(Press-News.org) Chirality refers to objects that cannot be superimposed to their mirror images through any combination of rotations or translations, much like the distinct left and right hands of a human. In chiral crystals, the spatial arrangement of atoms confers a specific "handedness", which, for example, influences their optical and electrical properties.
The Hamburg-Oxford team focused on so-called antiferro-chirals, a type of non-chiral crystals reminiscent of antiferro-magnetic materials, in which magnetic moments anti-align in a staggered pattern leading to a vanishing net magnetization. An antiferro-chiral crystal is composed of equivalent amounts of left- and right-handed substructures in a unit cell, rendering it overall non-chiral.
The research team, led by Andrea Cavalleri, used terahertz light to lift this balance in the non-chiral material boron phosphate (BPO4), in this way inducing finite chirality on an ultrafast time scale. “We exploit a mechanism termed nonlinear phononics," says Zhiyang Zeng, lead author of this work. “By exciting a specific terahertz frequency vibrational mode, which displaces the crystal lattice along the coordinates of other modes in the material, we created a chiral state that survives for several picoseconds,” he added. “Notably, by rotating the polarization of the terahertz light by 90 degrees, we could selectively induce either a left- or right-handed chiral structure,” continues fellow author Michael Först.
"This discovery opens up new possibilities for the dynamical control of matter at the atomic level," says Andrea Cavalleri, group leader at the MPSD. "We are excited to see potential applications of this technology and how it can be used to create unique functionalities. The ability to induce chirality in non-chiral materials could lead to new applications in ultrafast memory devices or even more sophisticated optoelectronic platforms"
This work received financial support from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft via the Cluster of Excellence ‘CUI: Advanced Imaging of Matter’. The MPSD is a member of the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science (CFEL), a joint enterprise with DESY and the University of Hamburg.
END
Terahertz pulses induce chirality in a non-chiral crystal
2025-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI judged to be more compassionate than expert crisis responders: Study
2025-01-23
By definition, robots can’t feel empathy — it requires being able to relate to another person’s human experience, to put yourself in their shoes.
But according to new U of T Scarborough research, artificial intelligence (AI) can create empathetic responses more reliably and consistently than humans, even when compared to professionals whose job relies on empathizing with those in need.
“AI doesn’t get tired,” says Dariya Ovsyannikova (HBSc 2023 UTSC), lab manager in Professor Michael Inzlicht’s lab at U of T Scarborough ...
Scale-up fabrication of perovskite quantum dots
2025-01-23
Quantum dots are tiny semiconductor nano materials with color-tunable and high-efficiency photoluminescence, which have been successfully applied in different display technology such as liquid crystal displays (LCDs), organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and micro light-emitting diodes (Micro-LEDs). In 2023, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry rewards the discovery and development of quantum dots. Perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) are emerging display materials with high absorption coefficient, low cost and easy processability, and less environmental impact. ...
Adverse childhood experiences influence potentially dangerous firearm-related behavior in adulthood
2025-01-23
Researchers at Rutgers University have found that adverse childhood experiences can make people more sensitive to potential threats from others, which in turn increases their risk of engaging in defensive gun use in adulthood.
Their study, published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research, used cross-sectional data from a subsample of 3,130 adults with firearm access drawn from a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults.
Those surveyed were asked about their childhood experiences with abuse and neglect, their levels of social distrust and sensitivity to perceived threats, depressive symptoms and their self-reported use of a gun for self-defense.
The authors first assessed the association ...
Bacteria found to eat forever chemicals — and even some of their toxic byproducts
2025-01-23
BUFFALO, N.Y. — In the quest to take the “forever” out of “forever chemicals,” bacteria might be our ally.
Most remediation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) involves adsorbing and trapping them, but certain microbes can actually break apart the strong chemical bonds that allow these chemicals to persist for so long in the environment.
Now, a University at Buffalo-led team has identified a strain of bacteria that can break down and transform at least three types of PFAS, and, perhaps even more crucially, some of ...
London cabbies’ planning strategies could help inform future of AI
2025-01-23
Researchers have measured the thinking time of London taxi drivers - famous for their knowledge of more than 26,000 streets across the city - as part of a study into the future of AI route-mapping.
Unlike a satnav, which calculates every possible route until it gets to the destination, researchers at the University of York, in collaboration with University College London and the Champalimaud Foundation, found that London taxi drivers rationally plan each route by prioritising the most challenging areas first and filling in the rest of the route around these tricky points.
Current computational models to understand ...
More acidic oceans may affect the sex of oysters
2025-01-23
Rising carbon dioxide levels affect more than just the climate; they also affect the chemistry of the oceans. When saltwater absorbs carbon dioxide, it becomes acidic, which alters the aquatic animal ecosystem. But how exactly does ocean acidification impact animals whose genetic makeup can shift depending on environmental cues? A study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology addresses this question through the “eyes” of oysters.
Oysters, unlike mammals and birds, do not have chromosomes that dictate their sex at the ...
Transportation insecurity in Detroit and beyond
2025-01-23
Images
More than a third of Detroit residents (36%) can't get from place to place in a safe or timely manner.
This is the main finding of a new study led by Alexandra Murphy, associate director of social science research at Mcity and assistant research scientist at U-M's Poverty Solutions, and first author Lydia Wileden, a U-M alum and assistant research professor at the University of Connecticut.
They measured this with a tool created by Murphy and her team called the Transportation Security ...
New tool enables phylogenomic analyses of entire genomes
2025-01-23
Researchers led by electrical engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a better way to perform the comparative analysis of entire genomes. This approach can be used to study relationships between different species across geological time scales.
This new approach is poised to unlock discoveries regarding how evolution has shaped present-day genomes and also how the tree of life is organized. The new method, named CASTER, is described in a paper published in Science on 23 January 2025.
CASTER ...
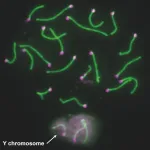
Uncovering the role of Y chromosome genes in male fertility in mice
2025-01-23
Researchers at the Crick have uncovered which genes on the Y chromosome regulate the development of sperm and impact fertility in male mice. This research could help us understand why some men don’t produce enough sperm and are infertile.
Males typically have one copy of the Y chromosome and one copy of the X chromosome, whereas females typically have two X chromosomes. Scientists know that the Y chromosome is essential for male fertility, but which genes are the most important and how they work is less clear.
In research published today in Science, a research team at the Crick resolved this question by generating thirteen different ...
A single gene underlies male mating morphs in ruff sandpipers
2025-01-23
Male ruff sandpipers engaging in the act of mating typically fall into one of three groups, with variations in how aggressive they are and how showy their plumage is, among other factors. Now, a new study reports a single gene – HSD17B2 – drives these dramatic differences among male ruff sandpiper morphs. The findings show how evolutionary changes in a single gene's structure, sequence, and regulation can drive significant diversity within a single species. The androgen testosterone plays a key role in male reproductive development. It influences ...