simple and mass-producible method for FZPs using a common semiconductor lithography system, or stepper,” said Associate Professor Kuniaki Konishi from the Institute for Photon Science and Technology. “This is due to a special type of photoresist or mask called a color resist, which was originally designed for use as color filters. By simply coating, exposing and developing this material, we produced lenses capable of focusing visible light down to only 1.1 microns, around 100 times thinner than a human hair.”
The current drawback with the new FZPs is that they only have a light-gathering efficiency of 7%, meaning they produce excessively noisy images. But already the team is working on ways to increase this fourfold by changing the way they use the color resists. However, this would require a greater degree of control over the color resists’ physical properties than was afforded the researchers at the time of this study, though the ability to do this does exist.
“In addition to efficiently fabricating FZPs, we also devised simulations which are confirmed to match our experiments very tightly. What this means is, we could tailor designs to match specific applications in different fields, such as medicine, before committing to production,” said Konishi. “Furthermore, we envisage environmental and economic benefits too, as unlike traditional manufacturing methods, the FZP production process eliminates the need for toxic etching chemicals and significantly reduces energy consumption.”
So, it might be a while before FZPs help you capture moments in high visual fidelity with your ultrathin smartphone, but this, or technology inspired by it, will likely come along soon.
###
Journal article:
Ryohei Yamada, Hiroyuki Kishida, Tomohiro Takami, Itti Rittaporn, Mizuho Matoba, Haruyuki Sakurai, Kuniaki Konishi. “Optical Fresnel zone plate flat lenses made entirely of colored photoresist through an i-line stepper”, Light: Science & Applications, DOI: 10.1038/s41377-024-01725-6
Funding: This research was supported by JSR-UTokyo Collaboration Hub, CURIE.
Useful links:
Konishi Lab - https://www.kkns.ipst.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/home
Institute for Photon Science and Technology - http://www.ipst.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index-e.php
Graduate School of Science - https://www.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
JSR Corporation - https://www.jsr.co.jp/jsr_e/
JSR-UTokyo Collaboration Hub, CURIE - https://curie.phys.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Research contact:
Associate Professor Kuniaki Konishi
Institute for Photon Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan
kkonishi@ipst.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact:
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
JSR Corporate Communications
Sayako Kitamura/Yichin Wang
jsr_koho@jsr.co.jp
About The University of Tokyo:
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on X (formerly Twitter) at @UTokyo_News_en.
About JSR Corporation:
JSR Corporation is developing its business globally on the strength of its technological capabilities, focusing on the digital solutions business, including semiconductor materials, and the life sciences business, while promoting innovation to provide value to leading industries around the world and exploring next-generation businesses to meet society's challenges.
END
Throughout history, volcanic eruptions have had serious consequences for human societies such as cold weather, lack of sun, and low crop yields. In the year 43 BC when a volcano in Alaska spewed large quantities of sulphur into the stratosphere, harvests failed the following years in the countries around the Mediterranean, causing famine and disease. This is well-documented in written sources from ancient Greece and Rome.
We do not have written sources from the Neolithic. But climate scientists from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen have analysed ice cores from the Greenland ice sheet and can now document that around 2,900 ...
Two new studies led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a possible way to block the progression of several forms of blood cancer using a drug already in clinical trials against breast cancer.
The studies — both conducted in patient samples and animal models — found that inhibiting a protein called RSK1 reduces inflammation and stops the progression of blood cancers called myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) as well as an aggressive form of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). With the RSK1 inhibitor already in clinical testing, the path to expanded use as a treatment for blood ...
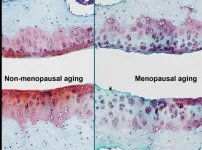
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a condition that disproportionally affects postmenopausal women, and the millions affected can attest to the pain, reduced mobility and diminished quality of life that comes from this disease. While the hormonal changes associated with menopause have long been known to accelerate the development and progression of OA, a deeper understanding of the biological mechanisms that underlie this correlation is crucial for developing effective treatments.
A new study led by researchers at Spaulding Rehabilitation, a member of the Mass General Brigham ...
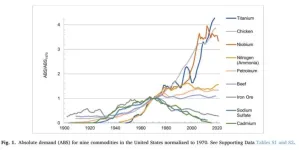
A new study documents the dramatic change in America’s material diet from 1900 to 2020 – ongoing shifts in US commodity consumption patterns with profound environmental, economic, and geopolitical implications.
Published by Iddo K. Wernick of The Rockefeller University’s Program for the Human Environment in the Elsevier journal Resources Policy, the paper details the consumption of 100 key commodities used to build cities, power cars, produce everyday products, and connect people. It charts transformative changes since the start of the 20th century in both absolute ...
Approximately 66 million years ago, the Chicxulub asteroid, estimated to be 10-15 kilometer in diameter, struck the Yucatán Peninsula (in current-day Mexico), creating a 200-kilometer-wide impact crater. This impact triggered a chain reaction of destructive events including a rapid climate change that eventually led to the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs and in total about 75% of species on Earth. The main culprit is most likely the “impact winter”, which was caused by massive release of dust, soot, and sulfur into the atmosphere, leading to extreme cold, darkness, and a collapse ...
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 16 January 2025 – Recently published research in the journal Weed Science shows promise for controlling herbicide-resistant weeds in soybean fields by using a seed impact mill at harvest. When installed on a combine, this harvest weed-seed control system (HWSC) mechanically damages weed seeds as they move through the mill to render them non-viable.
Iowa State University Researchers Alexis Meadows and Ram (Ramawatar) Yadav conducted seed impact mill field experiments ...
Amid an increase in suicidal behavior among teen girls, new research links this phenomenon to the significant increase in the number of female students identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or questioning (LGBQ).
“This finding suggests that the overall increase in female suicidality is not due to all female students becoming more suicidal, but rather to a larger proportion of students being part of a group that has historically experienced higher rates of suicidal thoughts and behaviors due to social and structural pressures,” says lead author Joseph Cimpian, ...
We see color because photoreceptor cones in our eyes detect light waves corresponding to red, green, and blue, while dimness or brightness is detected by photoreceptor rods. Many non-mammalian vertebrates like fish, however, are known to detect color and brightness with the pineal gland, which is part of the brain. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group has further elucidated on how the pineal organ of fish do so.
Previously, the research group led by Professor Akihisa Terakita and Professor Mitsumasa Koyanagi of the Graduate School of Science revealed that ...
Nipah virus (NiV), a zoonotic paramyxovirus with significant human health implications, has garnered considerable attention due to its high fatality rates and potential for human-to-human transmission, posing a global public health threat. Emerging in South and Southeast Asia, NiV is known for its recurrent outbreaks, with a particular focus on its genetic lineages, NiV-MY and NiV-BD, which differ in pathogenicity and transmissibility. The virus, initially isolated in Malaysia in 1998, has since caused outbreaks linked to contact with infected ...
FDA BANS RED DYE 3 IN FOOD AND INGESTED DRUGS
Citing two studies linking Red Dye 3 to cancer in laboratory male rats, the FDA today revoked authorization for the use of the dye in food and ingested drugs. The move came in response to a 2022 color additive petition. “This is long overdue,” said Tracy Crane, Ph.D., RDN., director of Lifestyle Medicine and Prevention at Sylvester. “Red Dye 3 has been banned for use in cosmetics and topical drugs for more than three decades,” she said. “Yet it gives more than 9,000 foods in the United States their red coloring. These colorful foods and drinks are particularly appealing to young children,” ...