MANCHESTER, ENGLAND, January 22, 2011 (Press-News.org) The UK's largest credit card provider, MBNA, has announced the start of its two-year programme that will see its 6 million customer base moved over to contactless cards by January 1st 2012.
To achieve this, MBNA will issue a new contactless credit card each time a new or replacement card request is made by a customer, the lender estimates that most of its card-holders will have the ability to pay without a PIN by the start of 2012. Contactless payment is a relatively new option at the checkout and is currently limited to GBP15 per transaction, but the card provider can see the benefit to customers of this easier and faster way of paying.
Speaking about the new programme on the MBNA website, Ian O'Doherty, Europe Card executive for Bank of America, which operates the MBNA brand, said: "With this two-year roll out of new and replacement contactless enabled cards we are reinforcing our support for the evolution of contactless technology in the UK."
He went on to say: "We are committed to offering simplicity, added value and choice in all of our products and services - enabling our customers to use contactless payments is a fantastic example of making that commitment a reality."
Using a contactless card is the very definition of ease, with those holding Oyster travel cards already familiar with the action required. When at the checkout of a store that has contactless technology, card-holders simply touch their card to the payment terminal. There's no need to enter your pin number; it's completely compatible with Visa and Mastercard systems and is available wherever the contactless symbol is shown.
Although transactions are limited to GBP15, MBNA estimates that adoption of the technology by customers may be slow due to potential security concerns. As a result, the card provider has outlined the multiple layers of security that the contactless system supports. This includes the requirement of a pin number on the first use and again for random transactions. MBNA credit card holders wanting to start using contactless payments can request a new card, otherwise there's no need to do anything, as the lender will provide a compatible new or replacement card when re-issued.
The number of retailers supporting contactless technology is rapidly increasing and with good reason as the estimated number of existing compatible cards is around ten million. This figure is expected to reach 25 million by 2012 as more card issuers adopt the technology. Current contactless retailers include: Subway, Pret a Manger and Caffe Nero with the Co-op, Clinton Cards, Boots, Spar, National Trust gift shops and Little Chef restaurants all either trialing the technology or rolling it out at the time of publication.
Website: http://www.mbna.co.uk
MBNA Announces Roll Out Of Contactless Cards
MBNA the UK's largest credit card provider, has announced by January 2012 its 6 million customers will have moved to contactless card technology.
2011-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Couples sometimes communicate no better than strangers
2011-01-21
Married people may think they communicate well with their partners, but psychologists have found that they don't always convey messages to their loved ones as well as they think — and in some cases, the spouses communicate no better than strangers.
The same communication problem also is true with close friends, a recent study has found.
"People commonly believe that they communicate better with close friends than with strangers. That closeness can lead people to overestimate how well they communicate, a phenomenon we term the 'closeness-communication bias,'" said Boaz ...
Coronary imaging enhances ability to identify plaques likely to cause future heart disease
2011-01-21
NEW YORK, NY – JANUARY 20, 2011 – Results from the PROSPECT clinical trial shed new light on the types of vulnerable plaque that are most likely to cause sudden, unexpected adverse cardiac events, and on the ability to identify them through imaging techniques before they occur.
The trial, Providing Regional Observations to Study Predictors of Events in the Coronary Tree (PROSPECT), is the first prospective natural history study of atherosclerosis using multi-modality imaging to characterize the coronary tree. The study findings were published in the January 20, 2011 ...
U of Alberta researcher working towards pharmacological targets for cholera
2011-01-21
Just over a year after the earthquake in Haiti killed 222,000 people there's a new problem that is killing Haitians. A cholera outbreak has doctors in the area scrambling and the water-borne illness has already claimed 3600 lives according to officials with Médicin Sans Frontières (Doctors without Borders).
Stefan Pukatzki, a bacteriologist in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry at the University of Alberta, is hoping that down the road he can help prevent deadly cholera outbreaks.
His lab studies Vibrio cholerae, the bacteria that makes up the disease, and he has discovered ...
Gene mutation play a major role in 1 cause of kidney disease
2011-01-21
Mutations in a gene called INF2 are by far the most common cause of a dominantly inherited condition that leads to kidney failure, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society Nephrology (JASN). The results may help with screening, prevention, and therapy.
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) attacks the kidney's filtering system and causes serious scarring. Approximately 20,000 persons are currently living with kidney failure due to FSGS in the United States, with an associated annual cost of more than $3 billion. In ...
Mammograms: Detecting more than breast cancer, may help assess heart risk in kidney disease patients
2011-01-21
Routine mammograms performed for breast cancer screening could serve another purpose as well: detecting calcifications in the blood vessels of patients with advanced kidney disease, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN).
Mammograms show calcium deposits in the breast arteries in nearly two-thirds of women with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), according to the study by W. Charles O'Neill, MD (Emory University, Atlanta). "Breast arterial calcification is a specific and useful marker of medial ...
Long-distance migration may help reduce infectious disease risks for many animal species
2011-01-21
Athens, Ga. – It's a common assumption that animal migration, like human travel across the globe, can transport pathogens long distances, in some cases increasing disease risks to humans. West Nile Virus, for example, spread rapidly along the East coast of the U.S., most likely due to the movements of migratory birds. But in a paper just published in the journal Science, researchers in the University of Georgia Odum School of Ecology report that in some cases, animal migrations could actually help reduce the spread and prevalence of disease and may even promote the evolution ...
Viral protein mimic keeps immune system quiet
2011-01-21
In a new paper published Jan. 21 in the journal Science, a team of researchers led by Microbiology and Immunology professor Blossom Damania, PhD, has shown for the first time that the Kaposi sarcoma virus has a decoy protein that impedes a key molecule involved in the human immune response.
The work was performed in collaboration with W.R. Kenan, Jr. Distinguished Professor, Jenny Ting, PhD. First author, Sean Gregory, MS, a graduate student in UNC's Department of Microbiology and Immunology played a critical role in this work.
The virus-produced protein, called ...
Study maps process used by T cells to discriminate pathogens from the body's own cells
2011-01-21
VIDEO:
This video shows the micropipette adhesion frequency assay used to study the mechanical interactions between a T cell and an antigen presented on a red blood cell.
Click here for more information.
Researchers have for the first time mapped the complex choreography used by the immune system's T cells to recognize pathogens while avoiding attacks on the body's own cells.
The researchers found that T cell receptors – molecules located on the surface of the T cell ...
Dino-era sex riddle solved by new fossil find
2011-01-21
The discovery of an ancient fossil, nicknamed 'Mrs T', has allowed scientists for the first time to sex pterodactyls – flying reptiles that lived alongside dinosaurs between 220-65 million years ago.
Pterodactyls featured prominently in Spielberg's Jurassic Park III and are a classic feature of many dinosaur movies where they are often depicted as giant flying reptiles with a crest.
The discovery of a flying reptile fossilised together with an egg in Jurassic rocks (about 160 million years old) in China provides the first direct evidence for gender in these extinct ...
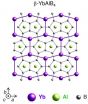
University of Tokyo, Rutgers physicists unveil unexpected properties in superconducting material
2011-01-21
In 2008, an international team of scientists studying an exotic new superconductor based on the element ytterbium reported that it displays unusual properties that could change how scientists understand and create materials for superconductors and the electronics used in computing and data storage.
But a key characteristic that explains the material's unusual properties remained tantalizingly out of reach in spite of the scientists' rigorous battery of experiments and exacting measurements. So members of that team from the University of Tokyo reached out to theoretical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] MBNA Announces Roll Out Of Contactless CardsMBNA the UK's largest credit card provider, has announced by January 2012 its 6 million customers will have moved to contactless card technology.