(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this study showed that adults ages 18 to 49 reporting medical-only or medical-nonmedical cannabis use vs nonmedical-only use had higher prevalence of cannabis use disorder at all severity levels and reported more frequent cannabis use. These findings suggest that medically recommended cannabis is not associated with reduced addiction risk compared with nonmedical use.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Nora D. Volkow, M.D., email nvolkow@nida.nih.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.4475)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.4475?guestAccessKey=072d10fe-2899-4515-ba75-24d2e99525e9utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=111224
END
Medically recommended vs nonmedical cannabis use among US adults
JAMA Psychiatry
2025-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Spanish scientists discover how the gut modulates the development of inflammatory conditions
2025-01-22
A study led by David Sancho at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid reveals how an increase in intestinal permeability allows the natural gut bacteria to cross the intestinal barrier and reach the bone marrow, where they induce epigenetic changes—modifications that alter gene activity without affecting DNA sequence—in the stem cells that give rise to immune cells. The epigenetic changes induced by the translocated gut bacteria generate “trained” immune cells primed to respond more efficiently to future infections. However, this same ability to amplify the immune response can also aggravate the inflammatory conditions such as ...
Compact comb lights the way for next-gen photonics
2025-01-22
In the world of modern optics, frequency combs are invaluable tools. These devices act as rulers for measuring light, enabling breakthroughs in telecommunications, environmental monitoring, and even astrophysics. But building compact and efficient frequency combs has been a challenge—until now.
Electro-optic frequency combs, introduced in 1993, showed promise in generating optical combs through cascaded phase modulation but progress slowed down because of their high power demands and limited bandwidth. This led to the field being dominated by femtosecond lasers and Kerr soliton microcombs, which, while effective, require complex tuning and ...
New research reveals how location influences how our immune system fights disease
2025-01-22
Seattle, WASH.—January 22, 2025—The human immune system is like an army of specialized soldiers (immune cells) each with a unique role to play in fighting disease. In a new study published in Nature, led by scientists at the Allen Institute, La Jolla Institute for Immunology, and UC San Diego, researchers reveal how cells known as tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells, play unique and specialized roles based on where they are located within the small intestine. Tissue-resident memory cells provide a local first ...
AI in cell research: Moscot reveals cell dynamics in unprecedented detail
2025-01-22
Thanks to a new technology called Moscot (“Multi-Omics Single-Cell Optimal Transport”), researchers can now observe millions of cells simultaneously as they develop into a new organ—for example, a pancreas. This groundbreaking method was developed by an international research team led by Helmholtz Munich and has been published in the renowned journal Nature.
Until now, biologists had only a limited understanding of how cells develop in their natural environment—for instance, when they form an organ in the ...
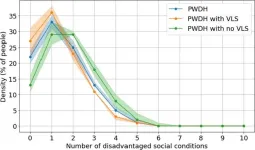
New study finds social programs could reduce the spread of HIV by 29%
2025-01-22
January 22, 2025
New Study Finds Social Programs Could Reduce the Spread of HIV by 29%
Although HIV was used as a case study, the UMass Amherst researchers say their assessment tool has applications for other diseases
AMHERST, Mass. — Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have quantified the impacts of a constellation of social factors on the spread of HIV. Their study, published in Health Care Management Science, found that a hypothetical 100% effective intervention addressing barriers to HIV treatment and care from depression, homelessness, ...
SIDS discovery could ID babies at risk of sudden death
2025-01-22
New University of Virginia School of Medicine research revealing the fingerprints of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome within blood samples could open the door to simple tests to identify babies at risk.
The findings also represent an important step forward in unraveling the causes of SIDS, an unexplained condition that is the No. 1 killer of babies between amonth and a year old.
The UVA researchers analyzed blood serum samples collected from infants who died ...
Ozone exposure linked to hypoxia and arterial stiffness
2025-01-22
Ozone (O3) exposure may reduce the availability of oxygen in the body, resulting in arterial stiffening due to the body’s natural response to create more red blood cells and hemoglobin, according to a study published today in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Researchers found that even brief exposure to elevated ozone levels reduced blood oxygen saturation, triggered hypoxia-related biomarkers, and increased arterial stiffness, highlighting the novel connection between ozone exposure and arterial stiffness, demonstrated through comprehensive biomarker analysis in a high-altitude ...
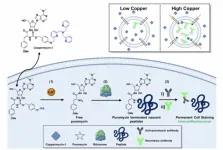
Princeton Chemistry develops copper-detection tool to discover possible chelation target for lung cancer
2025-01-22
The Chang Lab at Princeton Chemistry continues in its mission to elucidate the role of metal nutrients in human biology: last year, iron; this year, copper. The lab’s first paper of 2025 showcases its development of a revelatory sensing probe for the detection of copper in human cells and then wields it to uncover how copper may be regulating cell growth in lung cancer.
Researchers also offer a possible treatment modality in which copper chelation shows promising results in certain lung cancers where cells have two related phenomena: a heightened transcription factor responding to oxidative stress and a diminished level of bioavailable copper.
Their collaborative paper, A histochemical ...
Drug candidate eliminates breast cancer tumors in mice in a single dose
2025-01-22
Despite significant therapeutic advances, breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related death in women. Treatment typically involves surgery and follow-up hormone therapy, but late effects of these treatments include osteoporosis, sexual dysfunction and blood clots. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have created a novel treatment that eliminated small breast tumors and significantly shrank large tumors in mice in a single dose, without problematic side effects.
Most breast cancers are ...
WSU study shows travelers are dreaming forward, not looking back
2025-01-22
PULLMAN, Wash. – When it comes to getting people to want to go places, the future is ever more lovely than the past, according to a new Washington State University-led study in the Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research.
Led by Ruiying Cai, an assistant professor in the Carson College of Business, the study found that forestalgia-focused destination ads—those that emphasize an idealized future—are more effective at enticing travelers to click the purchase button for a vacation than ads based on fond recollections. The research also revealed that forestalgia advertising is particularly effective for getting people to book near-term trips, as imagining ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] Medically recommended vs nonmedical cannabis use among US adultsJAMA Psychiatry